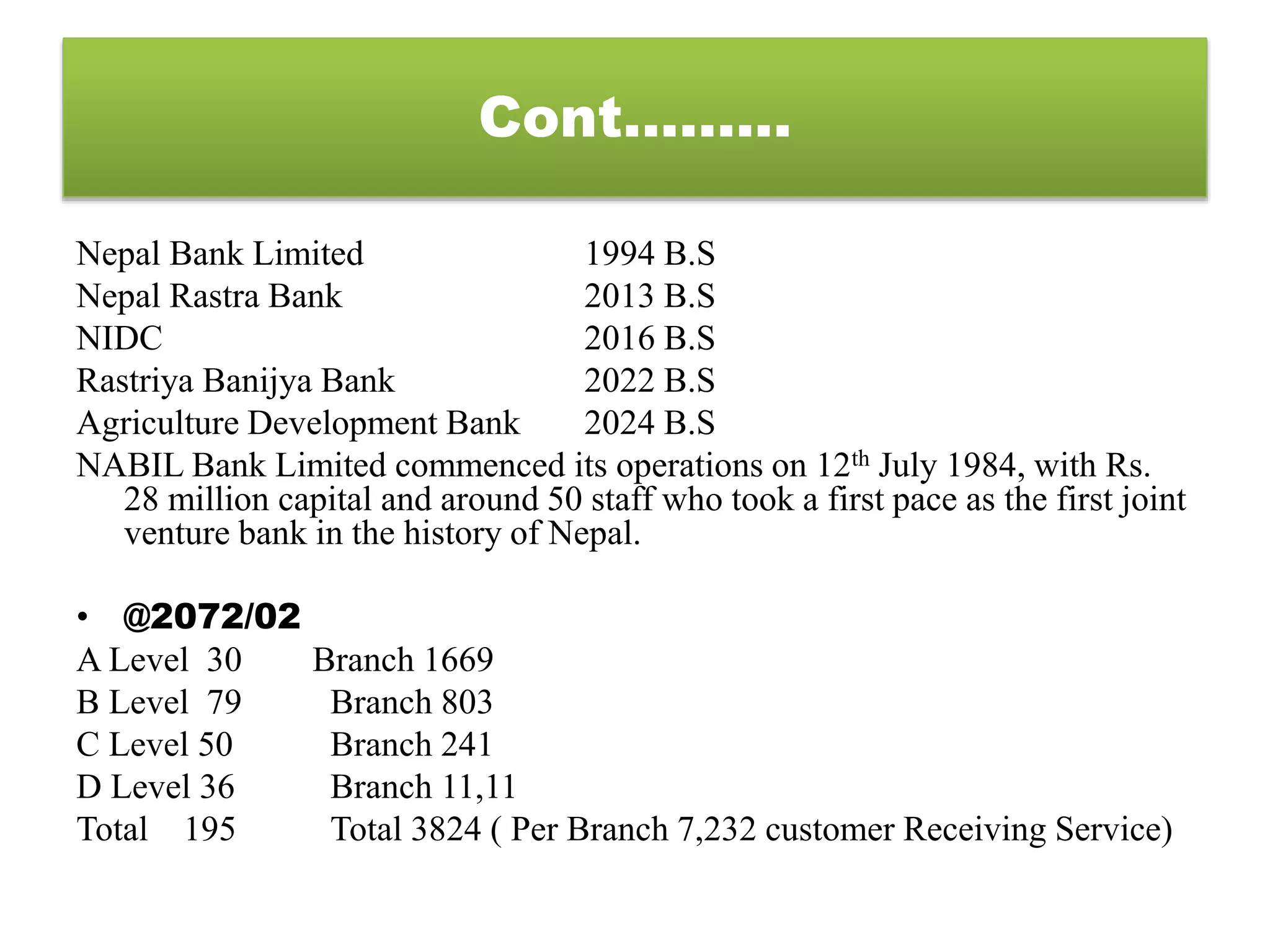
Major Functions of Bank and Financial Institutions in Nepal provides an overview of the various types of financial institutions in Nepal and their core functions. It discusses the history and development of banking in Nepal beginning with the Tejarath Adda in 1976 and establishment of Nepal Bank Limited in 1994 and Nepal Rastra Bank as the central bank in 2013. The core functions of commercial banks include accepting deposits, providing loans, foreign exchange services, credit/debit cards, and money transfers. Development banks focus on financing economic development through loans and credit guarantees. Finance companies specialize in short-term personal or consumer loans. Microfinance development banks specifically target small loans to low-income individuals and micro-enterprises.