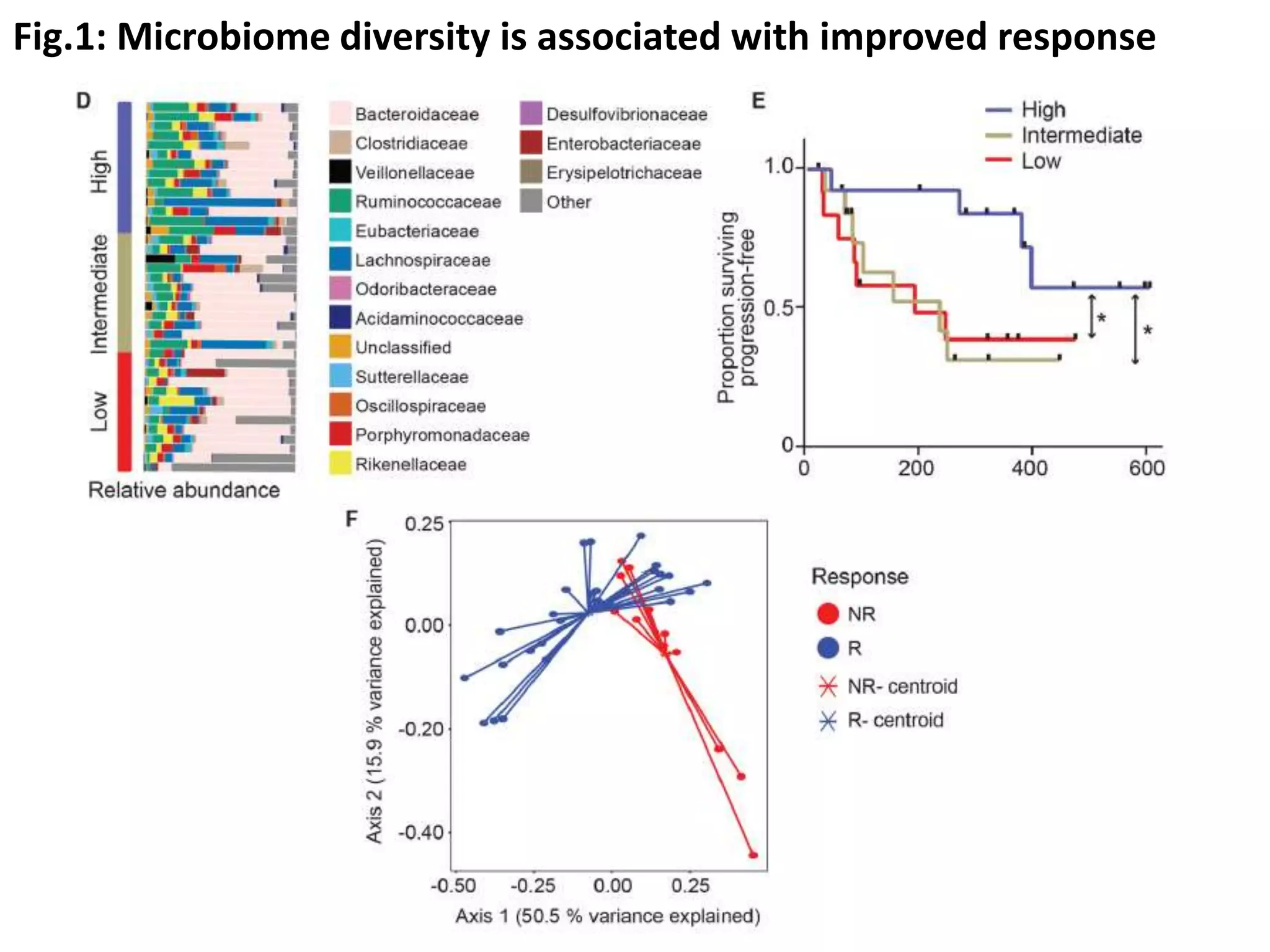
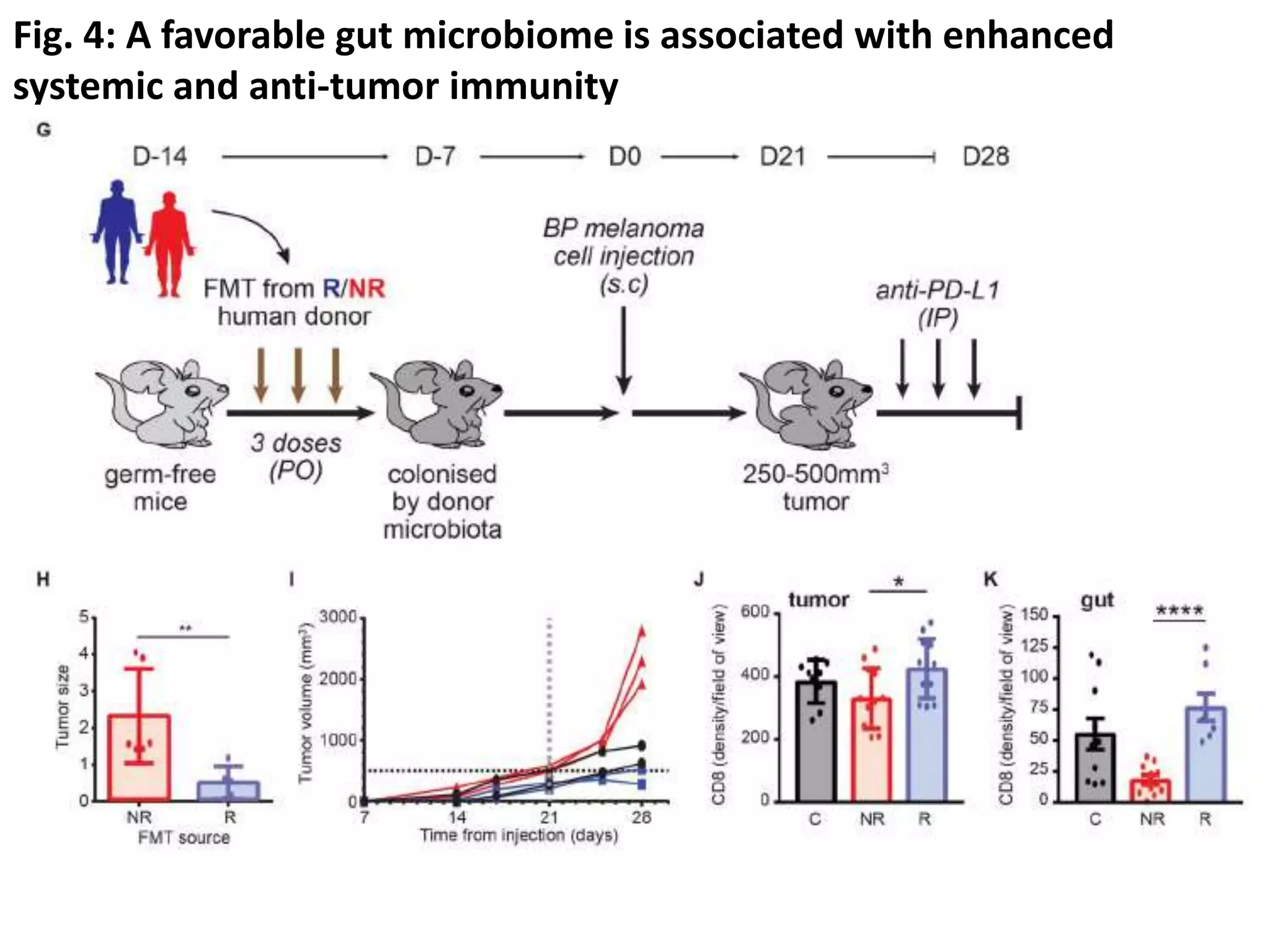
The journal club presentation discusses current treatments for advanced melanoma, highlighting targeted therapies and immunotherapies. While targeted therapies show a high response rate of 50-60%, their duration is limited, whereas immunotherapies have lower response rates but significant durability with longer survival outcomes. Additionally, the presentation explores biomarkers, including gut microbiome diversity, that may predict responses to immunotherapy.