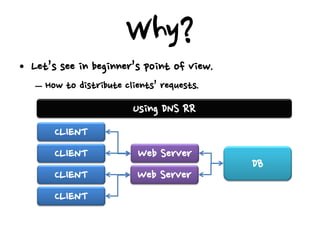
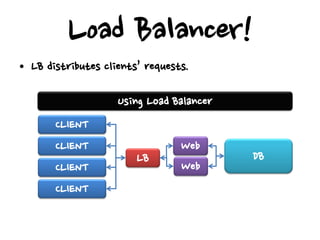
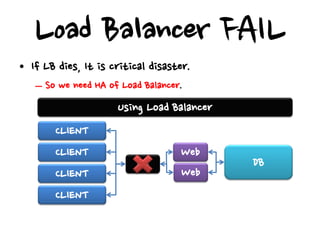
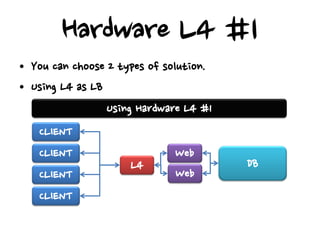
This document discusses high availability configurations for load balancers, especially for small companies. It presents options for dedicated servers in a data center using hardware load balancers or virtual IP addresses. It also discusses using Elastic Load Balancing and Elastic IP addresses on AWS. Key points covered are:
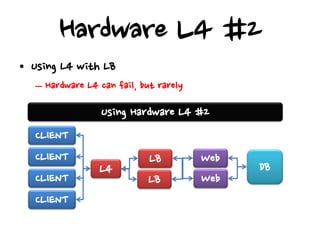
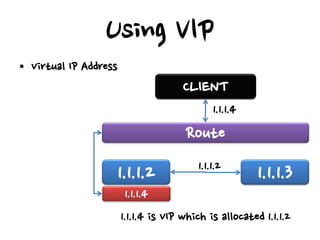
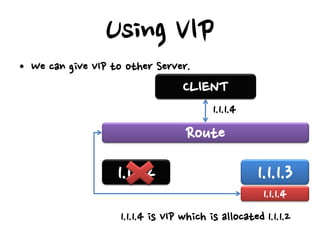
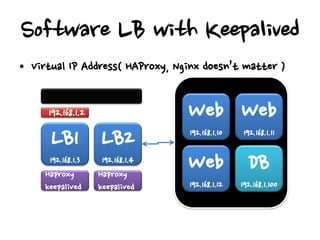
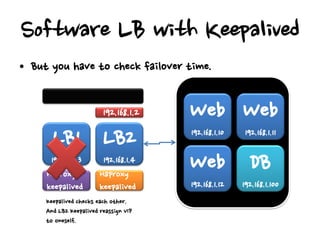
- Hardware load balancers can provide high availability but are an expensive solution, while virtual IP addresses require checking a load balancer's failover time.
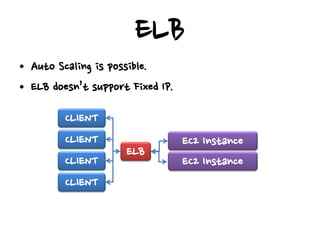
- On AWS, Elastic Load Balancing supports auto-scaling but doesn't support fixed IP addresses, while Elastic IP addresses can be associated and released like a virtual IP.
- Both ELB and EIP on AWS require ongoing payment, and neither can be used within internal AWS