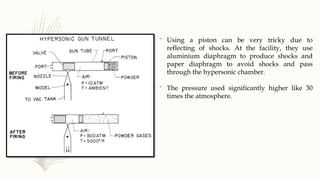
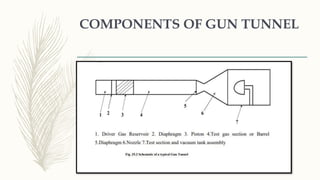
The document summarizes information about gun tunnels, which are a type of hypersonic wind tunnel that can produce flows up to Mach 30-40 by using a piston for isentropic compression. It describes the basic components and operating principles of gun tunnels, including how they use high pressure gases and diaphragms to accelerate test gases to hypersonic speeds over very short durations. Technological challenges of gun tunnels include reproducing equilibrium conditions at very high temperatures and pressures while also requiring fast instrumentation.