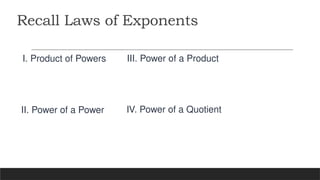
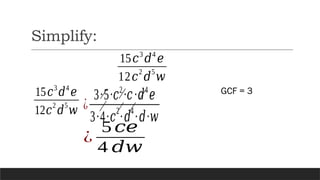
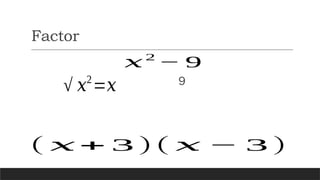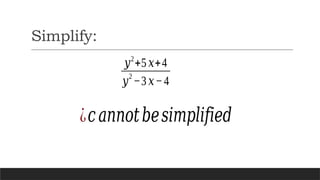The document explains operations involving rational algebraic expressions, including multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction, using the least common denominator. It also covers various factoring techniques such as the difference of squares, sum and difference of cubes, and perfect square trinomials, along with examples. Additionally, it discusses the simplification of rational expressions and provides group activities for practice.