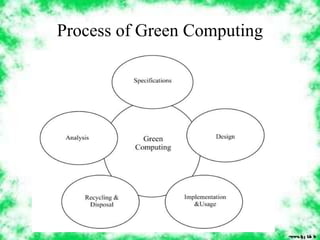
Green computing involves the environmentally sustainable and efficient use of computing resources. It includes designing and manufacturing computers with non-toxic, recyclable materials and maximizing energy efficiency during use and disposal. Adopting practices like turning off computers when not in use, using power saving modes, recycling electronics, and replacing toxic components can help reduce pollution and waste while still enabling computing. The overall goal of green computing is to reduce the environmental impact of computing through its entire lifecycle from creation to disposal.