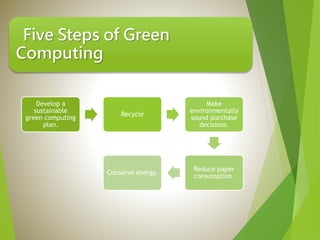
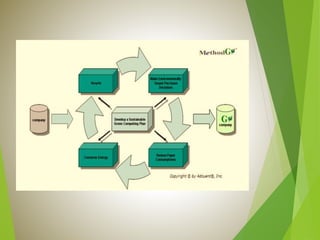
The document discusses green computing, defined as the environmentally responsible use of computers and their resources, which includes green disposal, design, use, and manufacture. It outlines the importance of energy efficiency, recycling, and sustainable practices in computing and offers practical steps to achieve these goals. The presentation aims to raise awareness of green computing's impact on the environment and provide strategies for implementation.