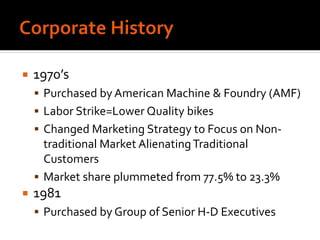
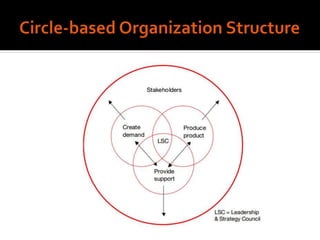
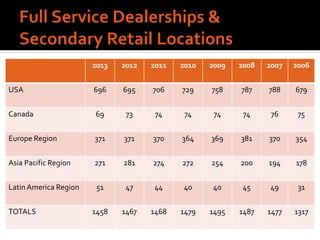
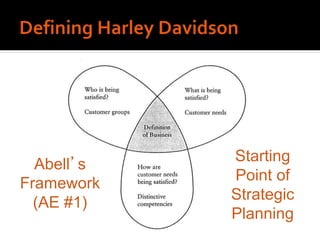
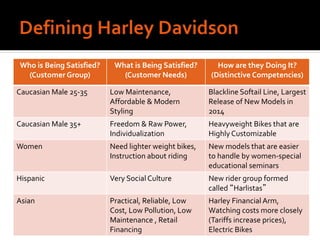
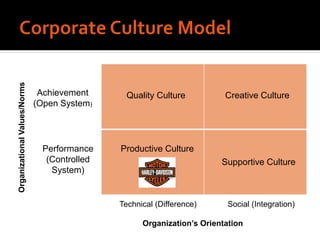
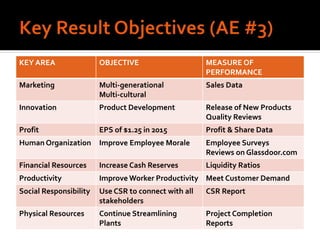
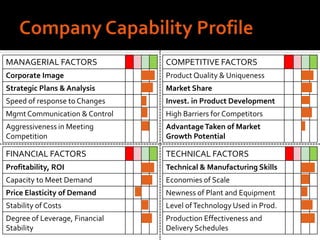
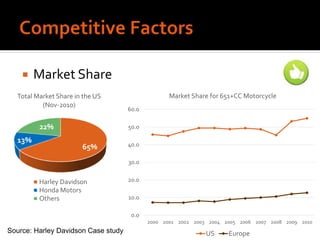
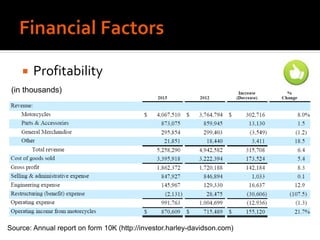
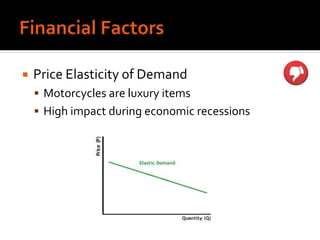
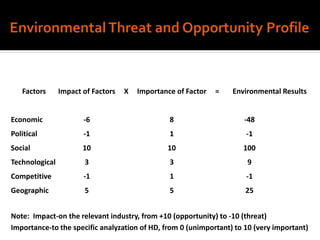
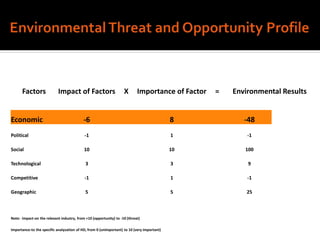
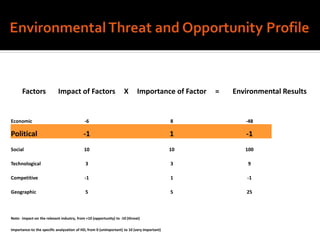
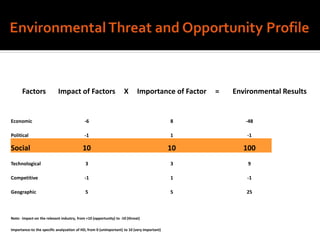
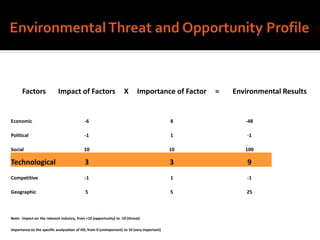
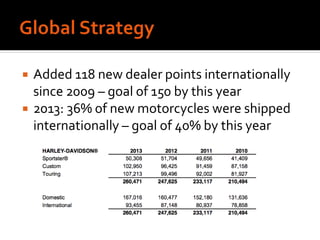
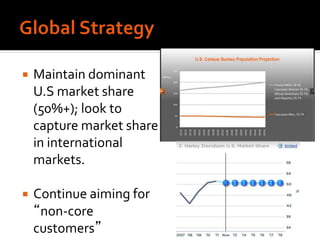
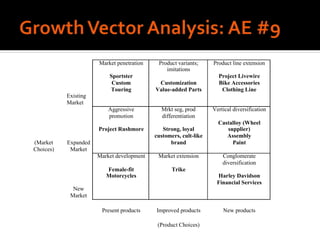
Harley-Davidson was founded in 1903 in Milwaukee, Wisconsin by William Davidson, Walter Davidson, Arthur Davidson and William Harley. It began as the Harley-Davidson Motor Company and produced its first motorcycle with a small engine for a regular pedal bike. Since then, Harley-Davidson has grown to become the largest motorcycle manufacturer in the world. It faces challenges attracting new demographics and expanding globally but utilizes strategies like international expansion, new product development, and a focus on its strong brand and culture to maintain its competitive advantage.