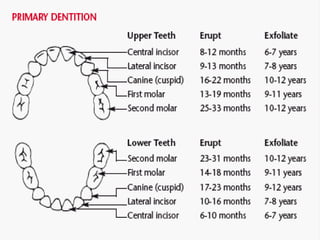
The document discusses growth, development, and maturation from infancy to adolescence. It defines the key terms and outlines the major developmental periods from prenatal to adolescence. The characteristics of growth and development are described as continuous, orderly processes that proceed in predictable stages and sequences from head to tail and center to periphery. Factors like heredity, environment, nutrition, and illness can influence growth. Physical, cognitive, and psychosocial developments are discussed for each developmental period.