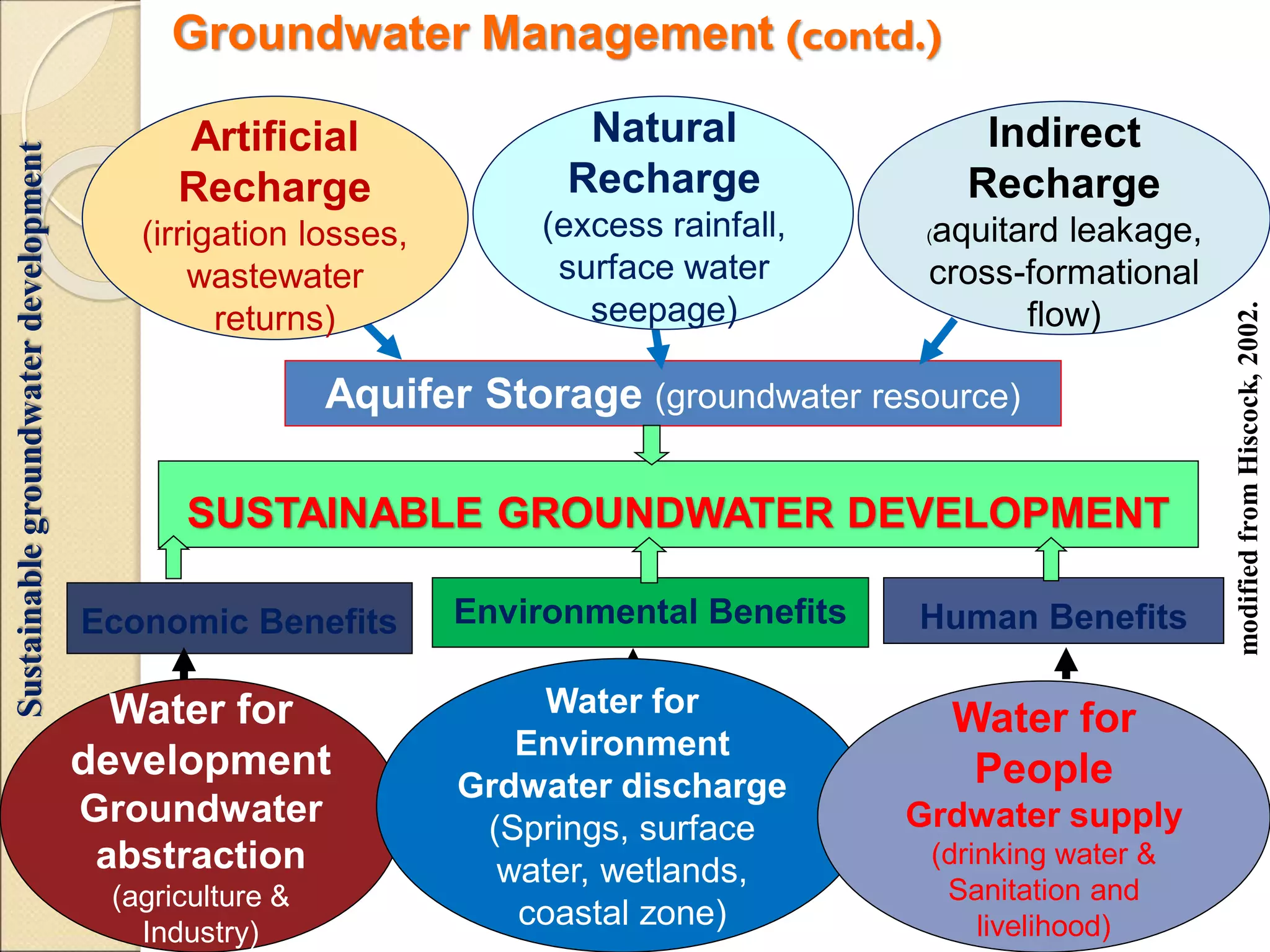
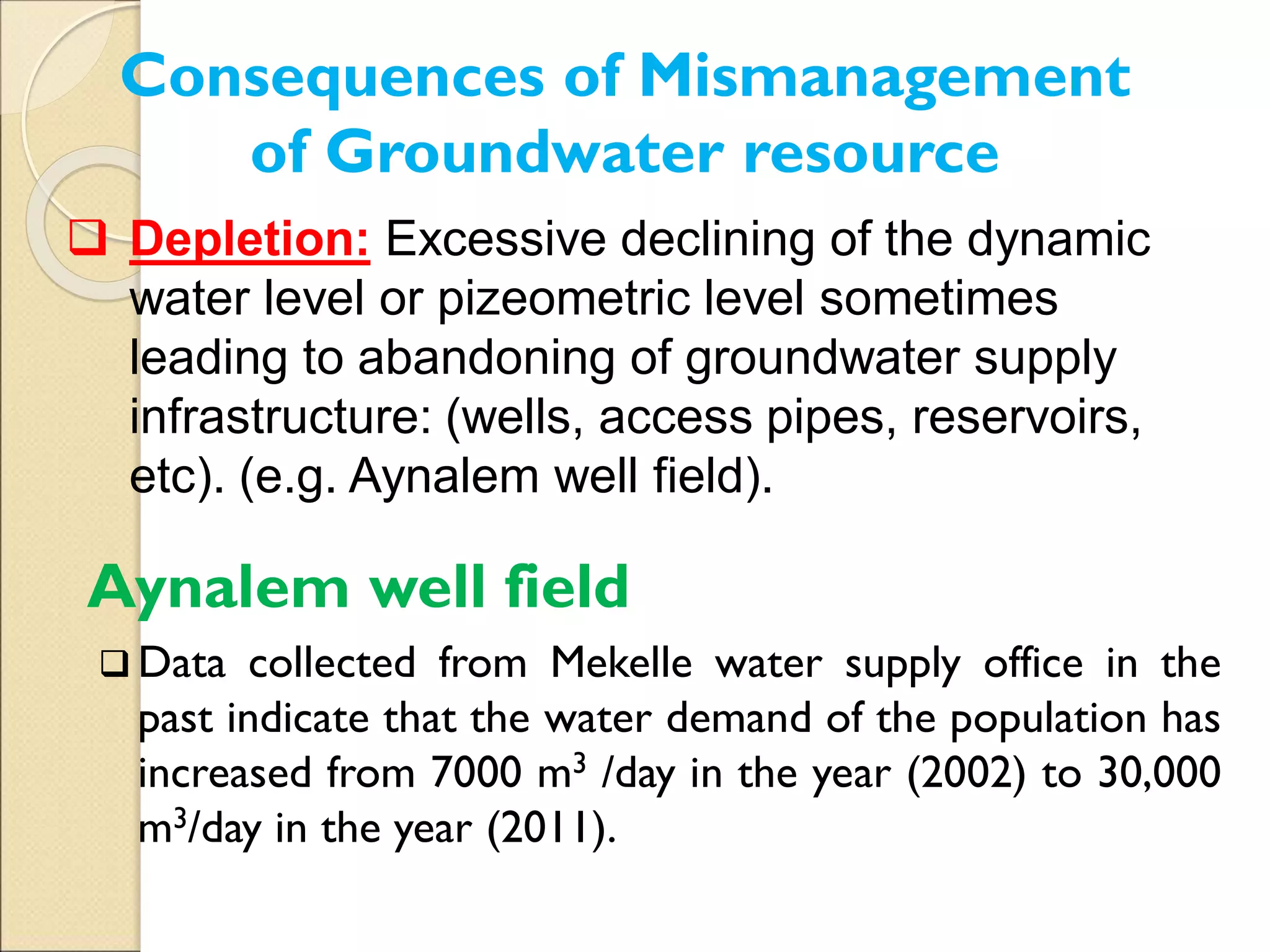
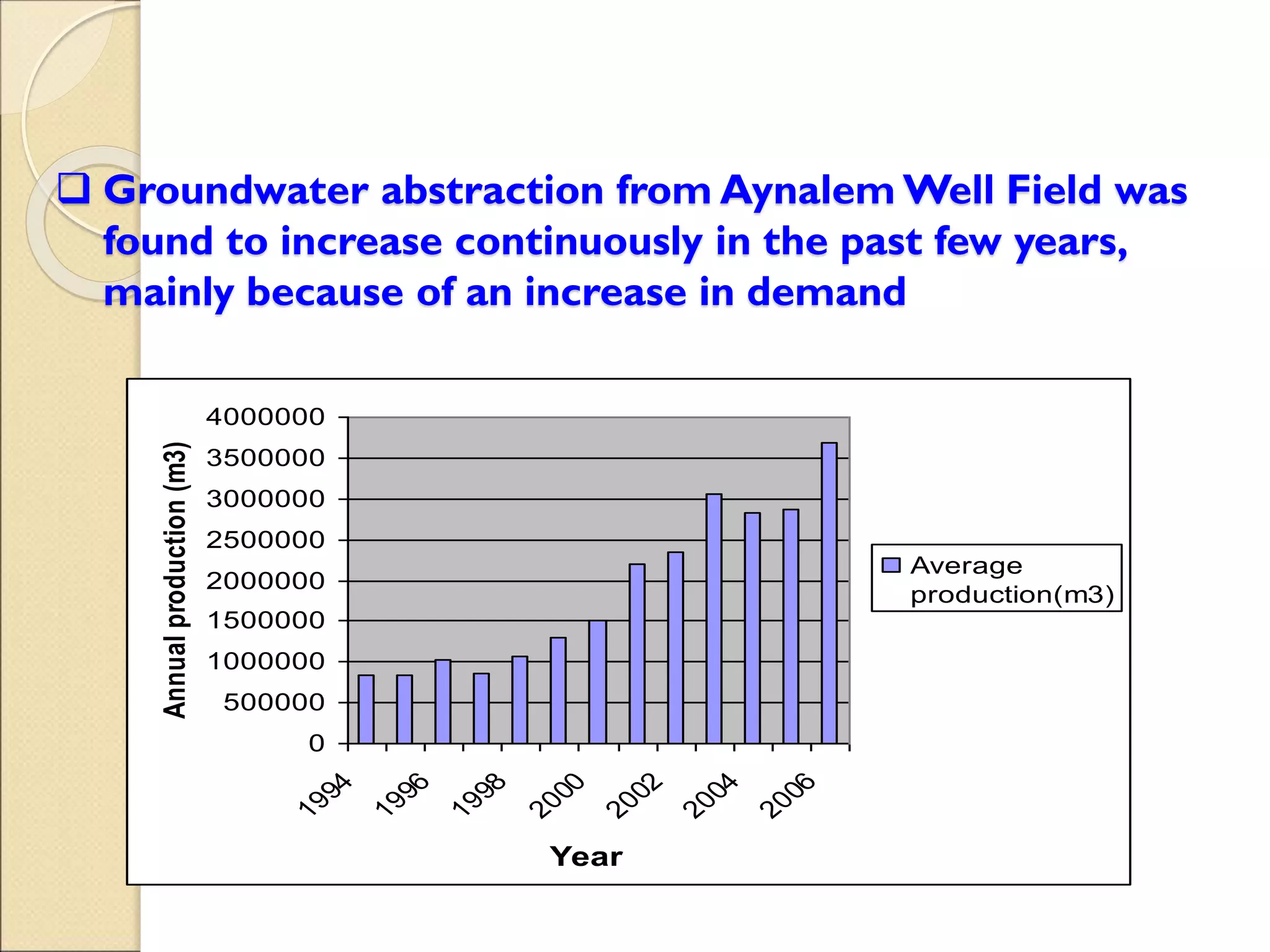
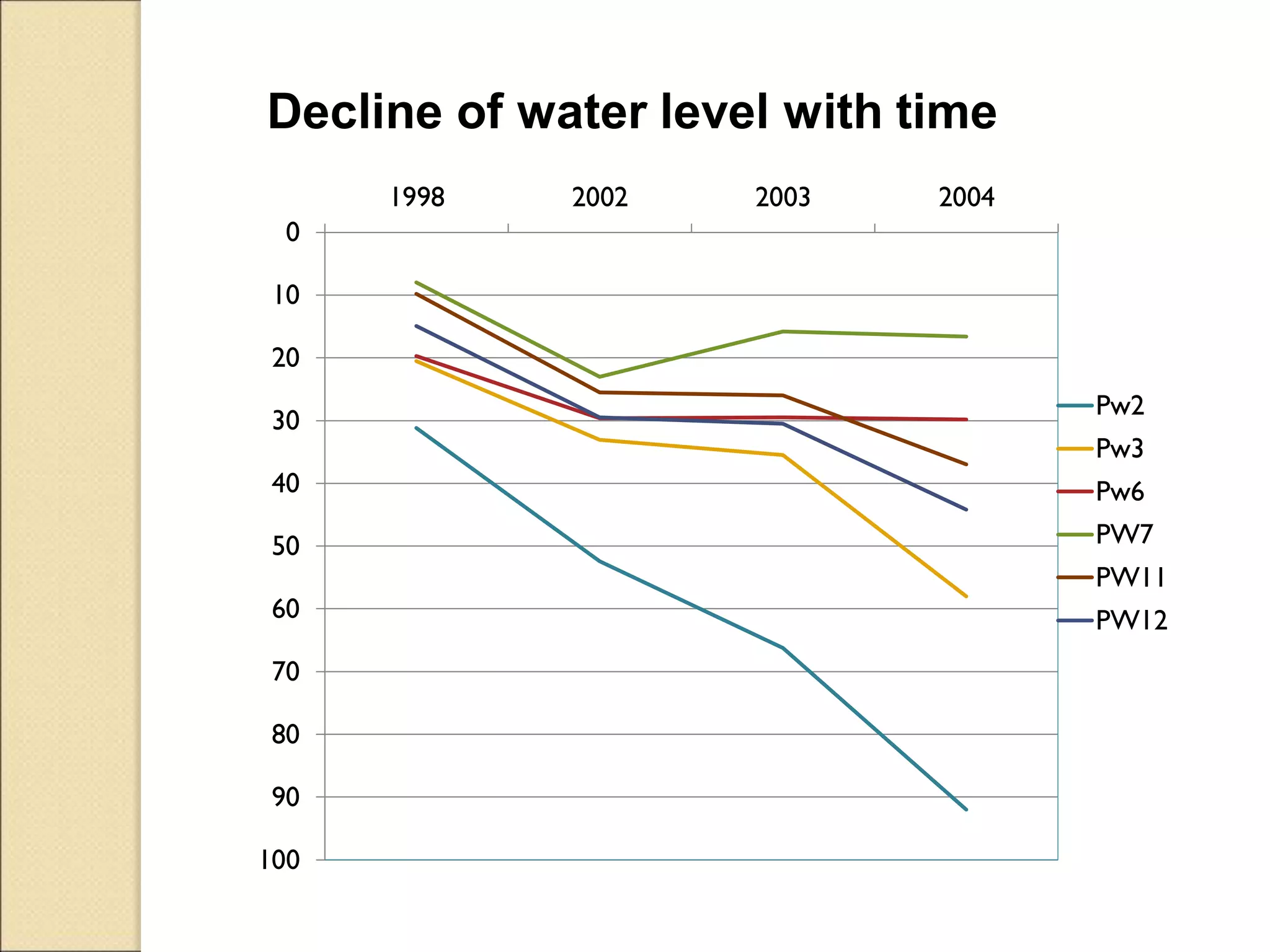
This document discusses integrated water resource management (IWRM) and groundwater resource management. It defines IWRM as an approach that promotes coordinated development and management of land and water resources, as well as surface and groundwater. Regarding groundwater specifically, the document states that management aims to balance groundwater recharge and withdrawals to ensure long-term sustainability of resources and water quality. It notes that excessive pumping from the Aynalem well field in Mekelle, Ethiopia led to a decline in water levels and abandonment of infrastructure due to unsustainable abstraction rates that did not account for aquifer recharge limits. Proper groundwater management is needed to avoid such consequences of mismanagement.