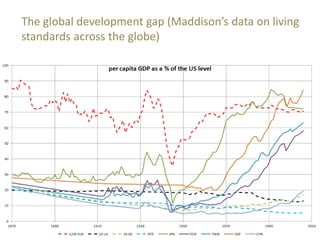
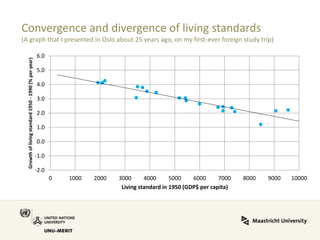
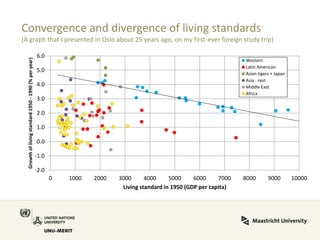
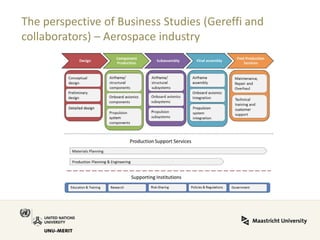
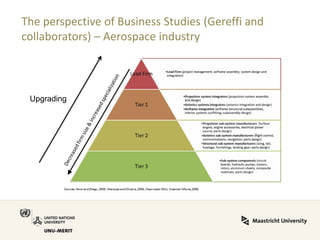
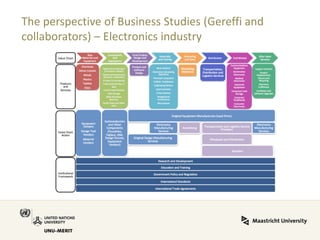
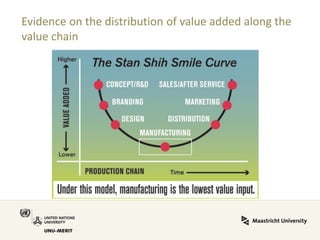
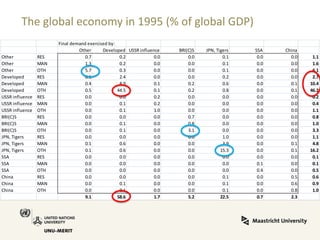
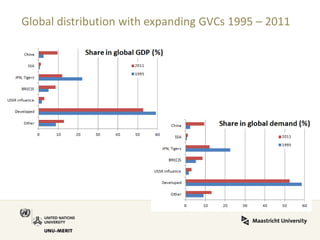
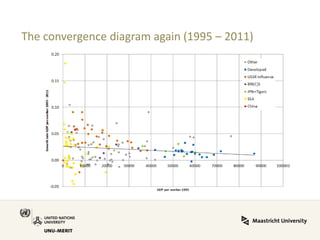
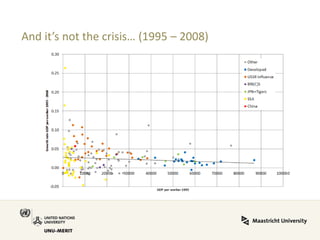
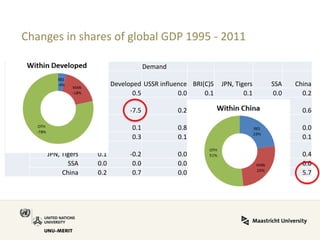
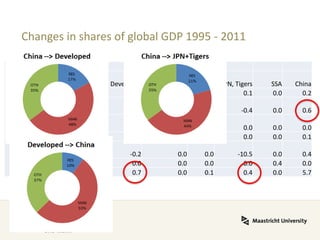
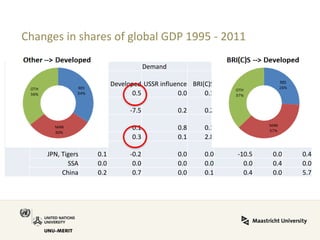
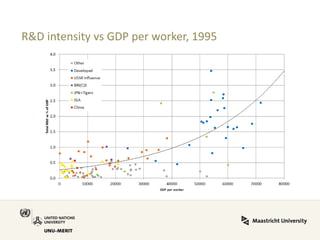
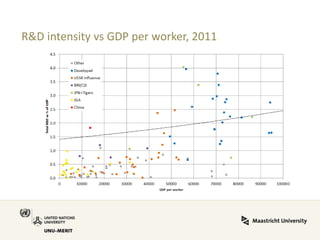
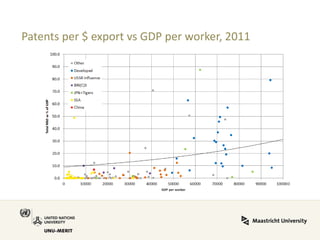
Global value chains have expanded significantly since 1995. While developed economies like the US and Japan have seen their share of global GDP decrease, emerging economies like China and countries in the BRICS bloc have experienced substantial growth. China in particular has grown from 0.5% to 5.7% of global GDP, reflecting its increasing participation and specialization in global manufacturing supply chains. However, capturing large shares of value added remains difficult for latecomers as knowledge-intensive activities tend to remain in developed countries. While globalization offers opportunities to enter international trade more easily, upgrading in global value chains requires strong innovation systems and policies to support learning and technology development domestically.