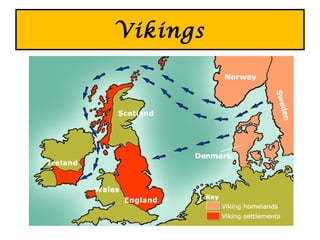
The United Kingdom is made up of England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. It has a varied landscape from mountains to lowlands. The UK has a temperate climate influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean. Many groups have invaded and settled in Britain over time, including the Romans, Anglo-Saxons, Vikings, and Normans, leaving behind cultural and linguistic influences. The country developed a strong monarchy and parliamentary system of government.