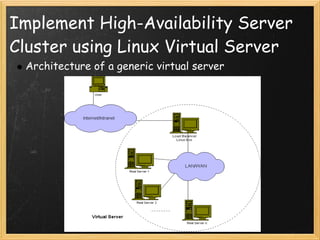
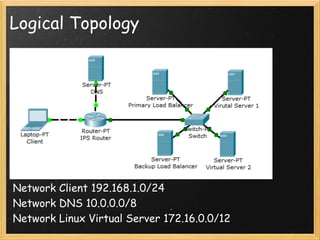
High-availability web server clusters use redundancy to ensure continuous service if any single component fails. They distribute workload across multiple servers for improved efficiency and scalability. The document proposes using Linux Virtual Server to implement such a cluster, with virtual servers distributing requests to real servers via network address translation, direct routing, or IP tunneling. Hardware requirements include servers, switches, and cabling to physically set up the redundant infrastructure.