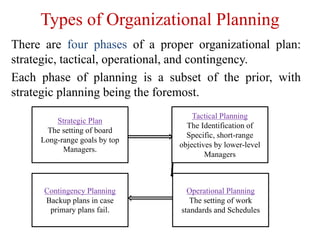
1. The document discusses operational planning, including defining it as turning a strategic plan into detailed weekly or daily actions. It outlines key objectives and goals and ensures clear responsibilities.
2. It provides examples of operational planning advantages like clarifying goals and defining daily tasks and responsibilities to measure against objectives.
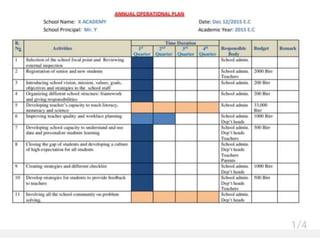
3. The document provides guidance on creating an operational plan, such as identifying goals and initiatives, defining assumptions, and outlining responsibilities and tasks.