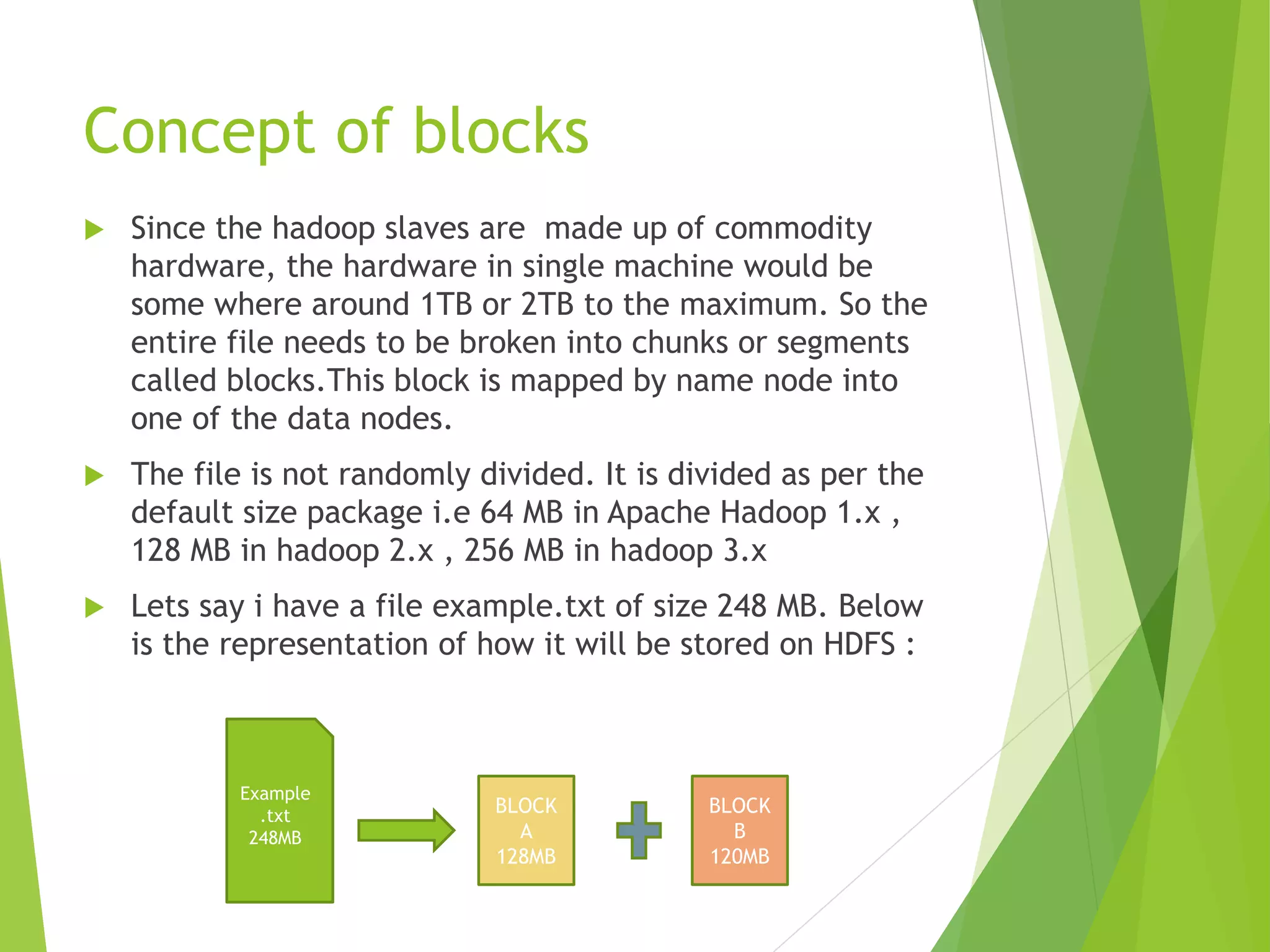
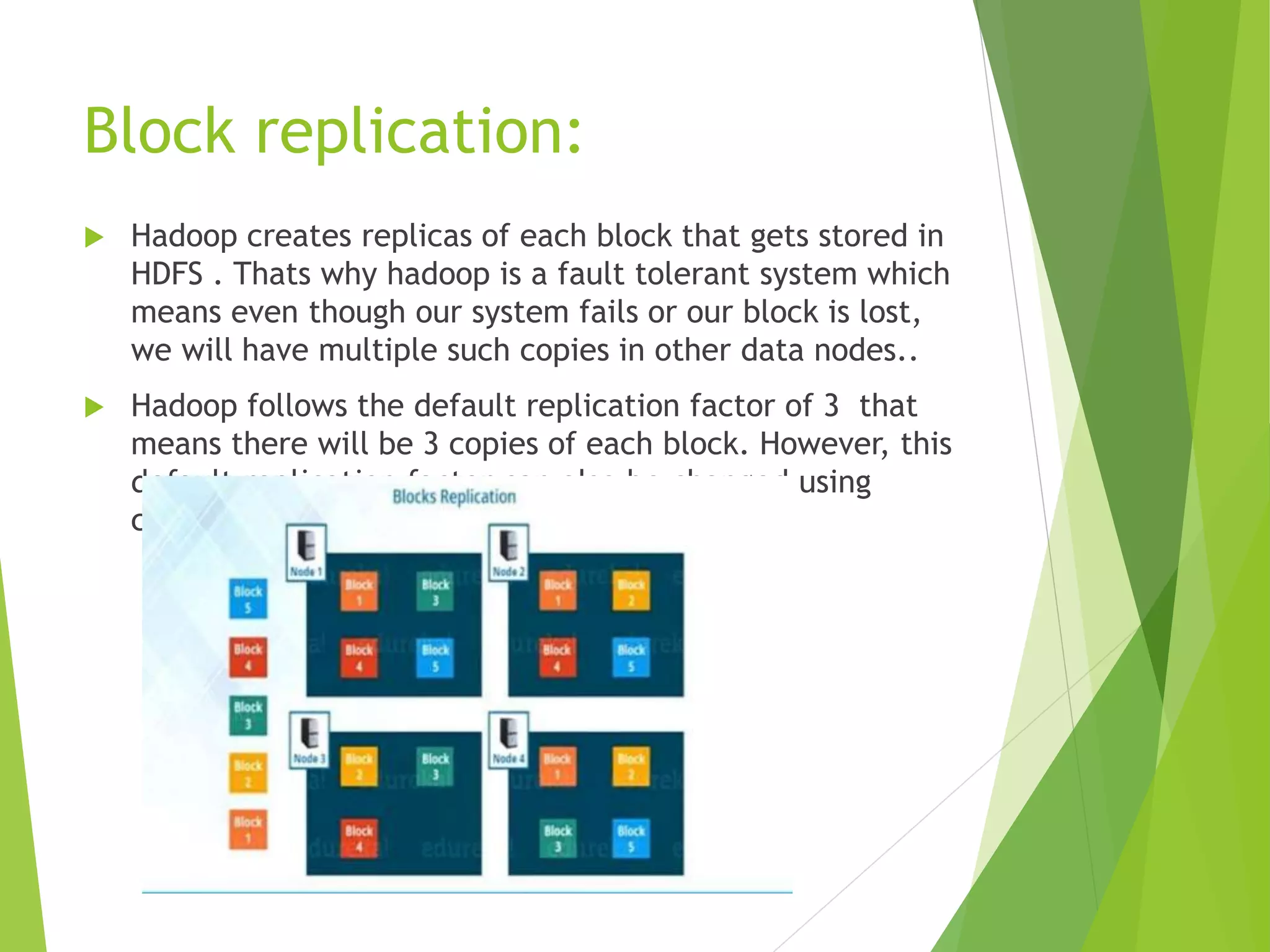
The document provides an introduction to Hadoop and its distributed file system (HDFS) design and issues. It describes what Hadoop and big data are, and examples of large amounts of data generated every minute on the internet. It then discusses the types of big data and problems with traditional storage. The document outlines how Hadoop provides a solution through its HDFS and MapReduce components. It details the architecture and components of HDFS including the name node, data nodes, block replication, and rack awareness. Some advantages of Hadoop like scalability, flexibility and fault tolerance are also summarized along with some issues like small file handling and security problems.