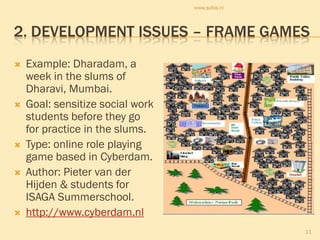
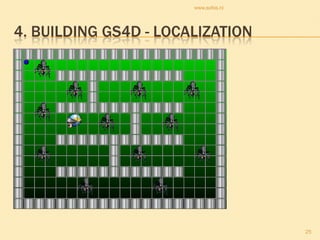
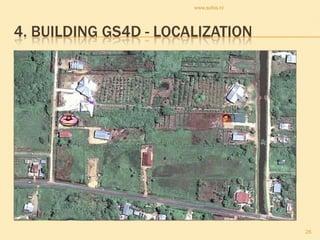
The document discusses gaming/simulation for development (GS4D). It presents examples of development issues that can be addressed through games, including frame games, global issues games, and specific issue games. Localization is key to building successful GS4D games, requiring adapting content for other cultures and languages. Building international teams is also important but challenging due to limitations of intercultural communication. GS4D has great potential when localization is properly handled, though internationalization of games is still a new concept.