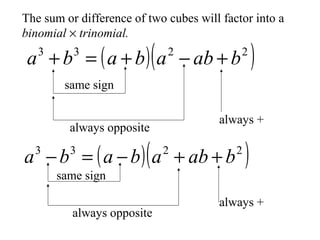
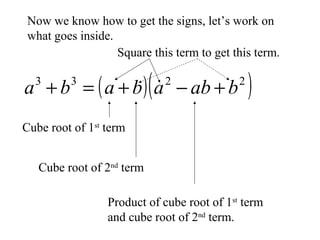
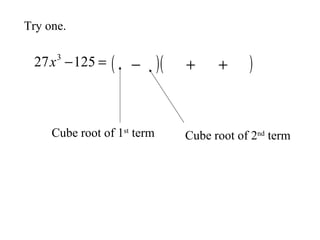
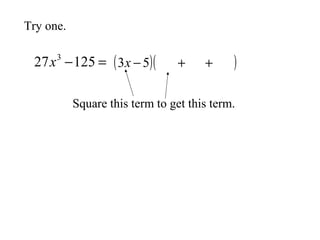
This document discusses factoring the sum and difference of two cubes. It explains that the sum or difference of two cubes can be factored into a binomial times a trinomial, with the first term of the trinomial being the cube root of the first term, the second term being the product of the cube roots, and the third term being the cube root of the second term. It provides an example of factoring 27x3 - 125 to show the process.