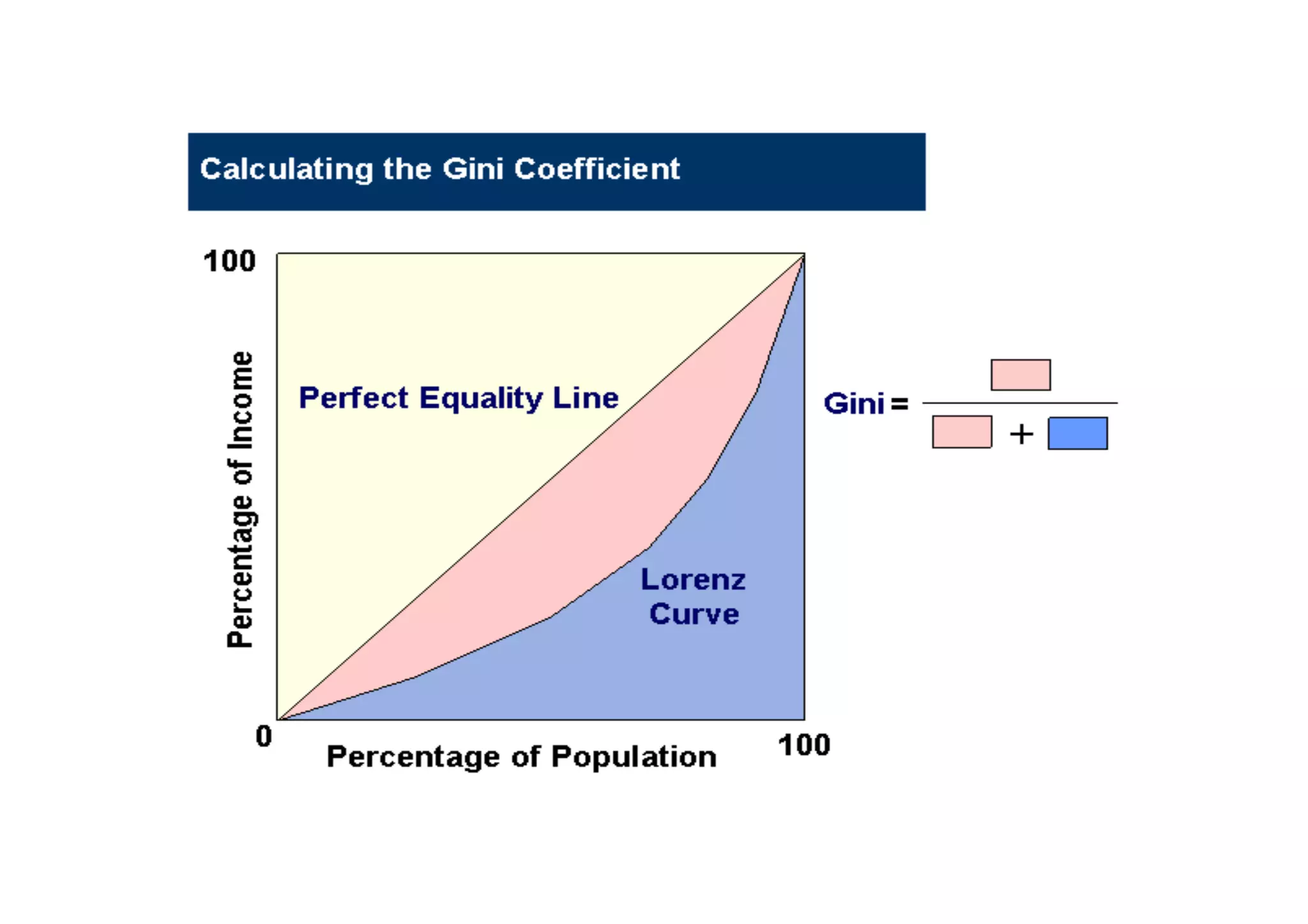
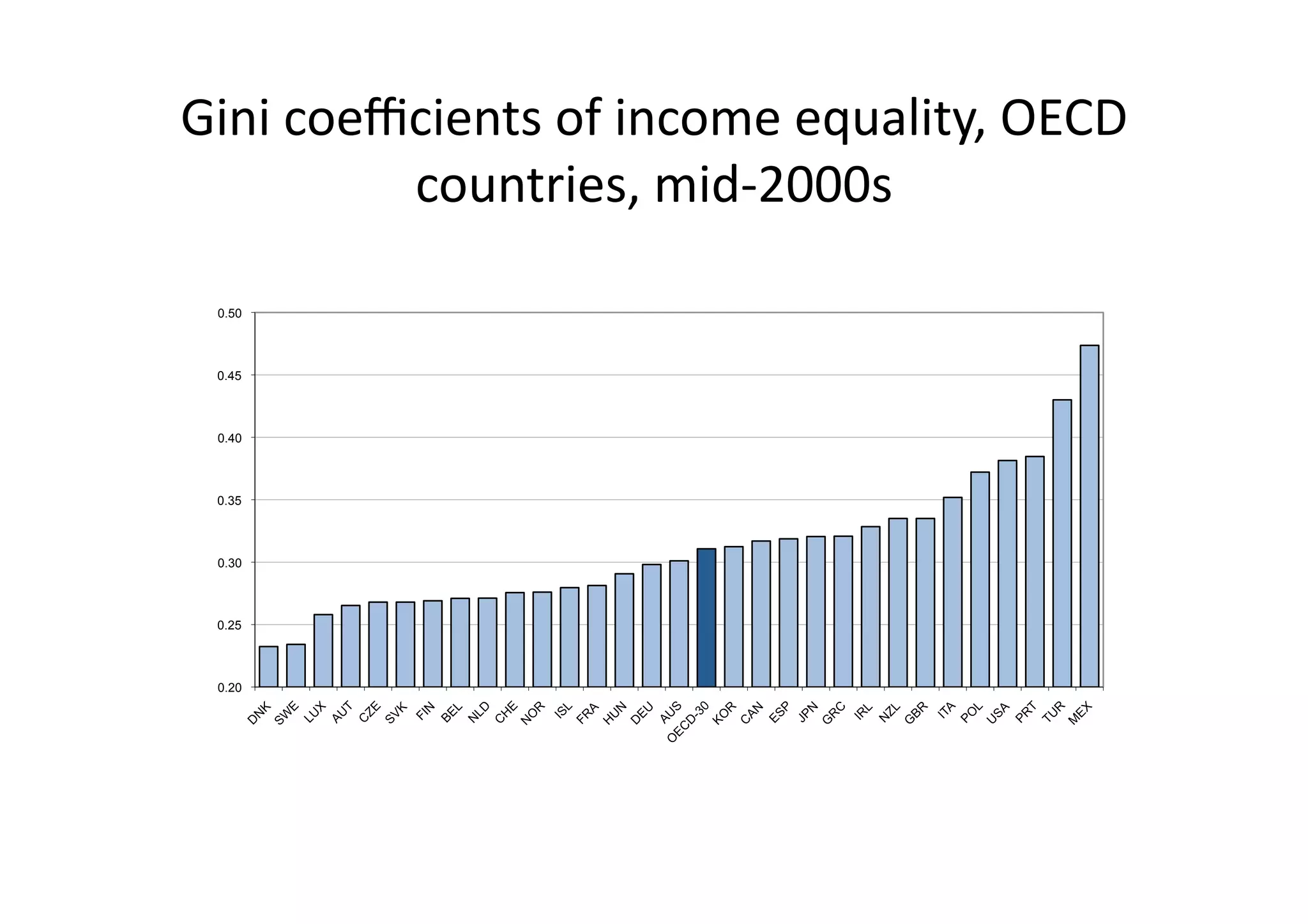
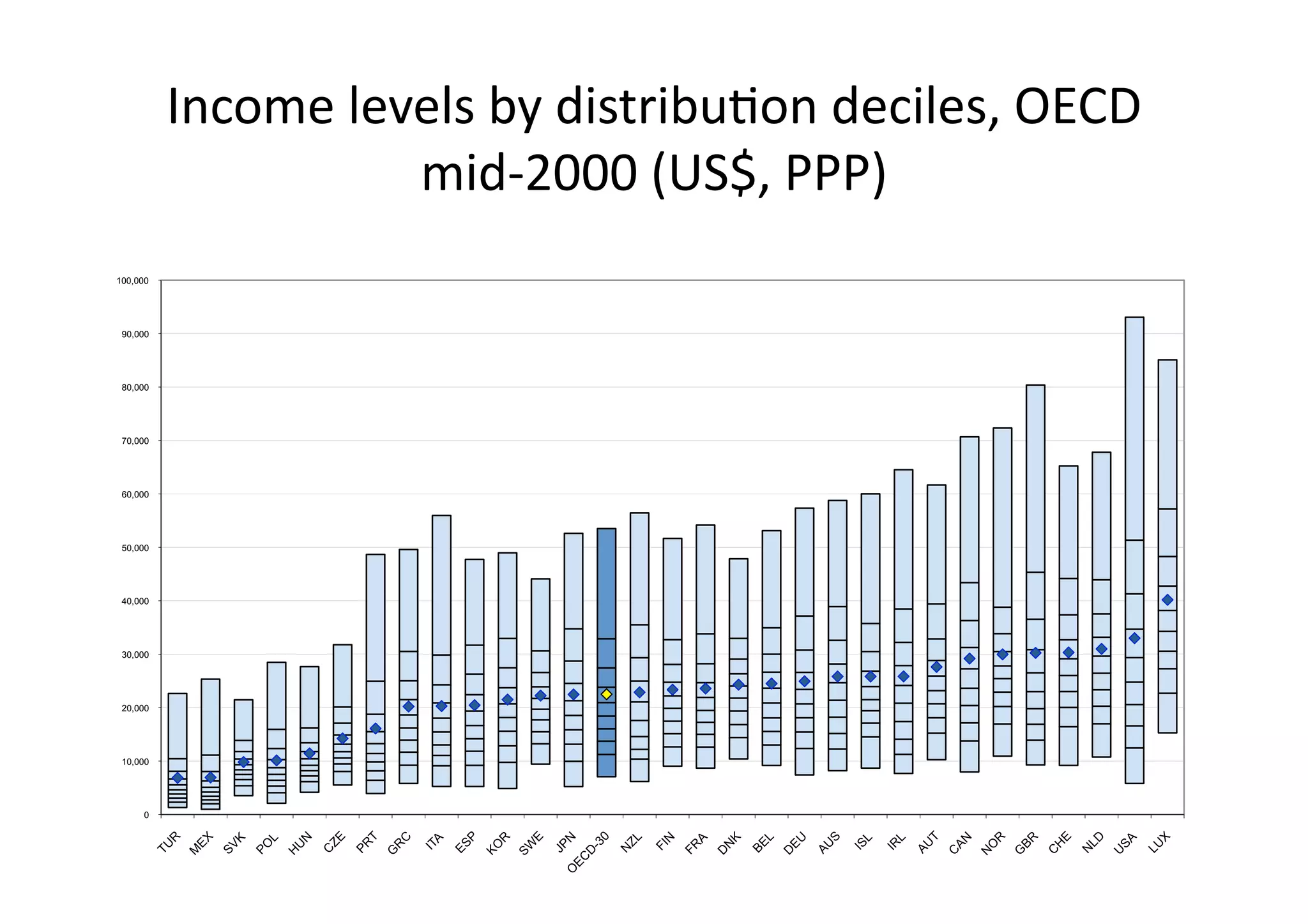
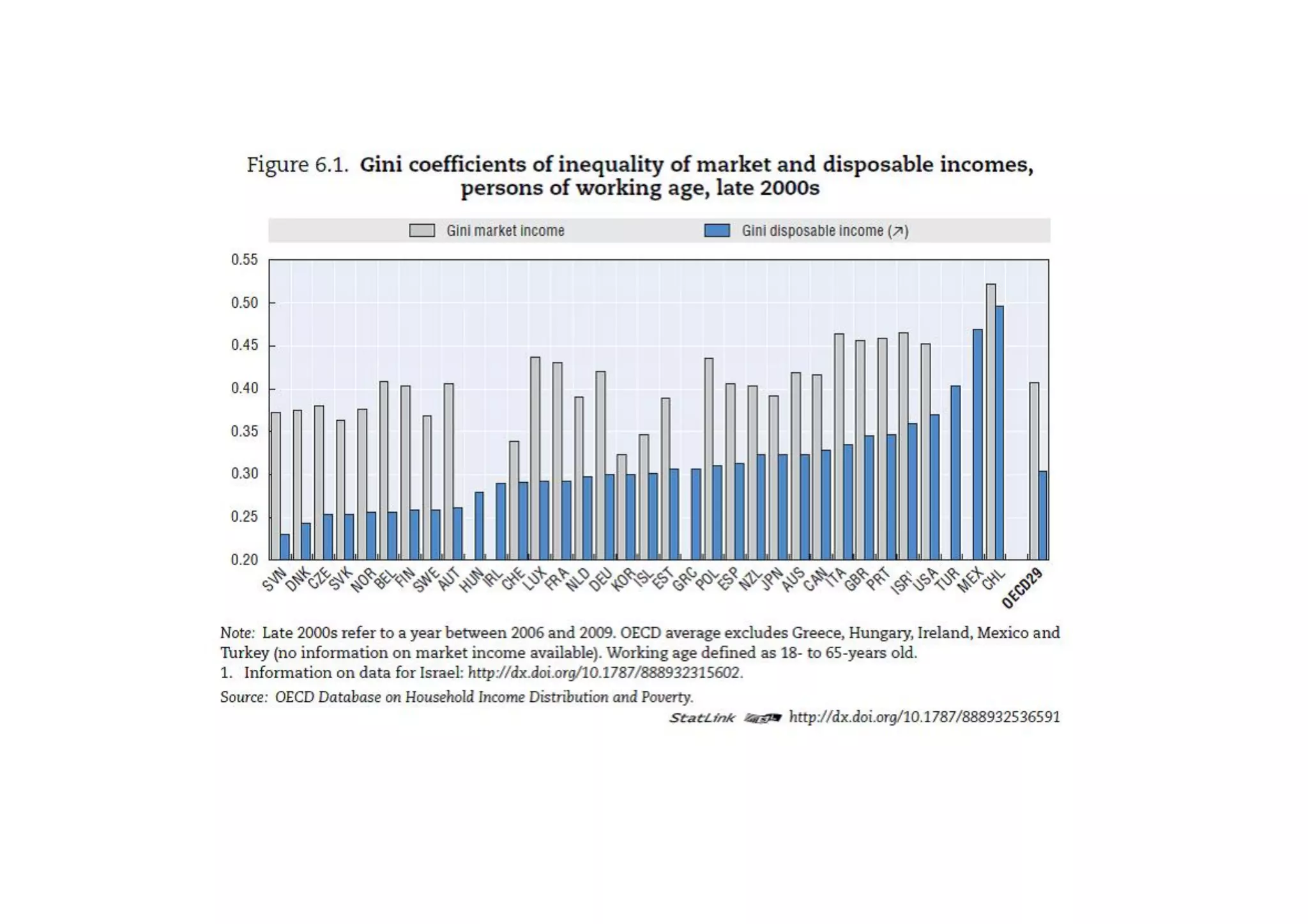
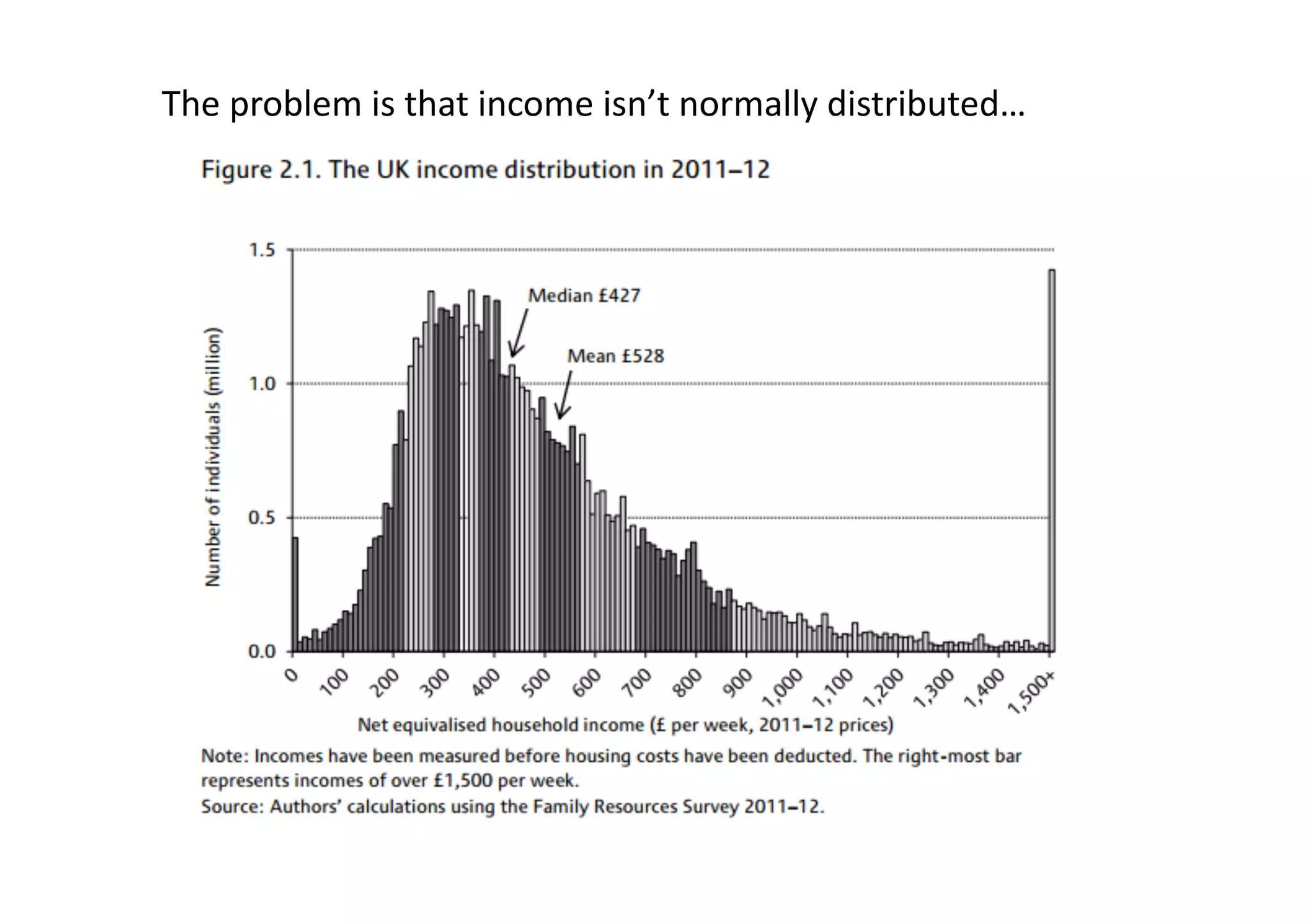
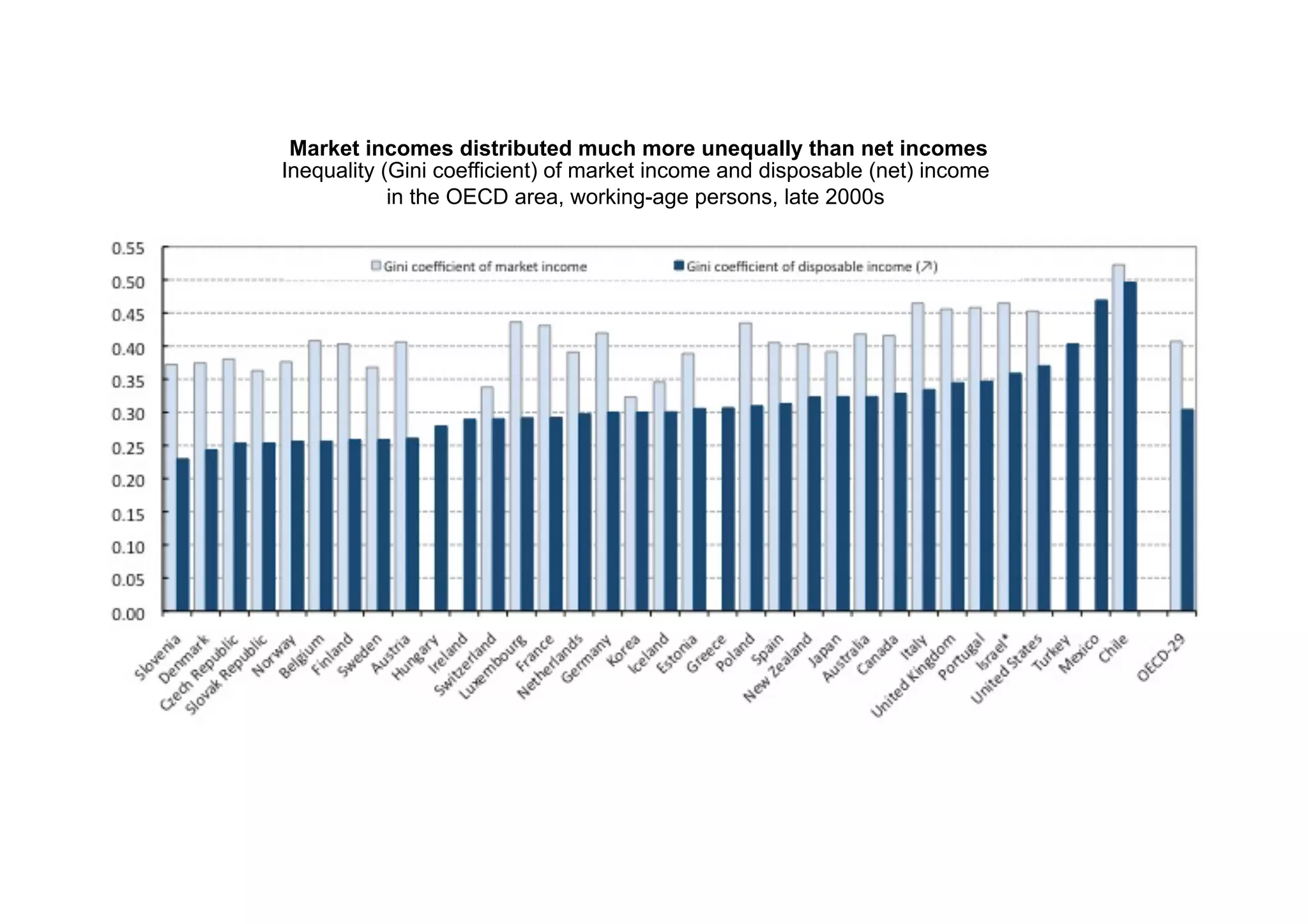
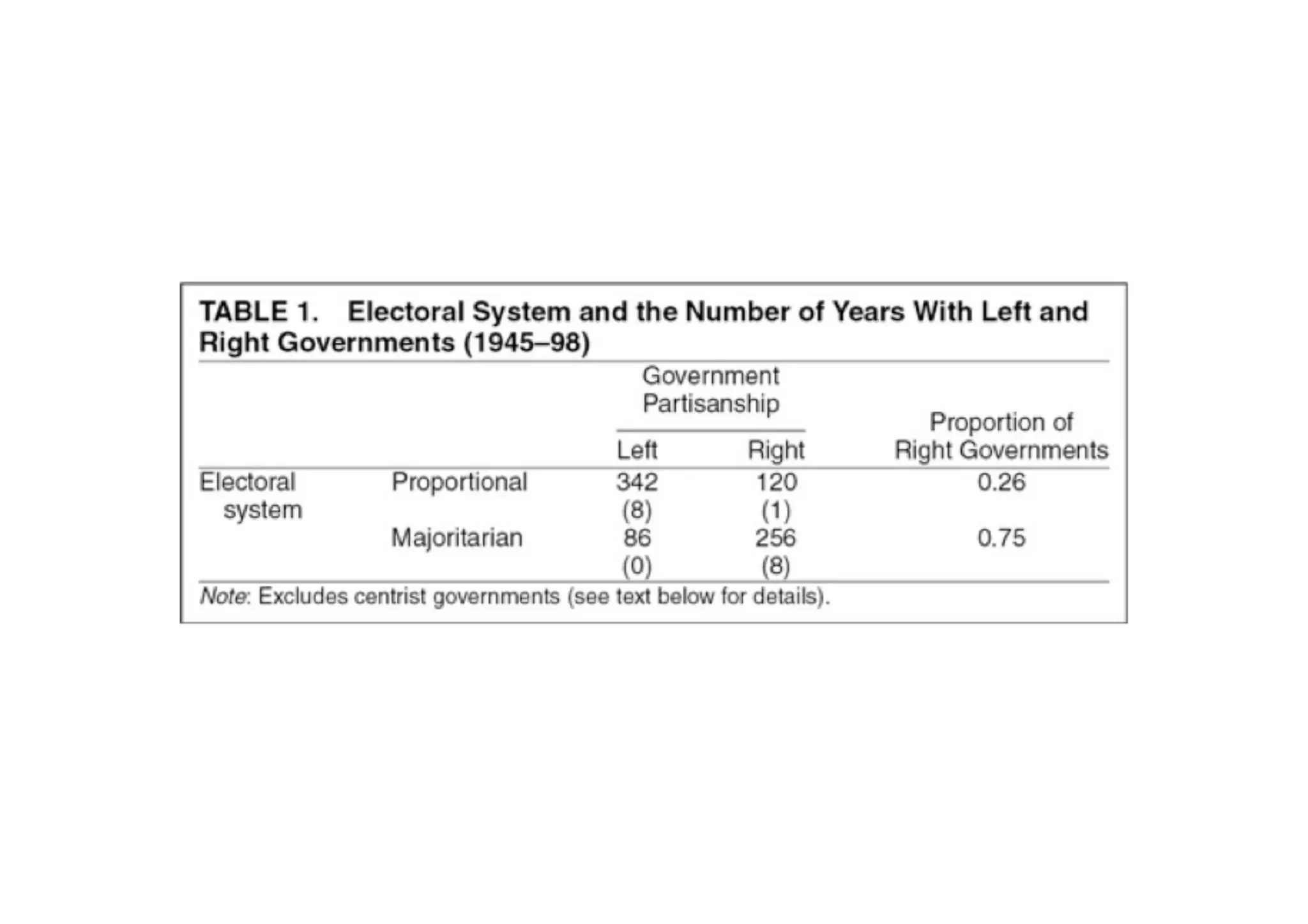
This document discusses measuring inequality and redistribution across advanced economies. It begins by explaining how inequality is typically measured using the Gini coefficient, with higher scores indicating higher inequality. Graphs show Gini coefficient scores for OECD countries in the mid-2000s, with the US and UK having among the highest inequality. The document also examines inequality within countries using income deciles and discusses factors that can influence inequality levels between nations, such as the strength of organized labor, economic openness, and welfare institutions.