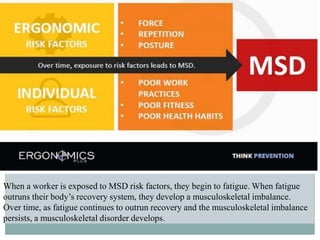
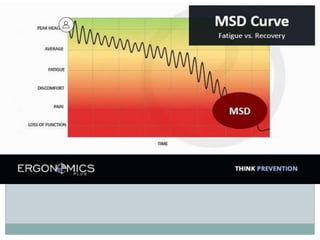
This document discusses ergonomics and health and safety issues related to computing. It begins by defining ergonomics as the science of optimizing the relationship between humans and products/work environments. Poor ergonomics when using computers can cause musculoskeletal issues like carpal tunnel syndrome and tendonitis due to repetitive motions. It also causes eye strain issues. The document provides tips to avoid these problems, such as taking regular breaks, stretching, adjusting equipment setup, and monitor settings. It briefly discusses e-waste and energy saving practices as well. Overall, the document outlines common health issues from improper computer use and provides recommendations to use computers safely and ergonomically.