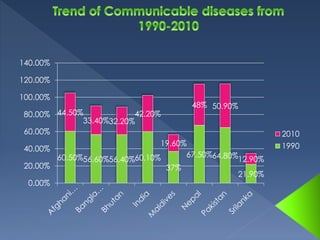
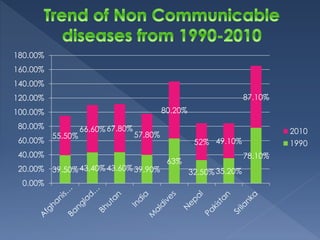
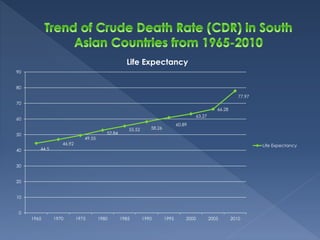
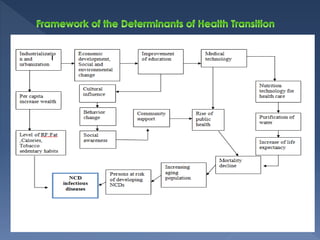
The document discusses health transition, focusing on epidemiological and demographic shifts from infectious to chronic diseases, highlighting the role of economic, socio-cultural, and medical determinants. It outlines historical stages of health transitions and the increasing life expectancy alongside decreasing infectious disease mortality. Key determinants include economic growth, education, social awareness, and advancements in medical technology and public health infrastructure.