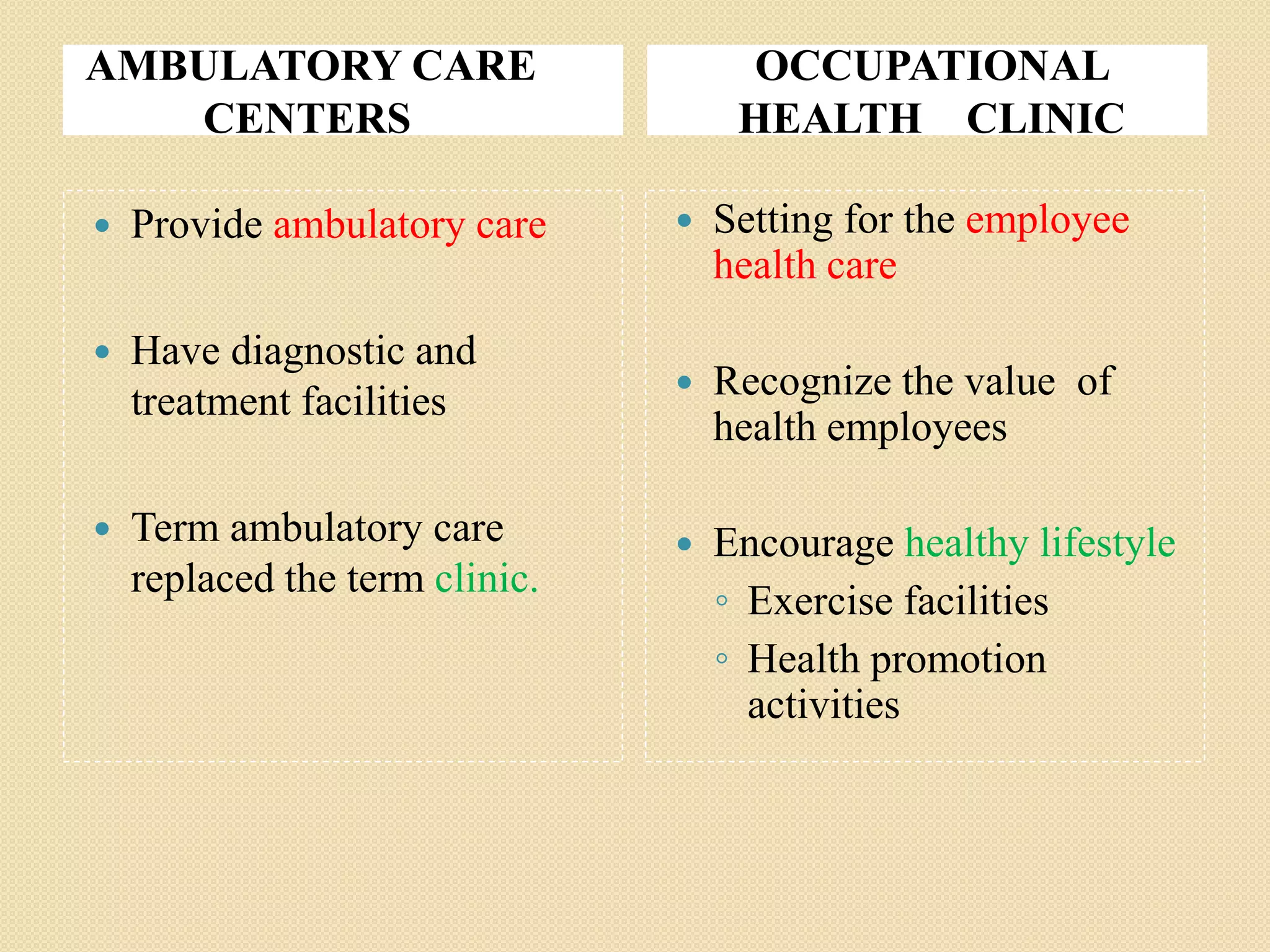
The document describes the various components of a health care system and types of health care services. It discusses public health services, physicians' offices, ambulatory care centers, occupational health clinics, hospitals, substance abuse facilities, extended care facilities, rehabilitation centers, home health care agencies, day care centers, rural care, hospice services, crisis centers, and mutual support/self-help groups. The purpose of a health care system is to provide care for the ill/injured and achieve optimal health levels for a defined population.