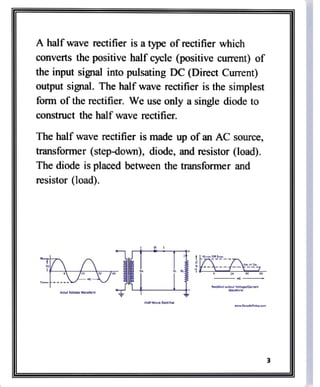
The document is a physics investigatory project focusing on measuring current using a half-wave rectifier, which is a device that converts alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC). It discusses the construction and functioning of the half-wave rectifier, explaining the role of diodes and transformers in the process. Acknowledgements are given to teachers and peers for their support in completing the project.