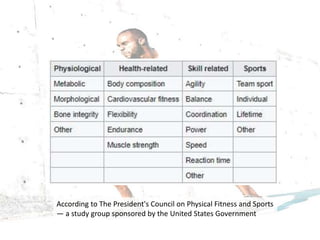
The document discusses the multifaceted nature of health, emphasizing the importance of various components such as a healthy lifestyle, good diet, physical exercise, sleep, hygiene, and emotional well-being. It highlights the roles of individuals, families, communities, and governmental organizations in maintaining health, while also addressing the impact of addiction, environment, and health education. Ultimately, the document asserts that health is essential for individual and community development.