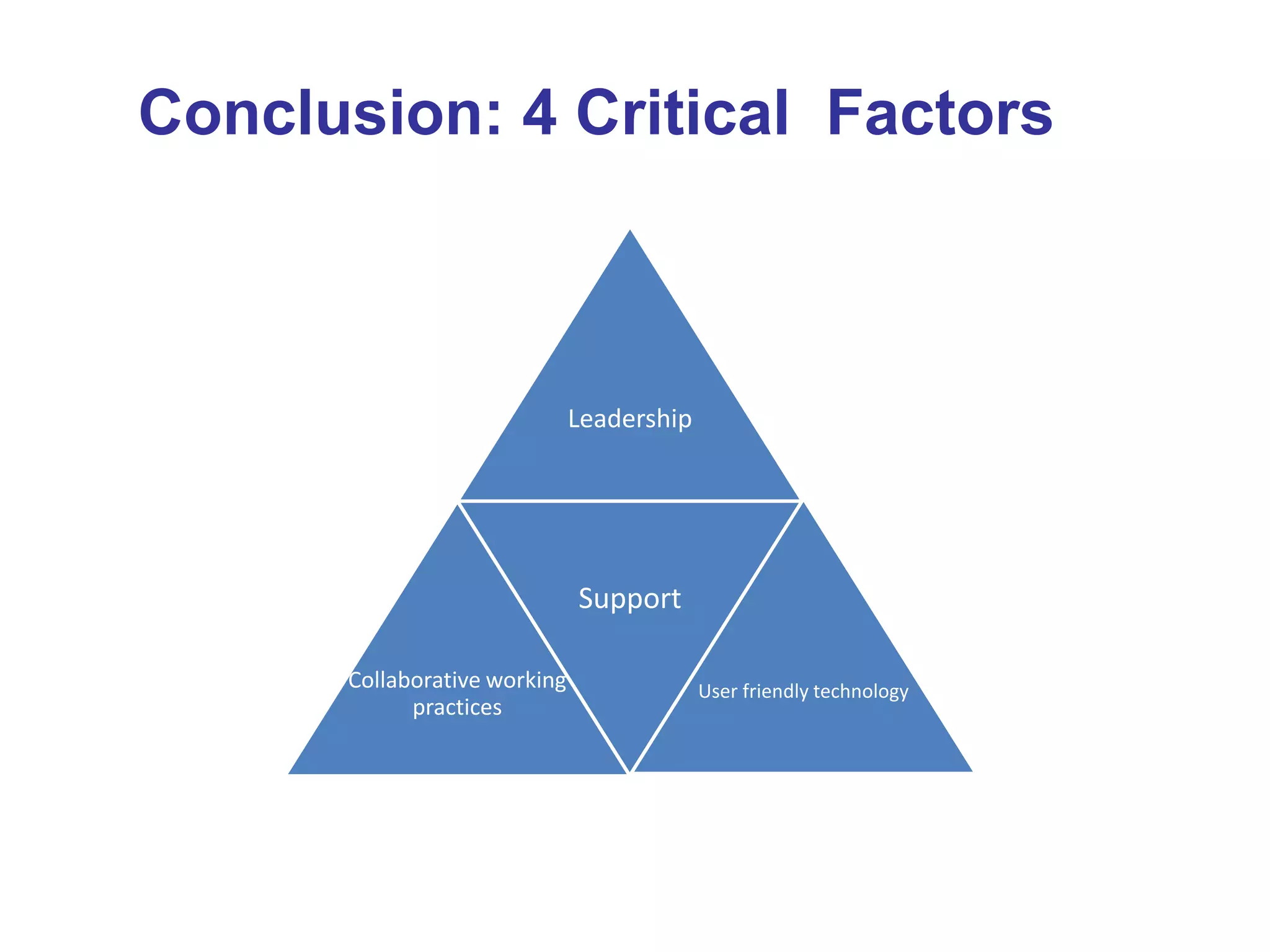
The document discusses four critical factors necessary for sustaining technology-enhanced learning in educational organizations, emphasizing leadership support, collaborative working practices, and user-friendly technology. It describes the roles of key institutions, such as Paris Descartes University and the London School of Economics, in implementing e-learning strategies and highlights the complexity involved in these processes. Furthermore, it introduces the resource-based view and actor-network theory, illustrating the interplay of various elements in the development of e-learning systems.








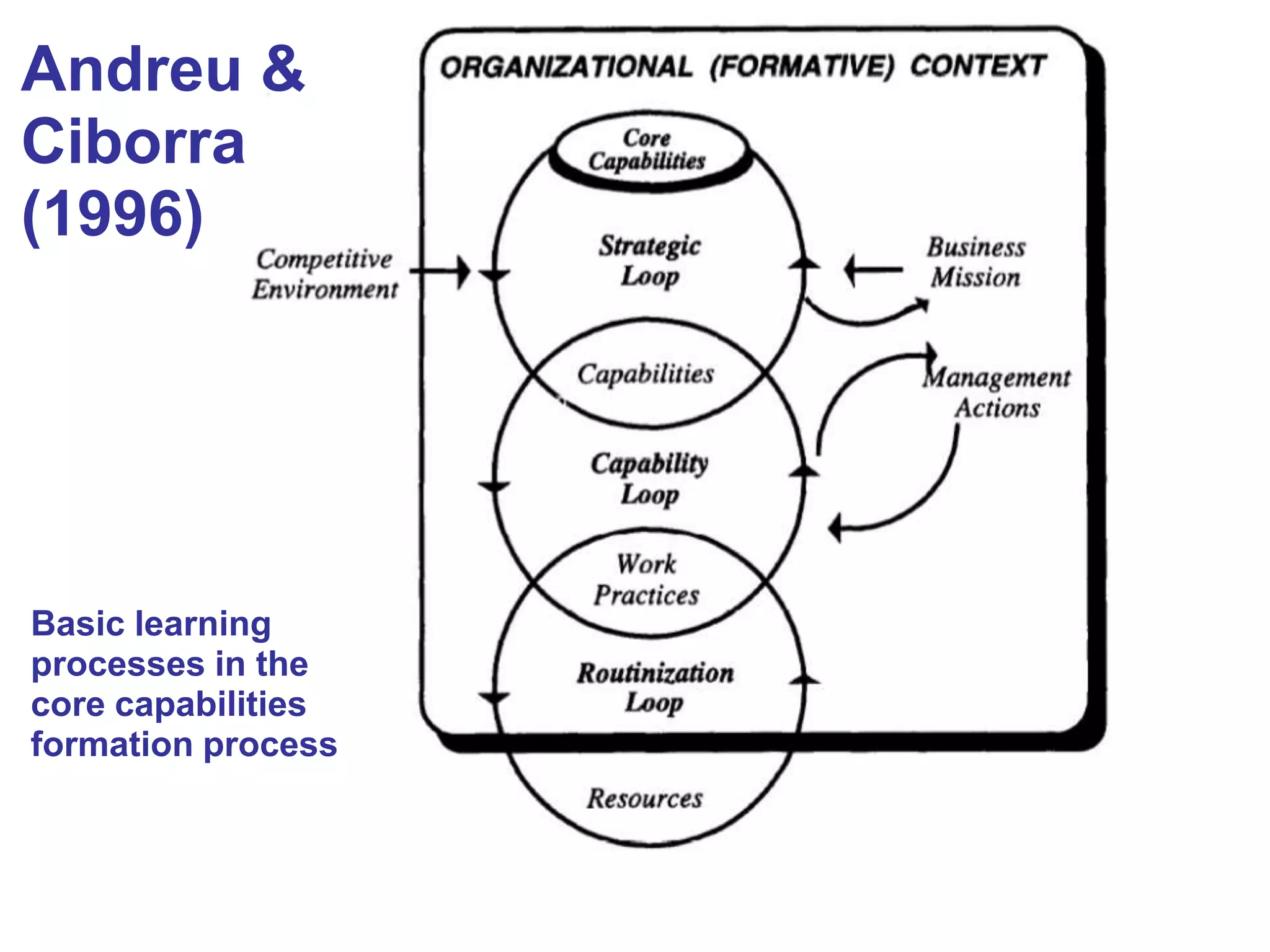
![Amit & Shoemaker (1993)
“Capabilities refer to a firm’s capacity to
deploy Resources, usually in combination,
using organizational processes, to effect a
desired end […] Unlike Resources,
Capabilities are based on developing,
carrying and exchanging information
through the firm’s human capital”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdcsuccess01-131103134655-phpapp02/75/4-Critical-Factors-to-Sustain-the-Development-of-Technology-Enhanced-Learning-in-Educational-Organizations-11-2048.jpg)