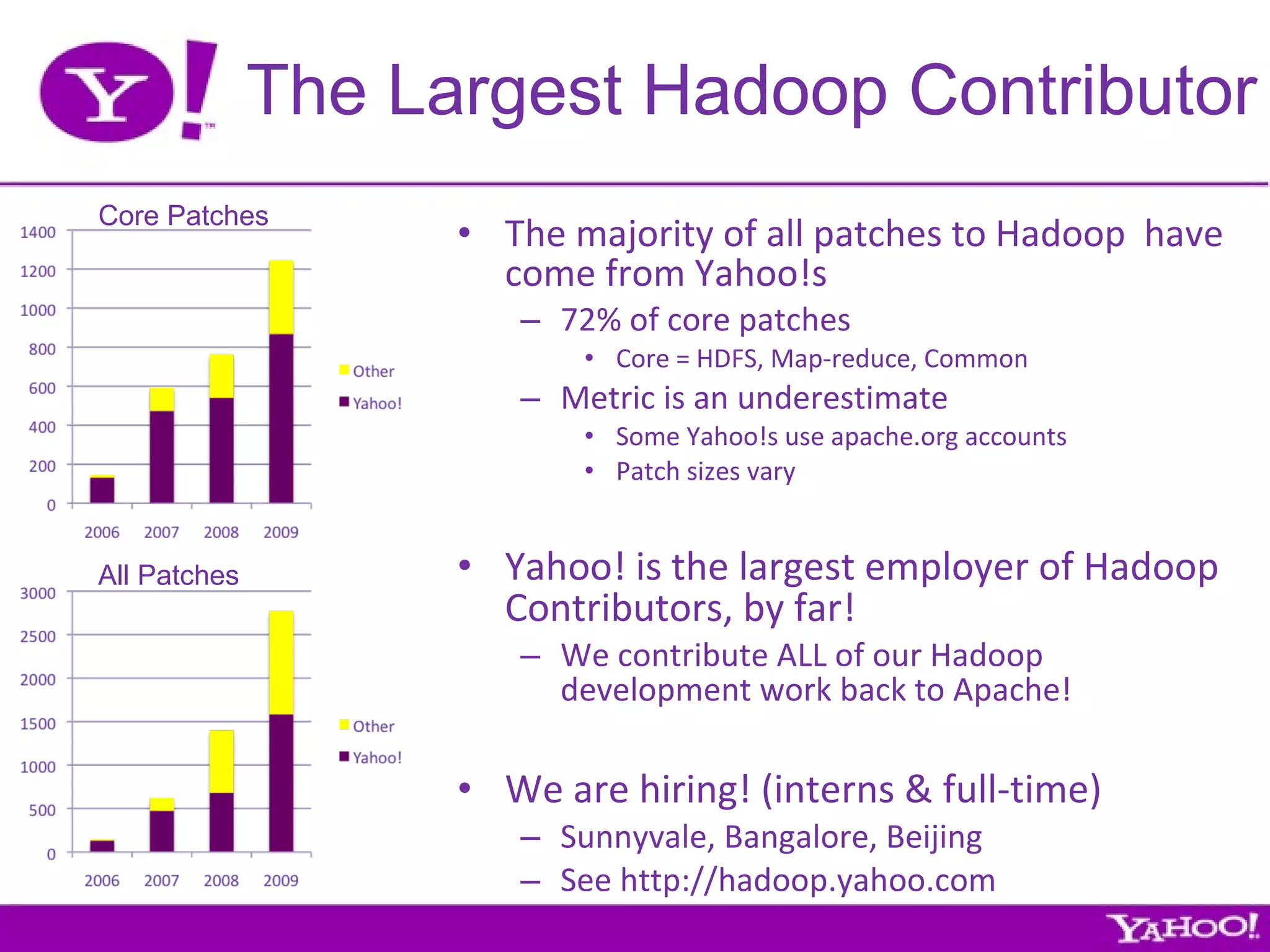
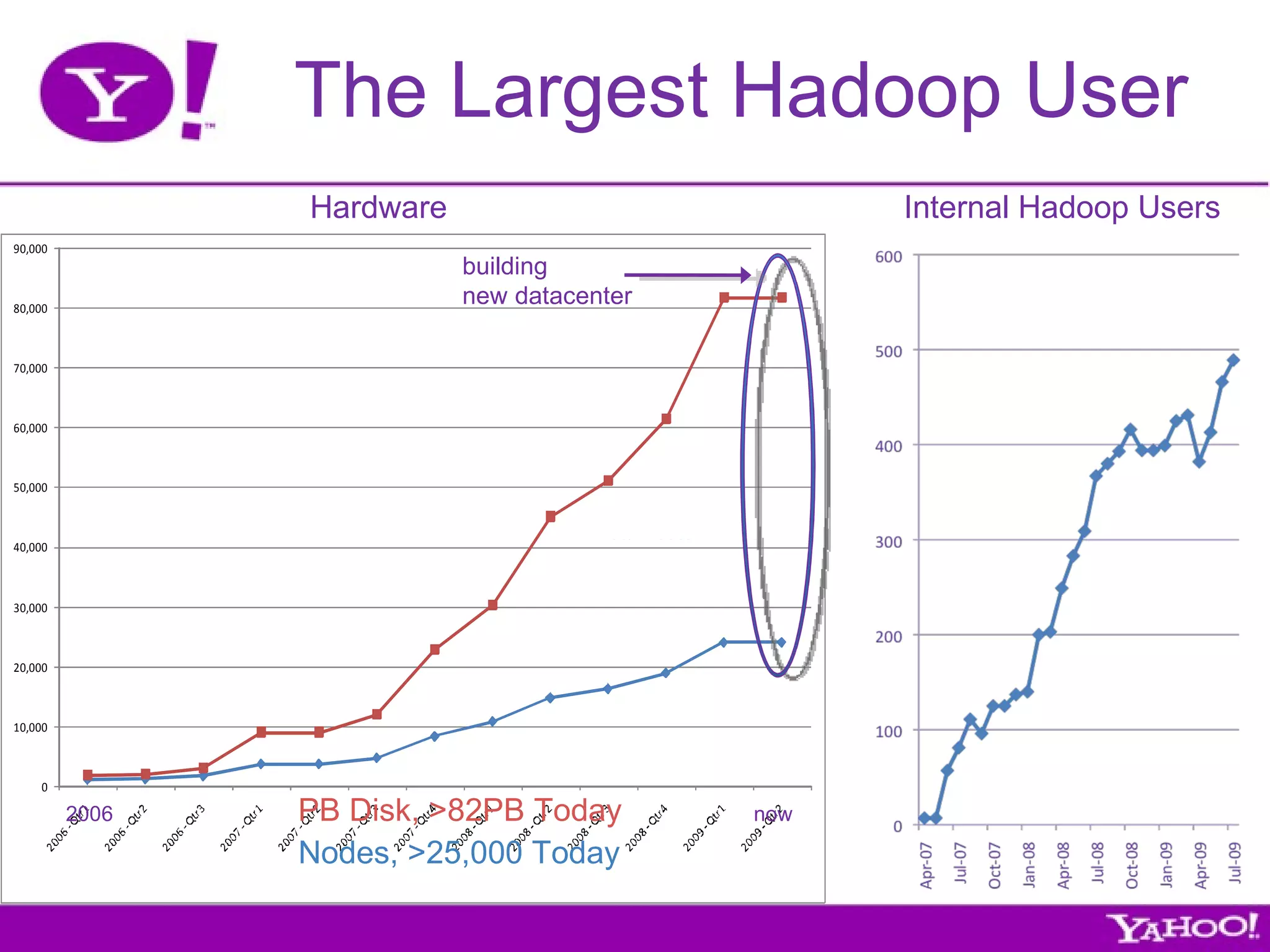
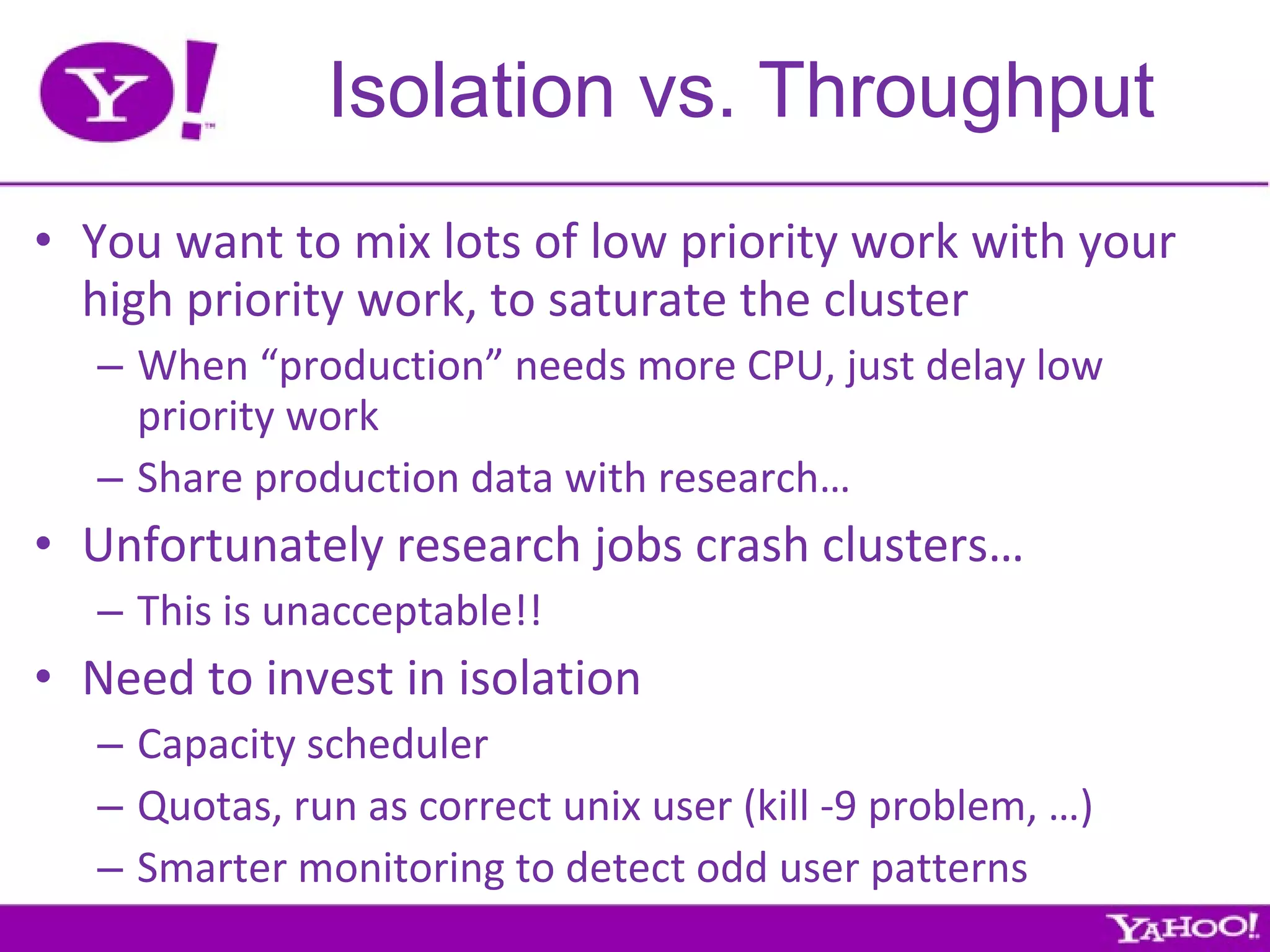
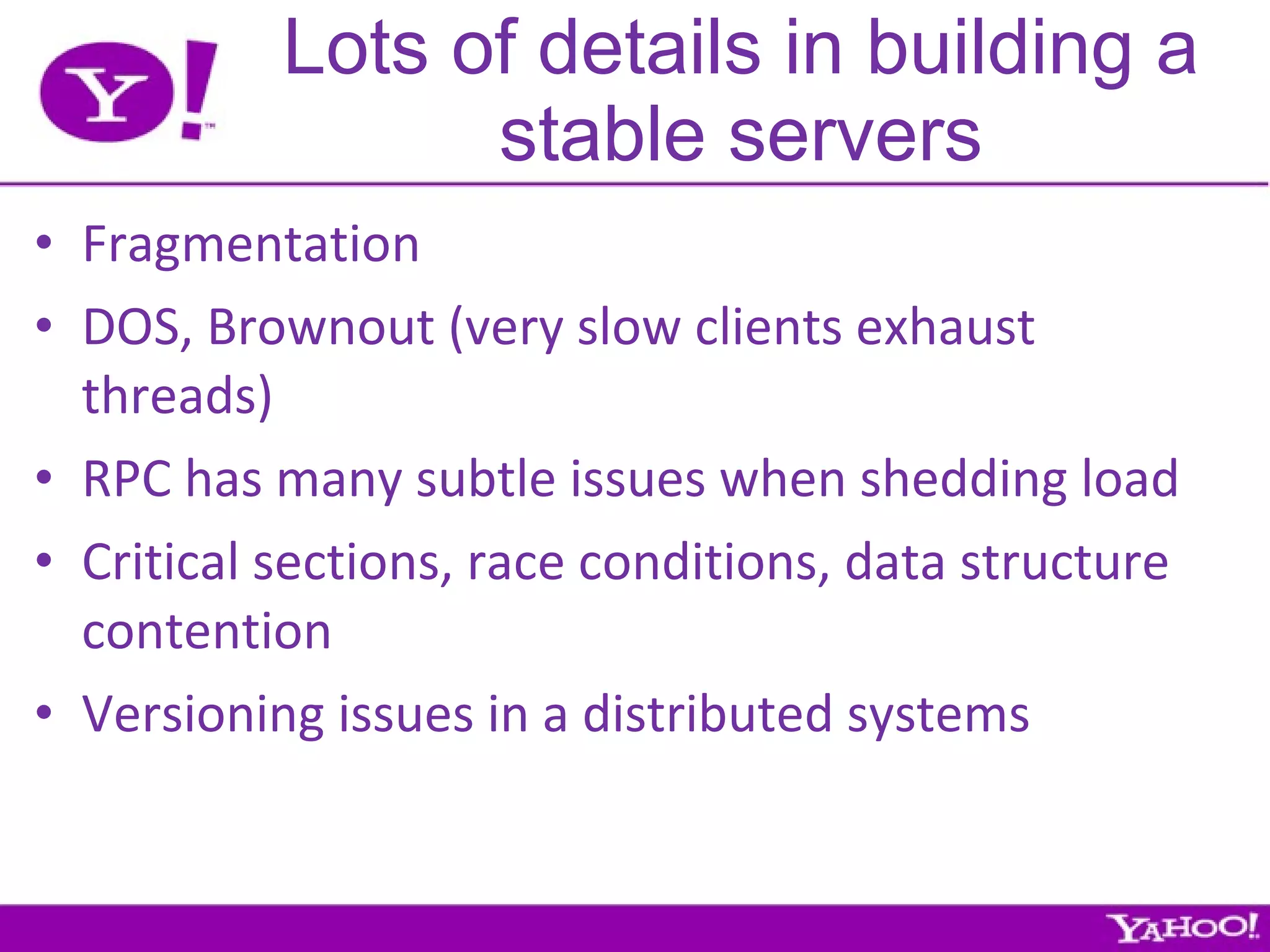
Yahoo is the largest corporate contributor, tester, and user of Hadoop. They have 4000+ node clusters and contribute all their Hadoop development work back to Apache as open source. They use Hadoop for large-scale data processing and analytics across petabytes of data to power services like search and ads optimization. Some challenges of using Hadoop at Yahoo's scale include unpredictable user behavior, distributed systems issues, and the difficulties of collaboration in open source projects.
![Hadoop at Yahoo! Eric Baldeschwieler VP Hadoop Software Development [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/universityq409v1-091029003657-phpapp01/75/Hadoop-at-Yahoo-University-Talks-1-2048.jpg)


















![Questions? Eric Baldeschwieler VP Hadoop Software Development [email_address] For more information: http://hadoop.apache.org/ http://hadoop.yahoo.com/ (including job openings)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/universityq409v1-091029003657-phpapp01/75/Hadoop-at-Yahoo-University-Talks-31-2048.jpg)