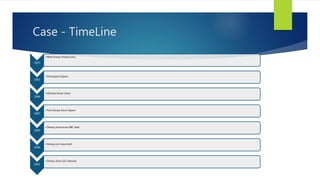
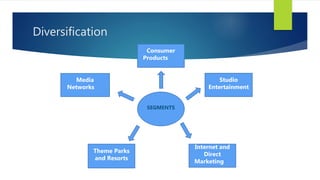
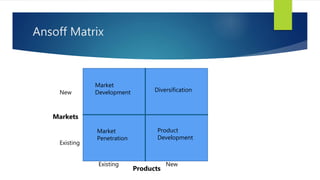
Walt Disney started as a cartoon studio in 1923 and has since diversified into a mass media and entertainment conglomerate. Key events in Disney's timeline include opening Disneyland in 1955, hiring Michael Eisner in 1984, opening the first Disney Store in 1987, and announcing a deal to acquire ABC in 1995. Under Eisner's leadership in the 1980s and 1990s, Disney pursued strategies like cost cutting, corporate synergy, international expansion, and managing its brand and creativity. Disney has grown through diversification, horizontal and vertical integration, and leveraging media synergy across its businesses.