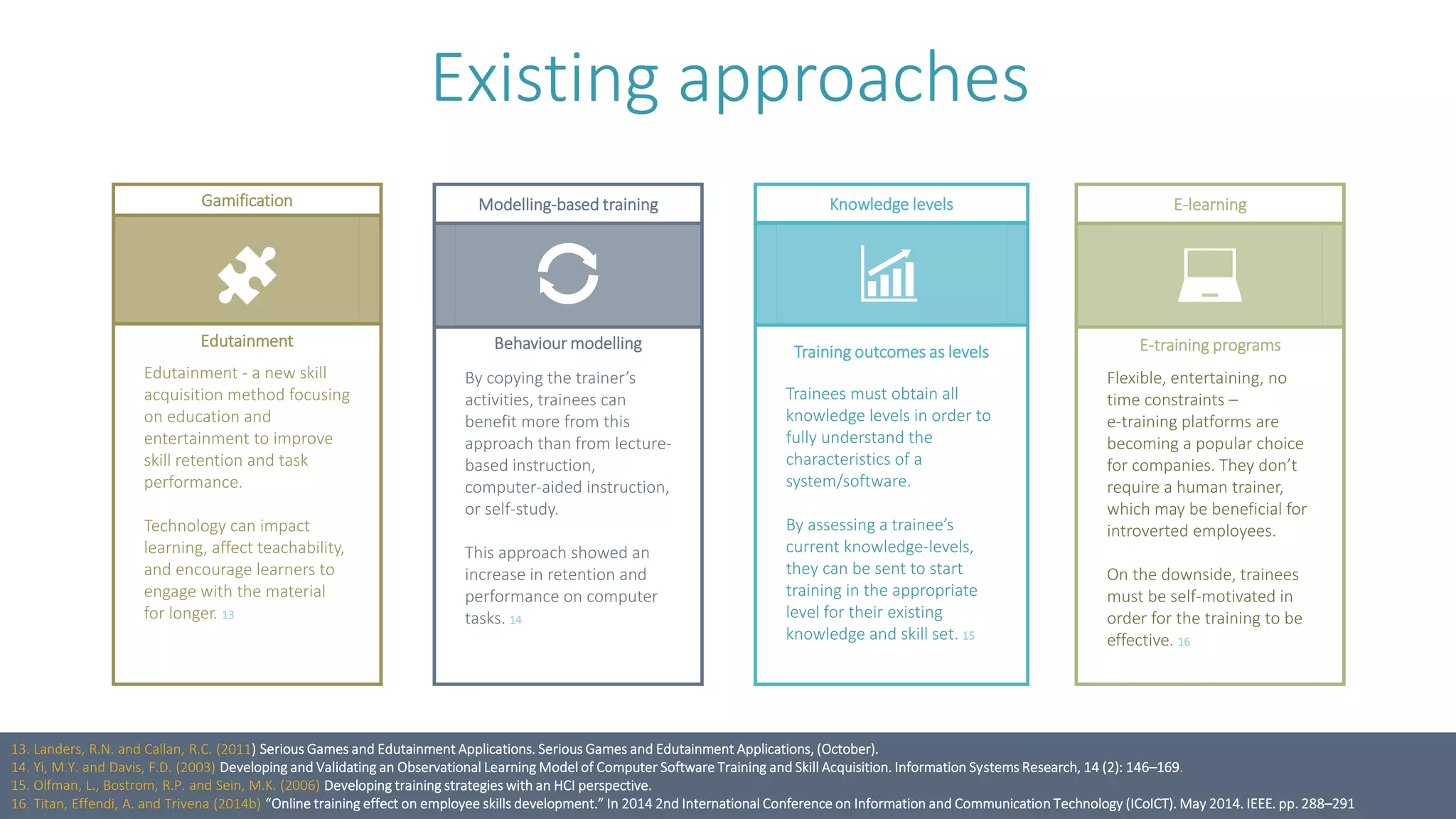
HCI approaches can improve employee software training frameworks in the following ways:
1. E-training interfaces are well-suited for adopting HCI principles to create intuitive, usable training programs. However, e-training must meet usability guidelines to be effective.
2. Increasing trainee's computer self-efficacy prior to training through activities that improve confidence can boost skill acquisition and performance.
3. For training outcomes to be successful, companies must foster a culture where skill-sharing and life-long learning are encouraged, and employees are supported in continuing education.