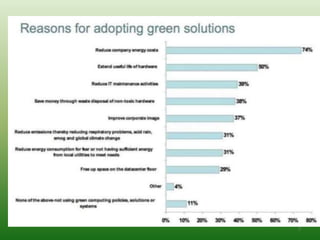
Green computing aims to reduce the environmental impact of computing through more efficient use of computing resources and environmentally friendly design and disposal of computer technologies. It seeks to minimize energy consumption and promote renewable energy sources, reduce paper usage, and ensure easy recycling of electronic equipment. The goals of green computing are to reduce hazardous materials usage, maximize energy efficiency over the lifetime of products, and promote recyclability. Recent implementations of green computing principles include search engines like Blackle that reduce energy usage and very low power computers like the Zonbu and Fit PC. The future of green computing is expected to see more eco-friendly components and emphasis on energy savings across enterprises.