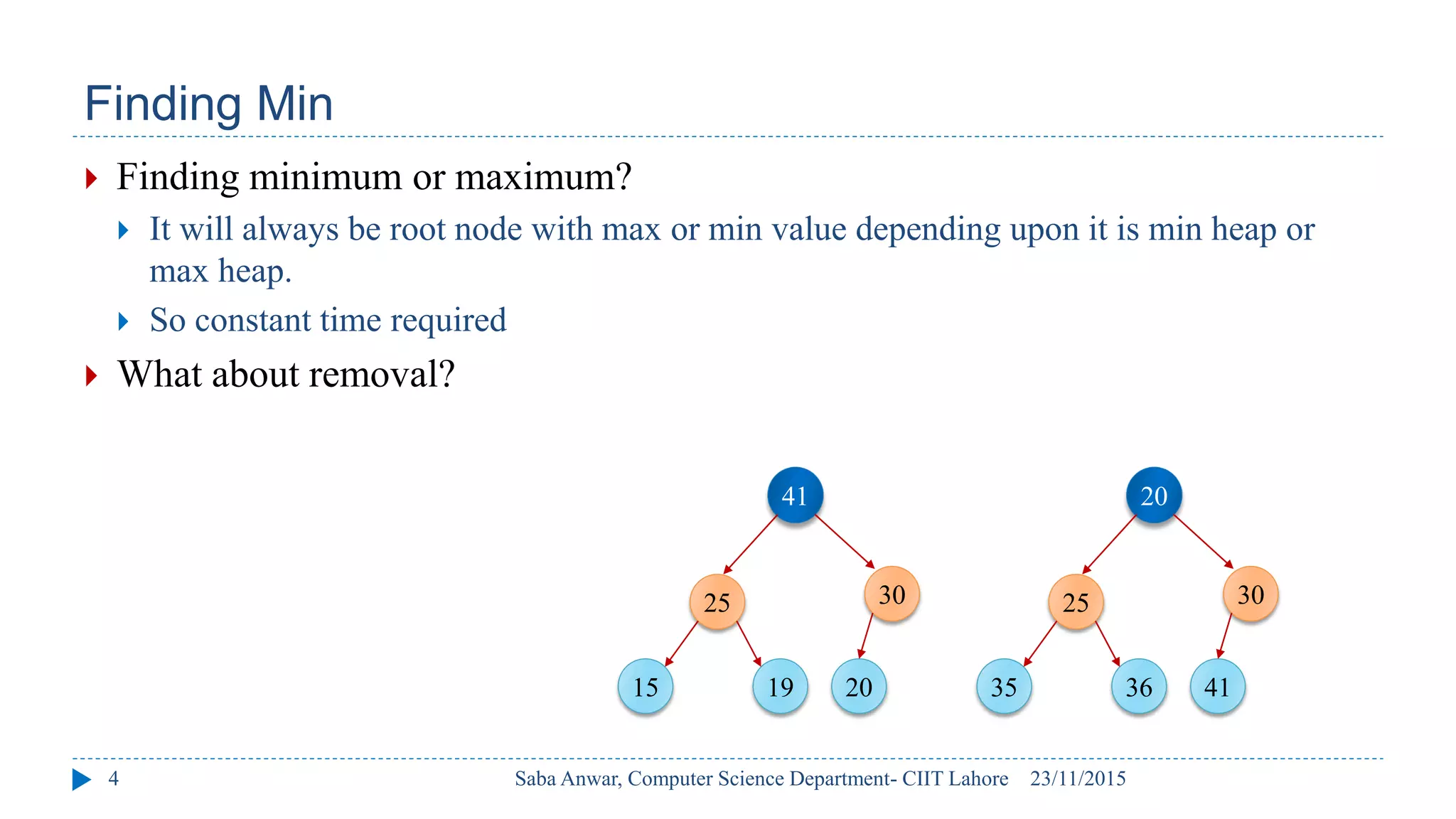
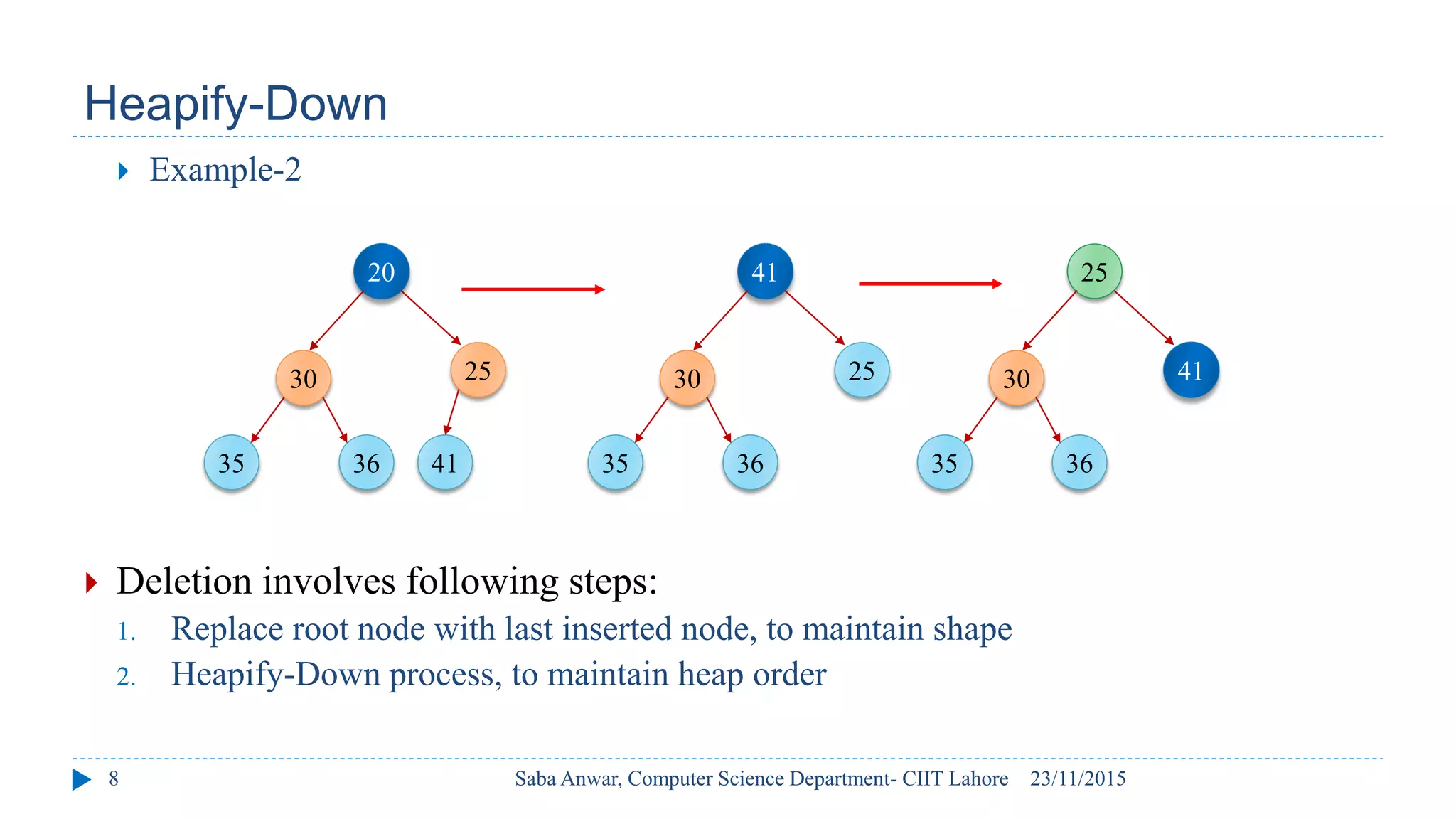
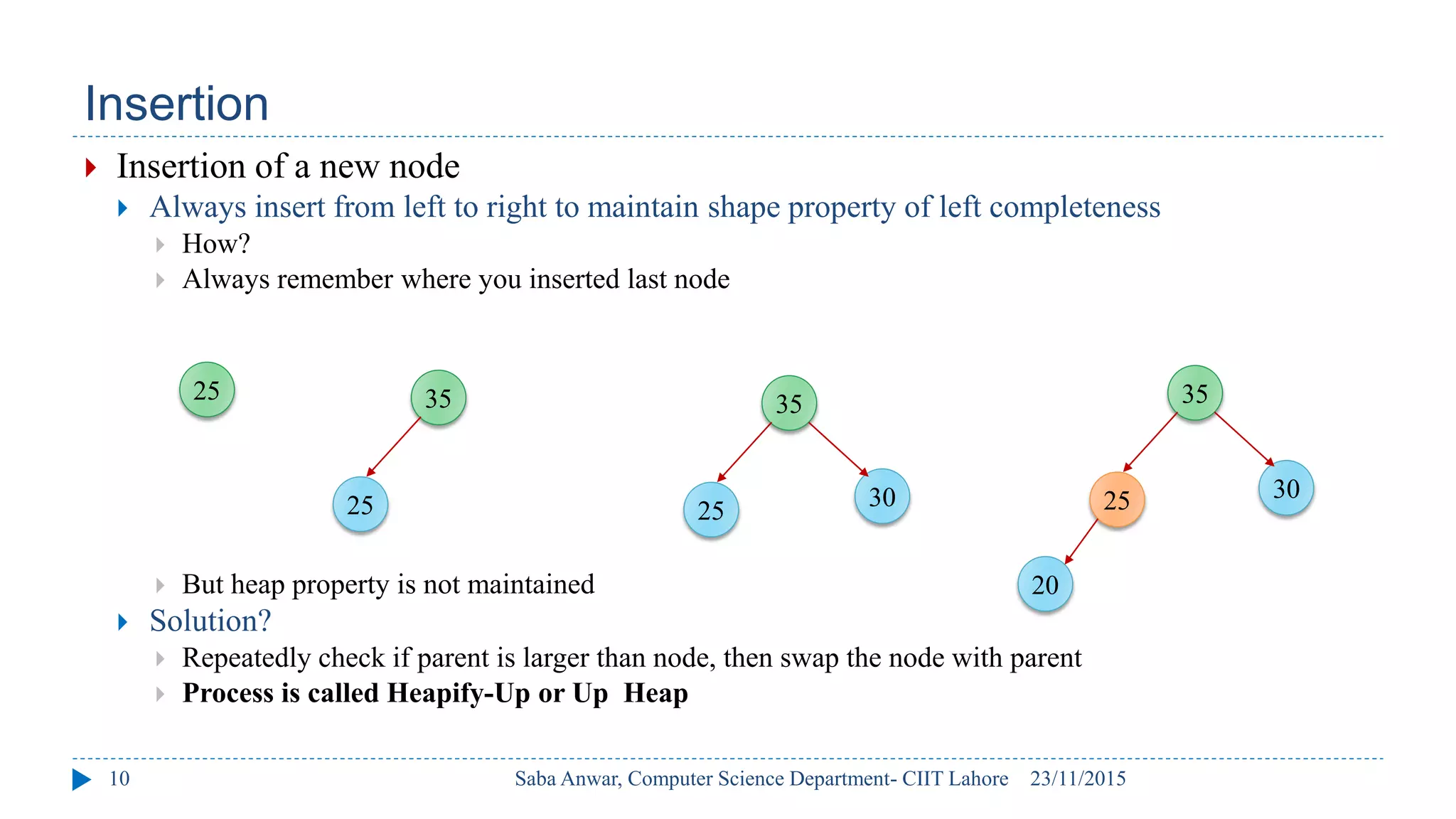
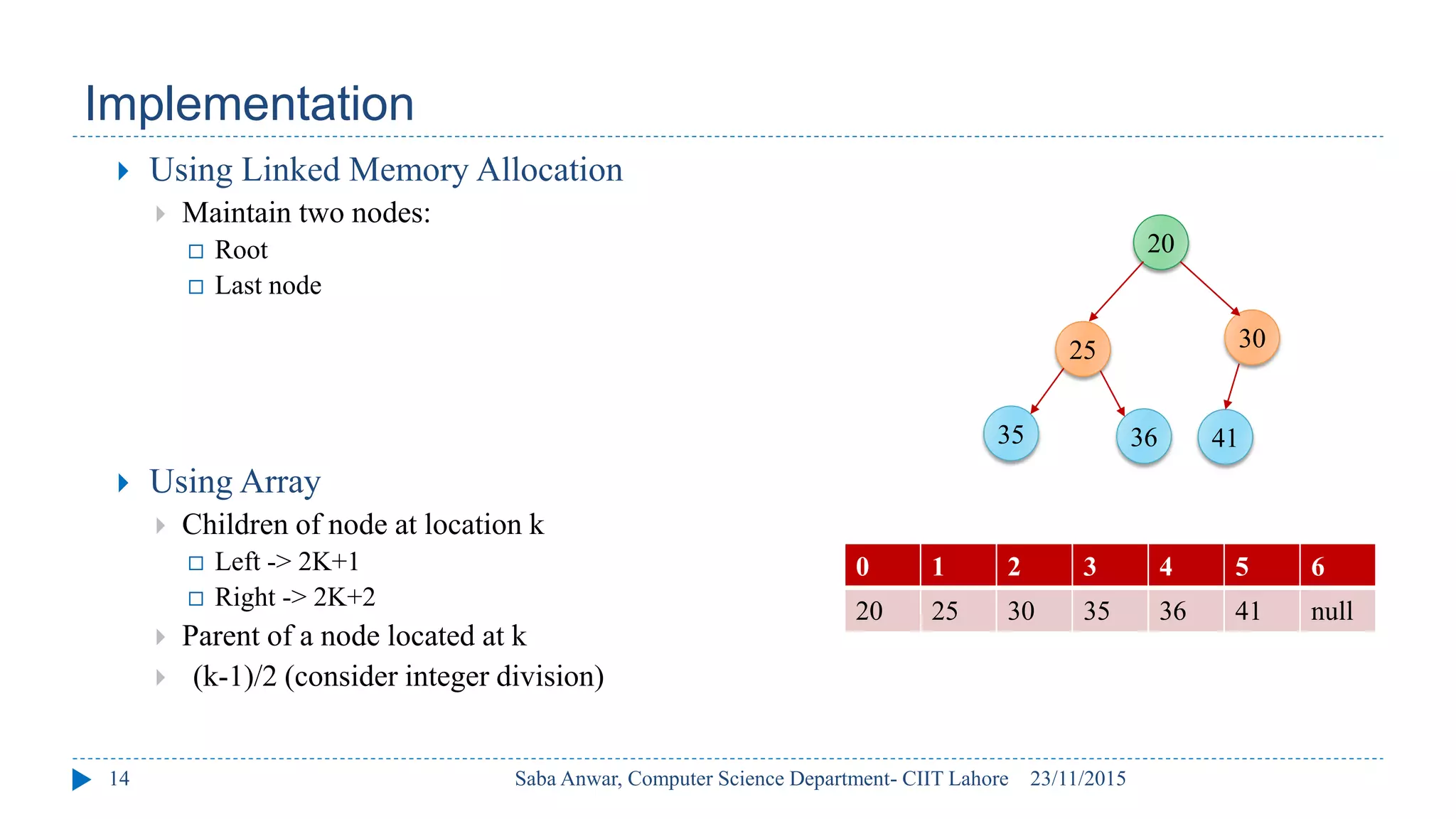
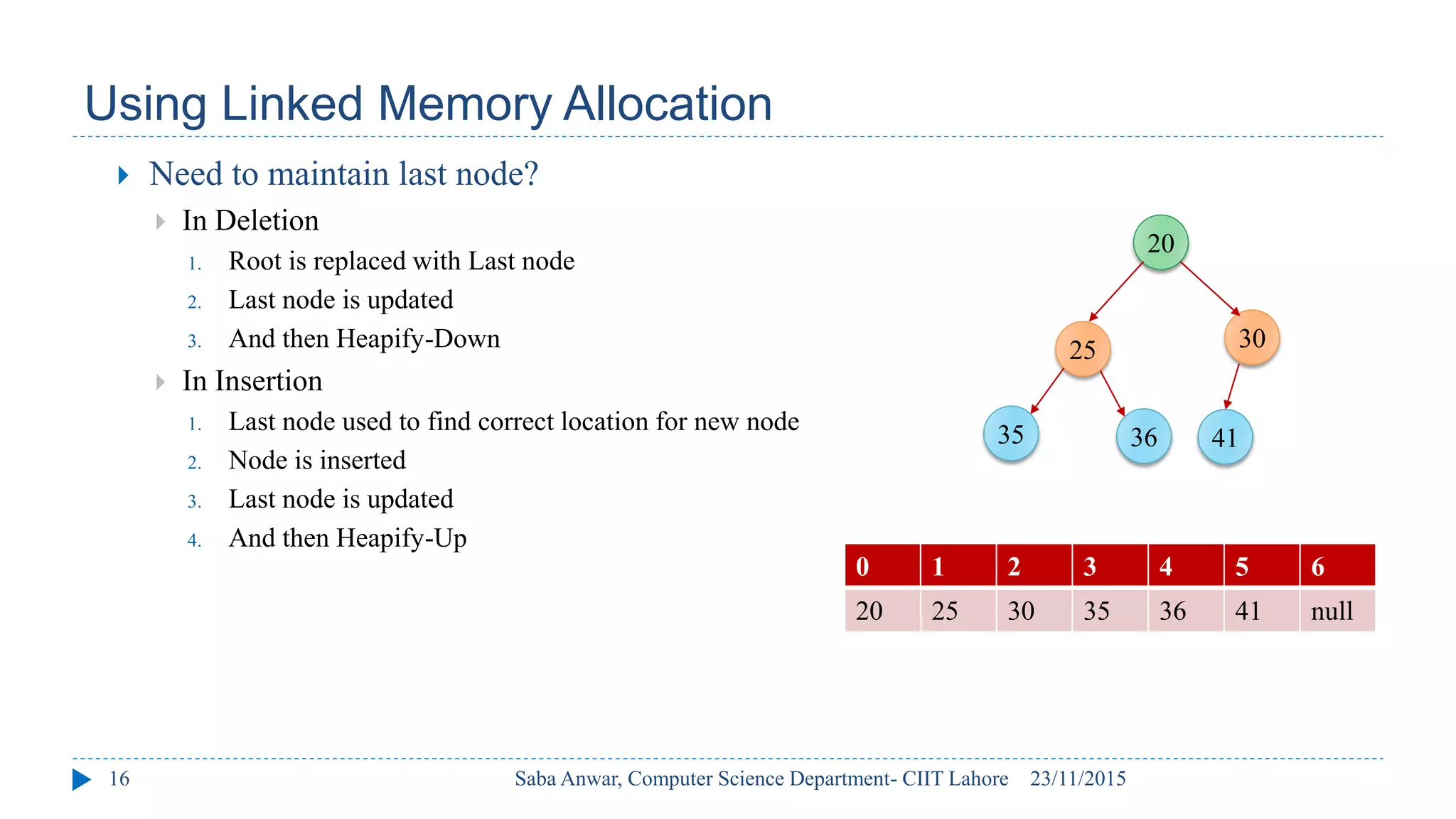
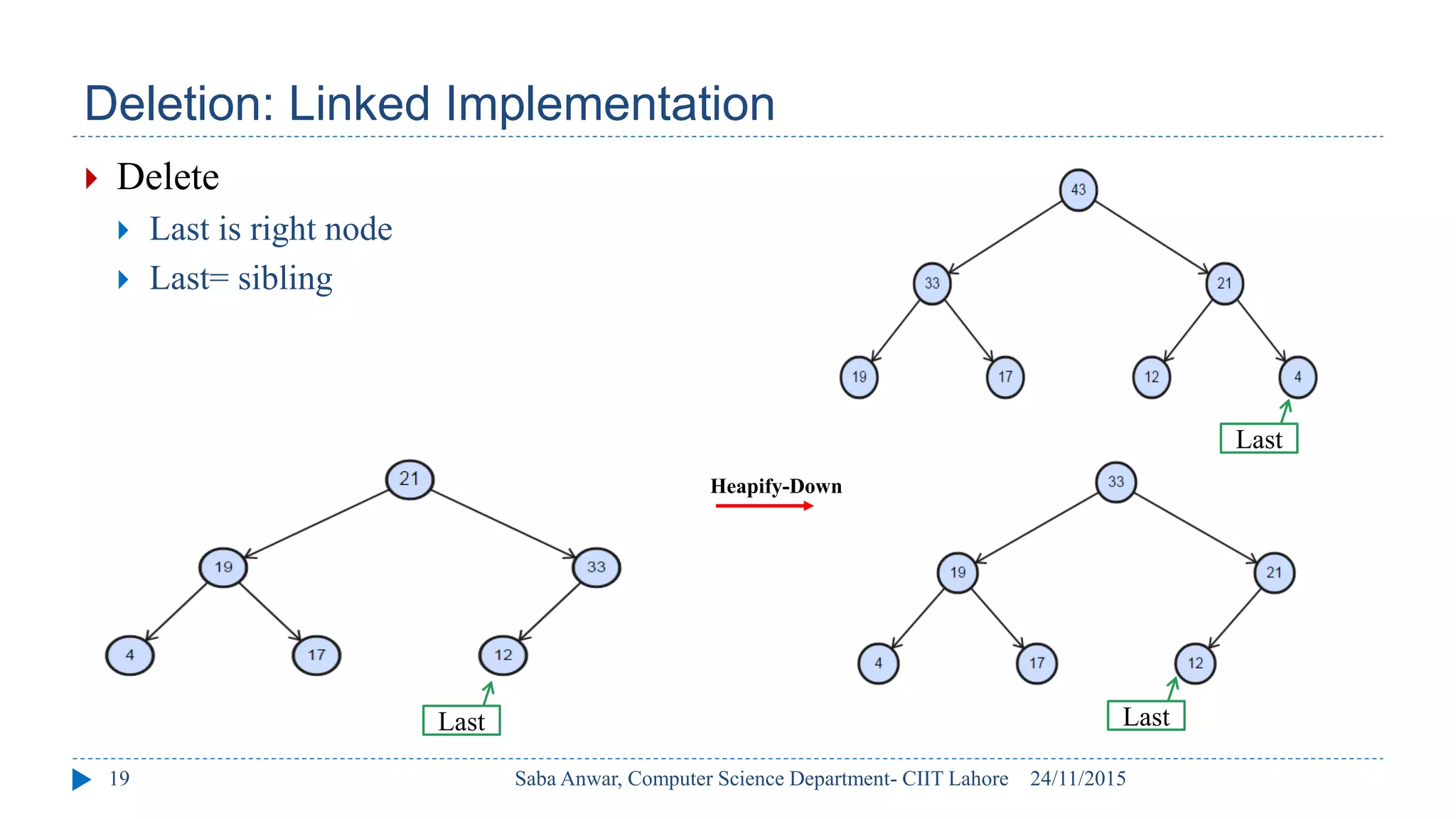
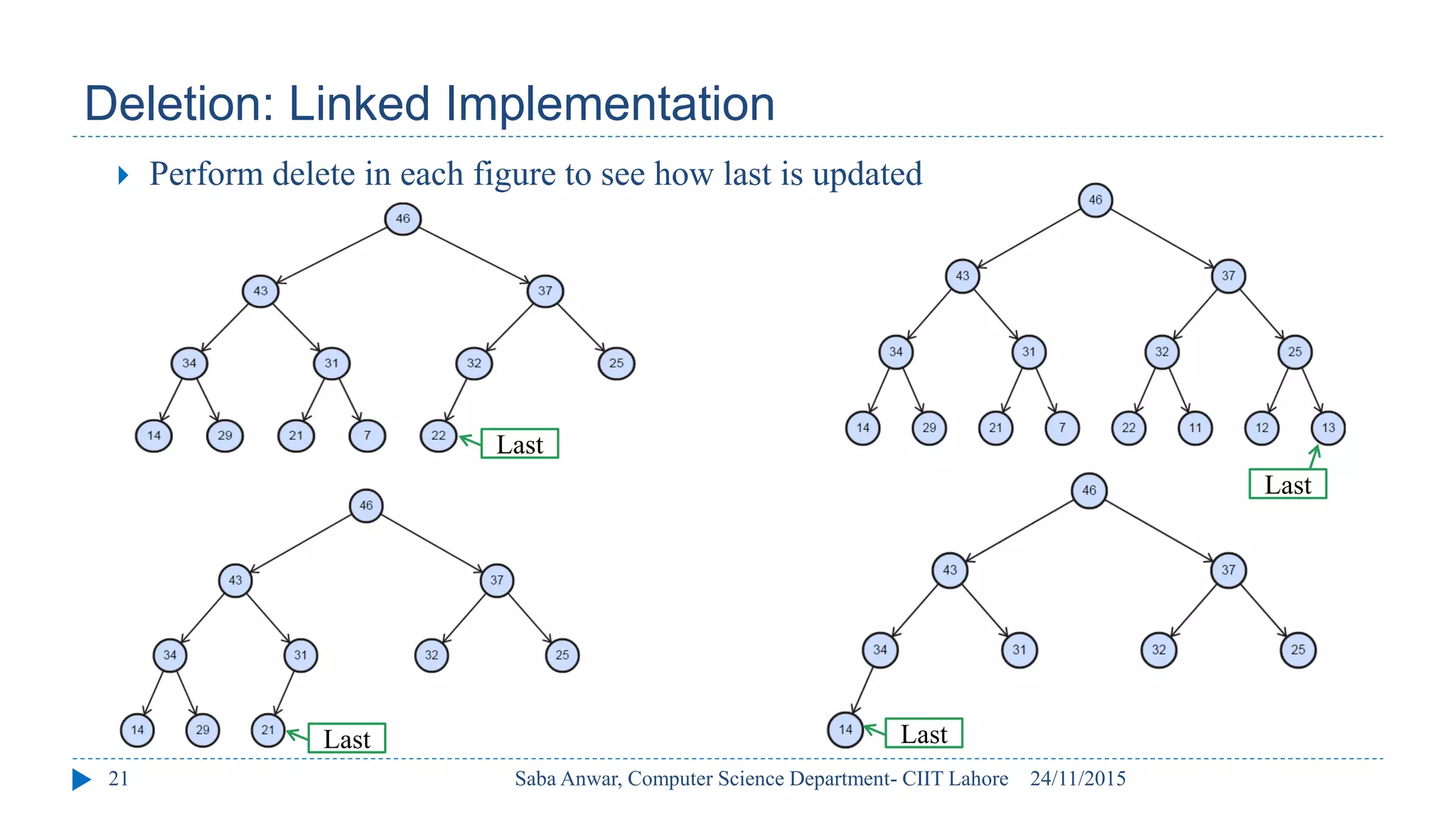
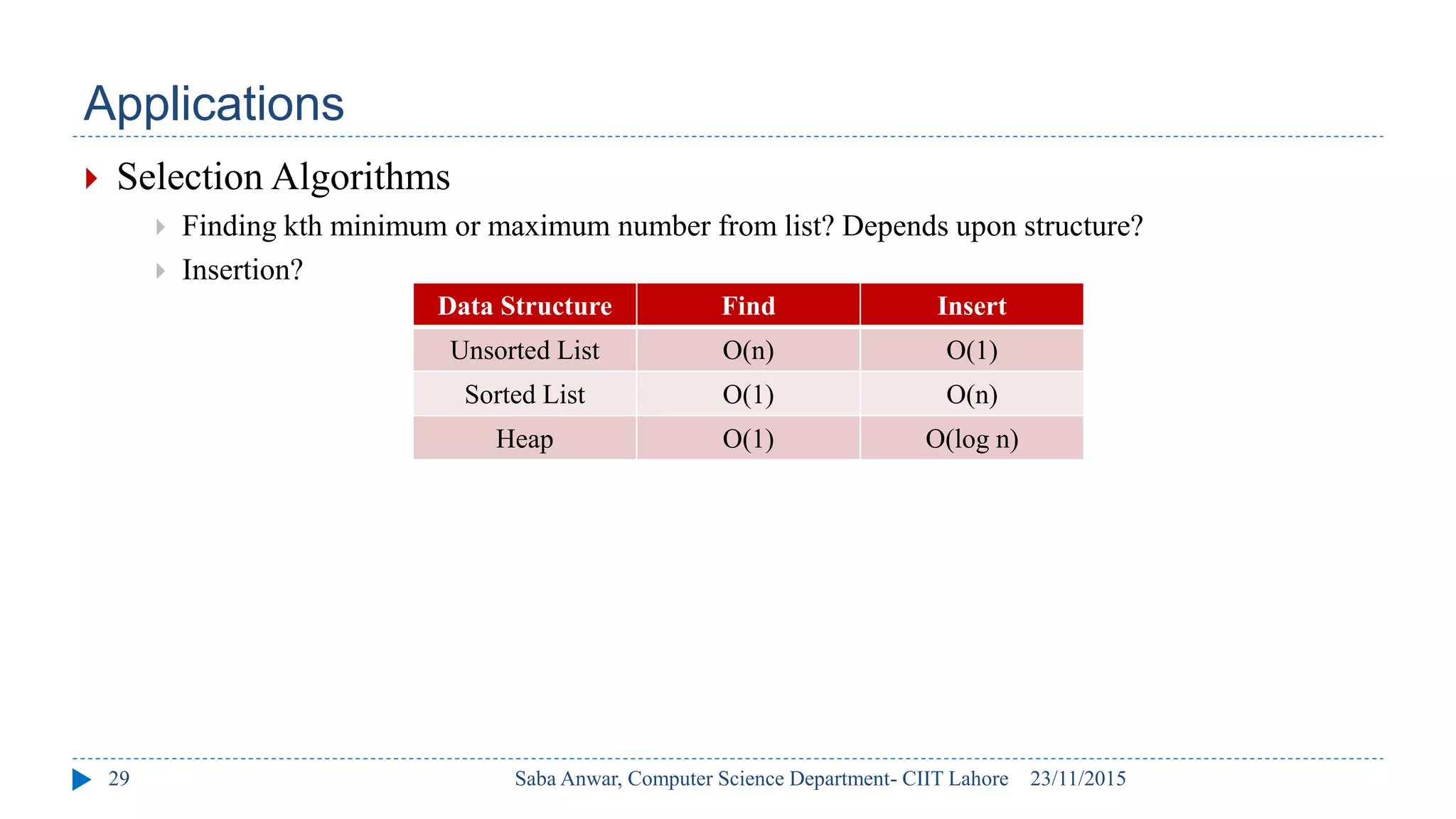
The document outlines key concepts of binary heaps, covering their properties, operations like insertion and deletion, and the heapify processes involved. It explains the maintenance of the heap's shape and order during these operations and discusses implementations using linked memory and arrays. Additionally, it highlights the applications of heaps in priority queues and sorting algorithms, emphasizing their efficiency compared to other data structures.