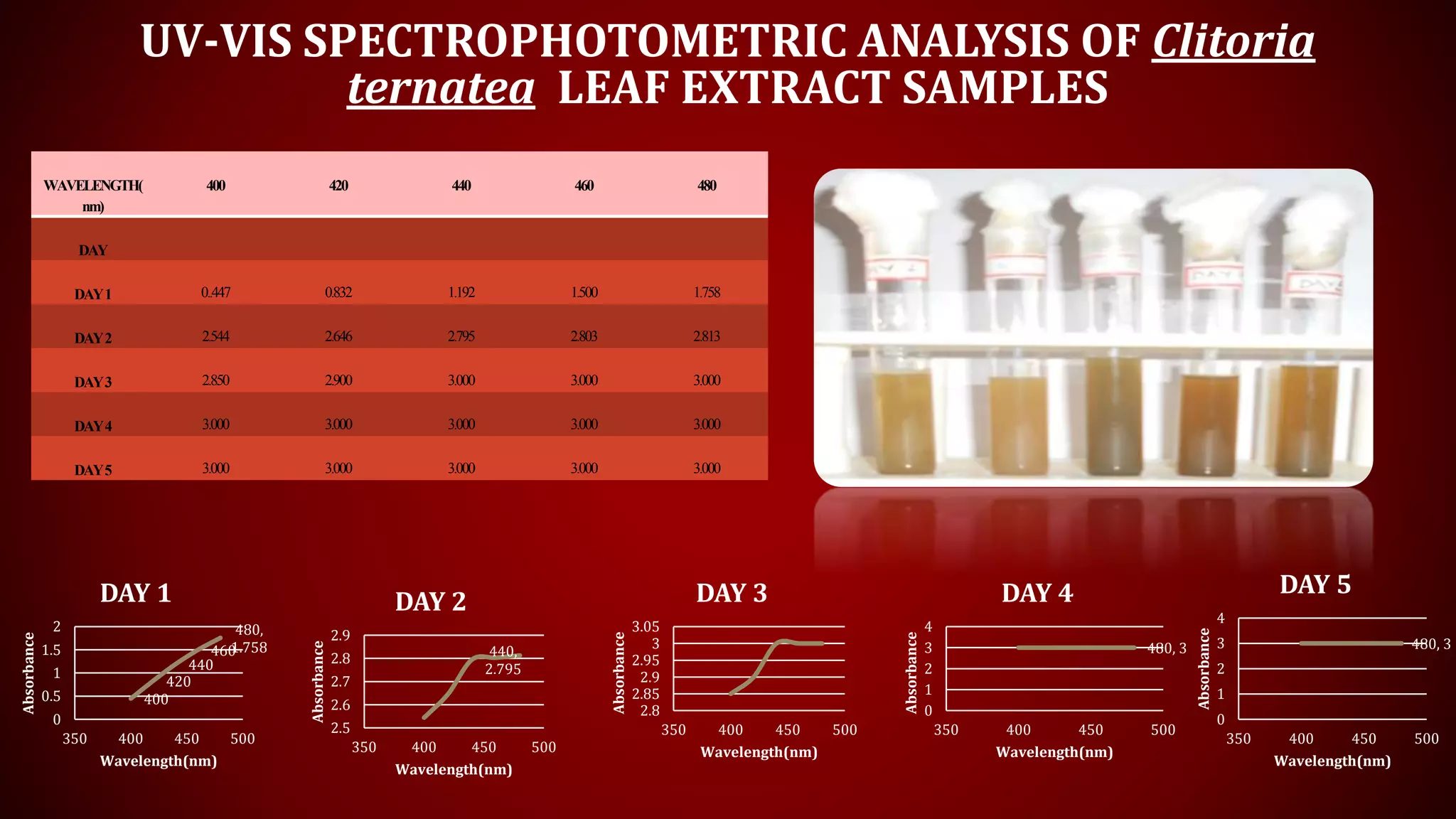
The document discusses the green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Clitoria ternatea, detailing the extraction process and characterization techniques such as UV-Vis spectroscopy and FE-SEM. It highlights the advantages of using silver nanoparticles for their antibacterial and antifungal properties in medical and environmental applications. The conclusion emphasizes the eco-friendly nature of the synthesis method and its potential to combat antibiotic resistance.