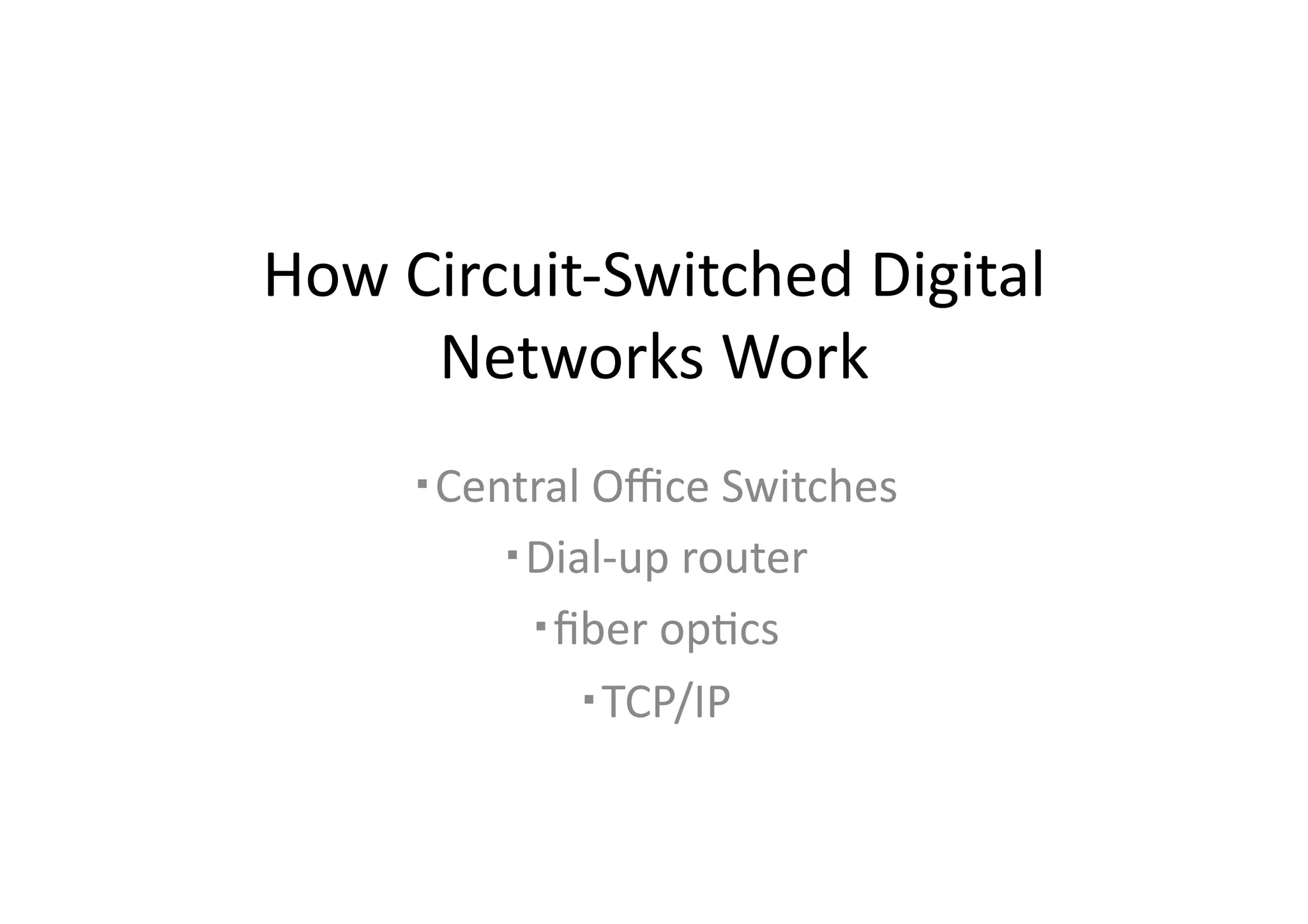
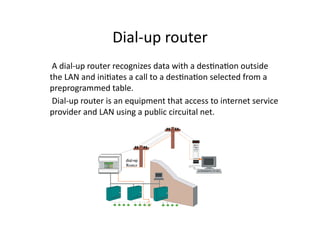
This document summarizes how circuit-switched digital networks work. It discusses the key components including central office switches located in telephone company offices that route calls locally or to long-distance carriers. Dial-up routers recognize outbound data and initiate calls to internet service providers over public circuits. High-speed fiber optic links transmit data between switches at minimum speeds of 45 megabits per second. TCP/IP packets are used to transmit data across local and wide area networks with TCP/IP being the standard internet protocol.