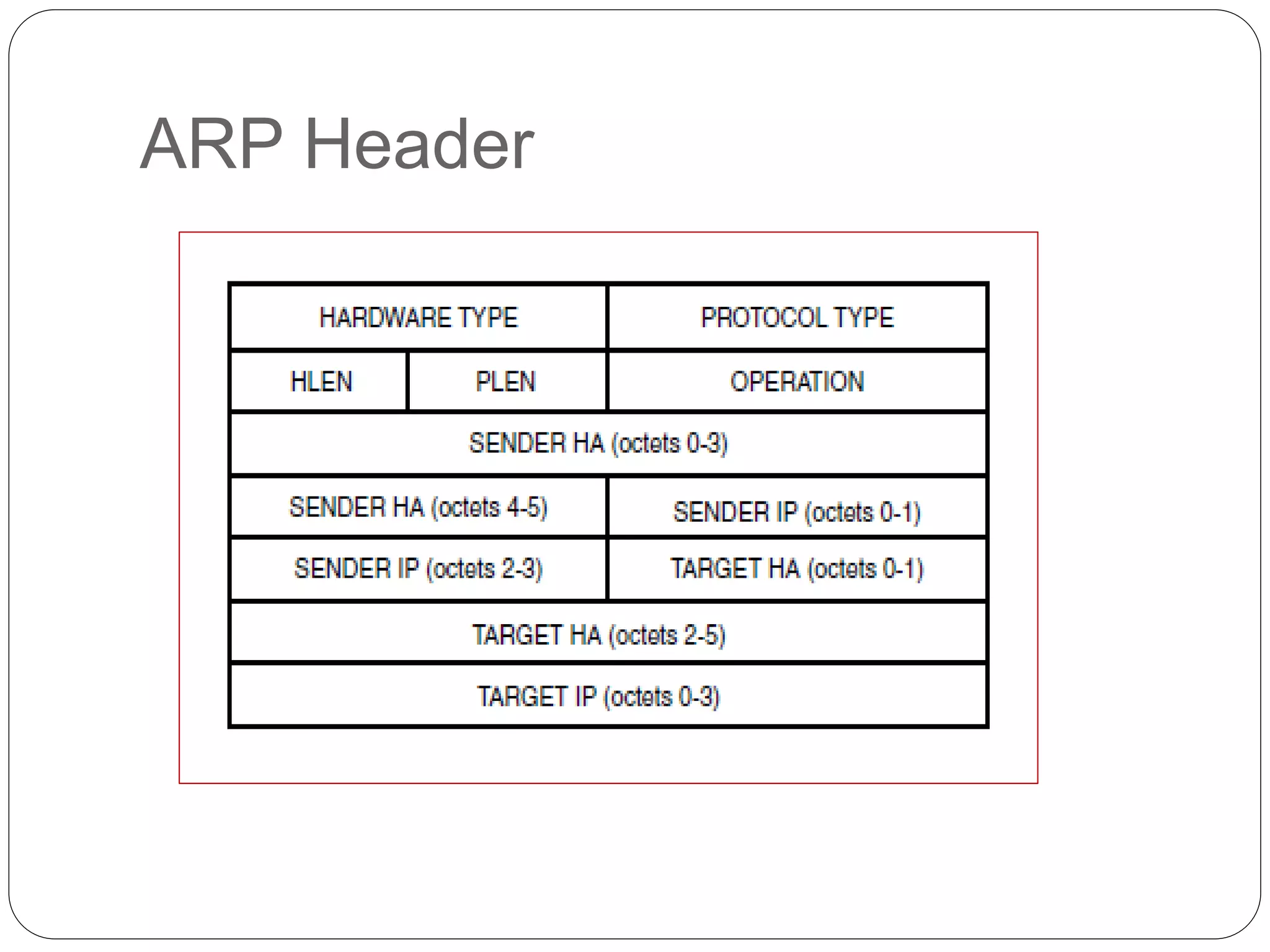
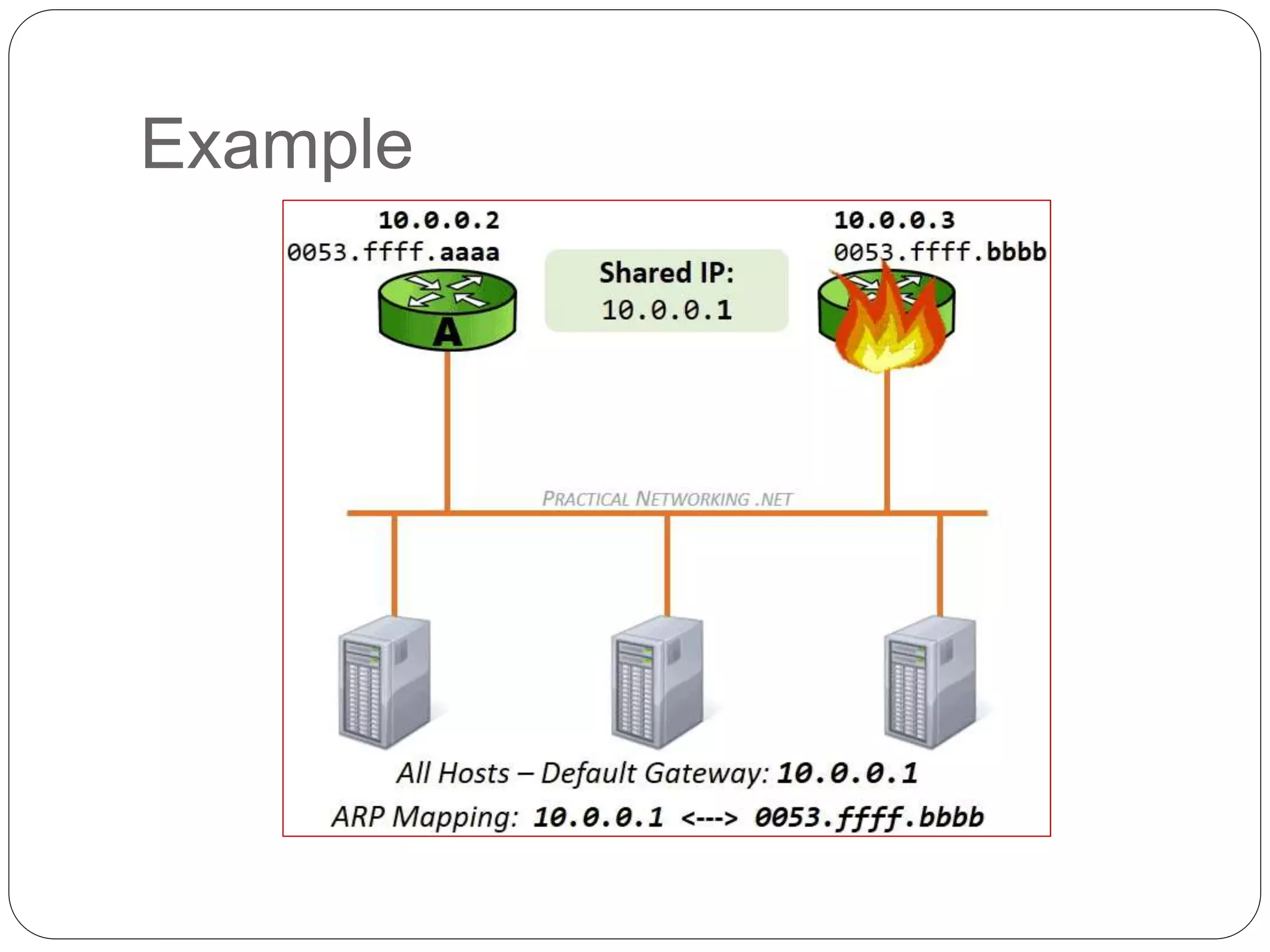
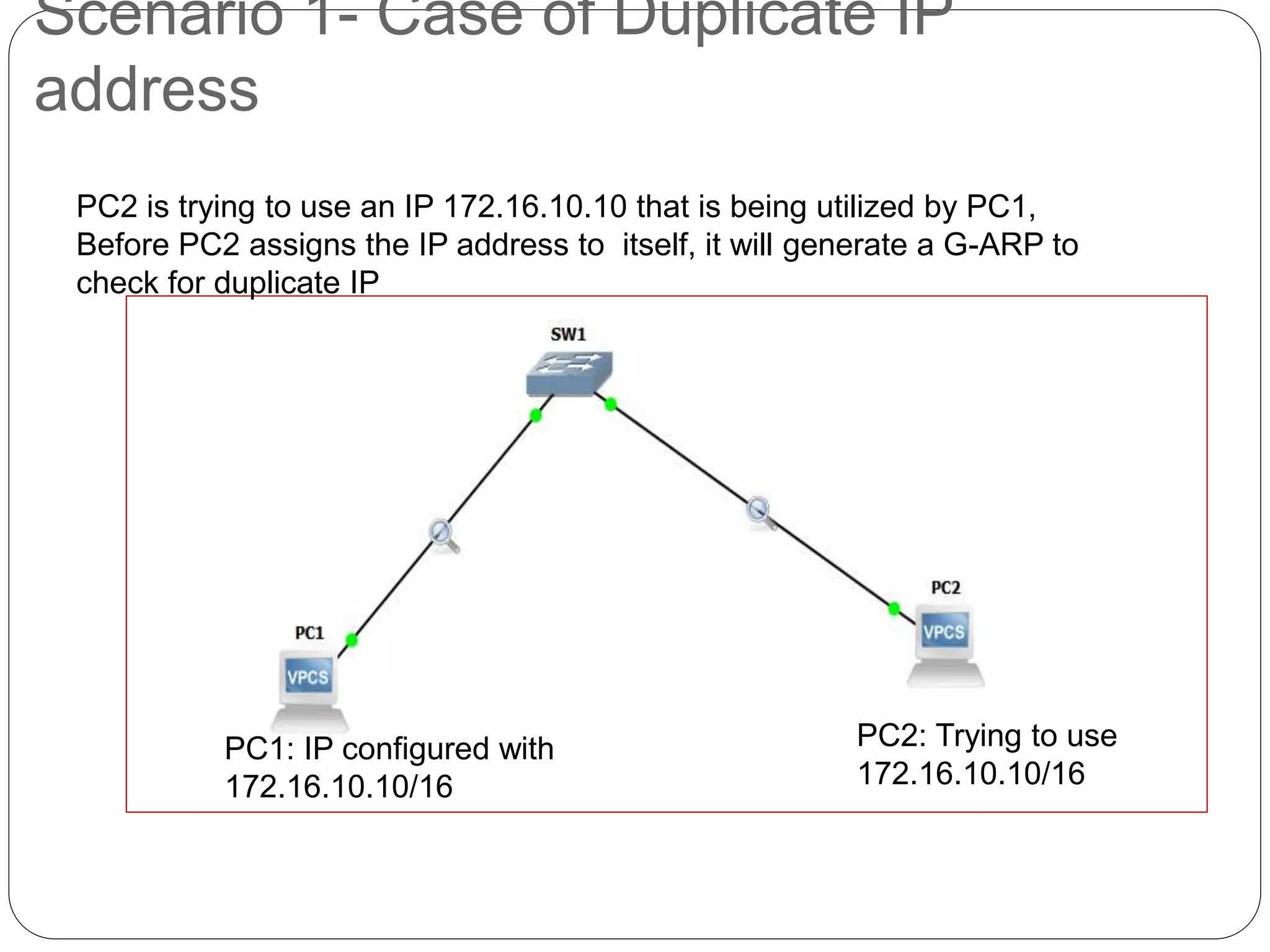
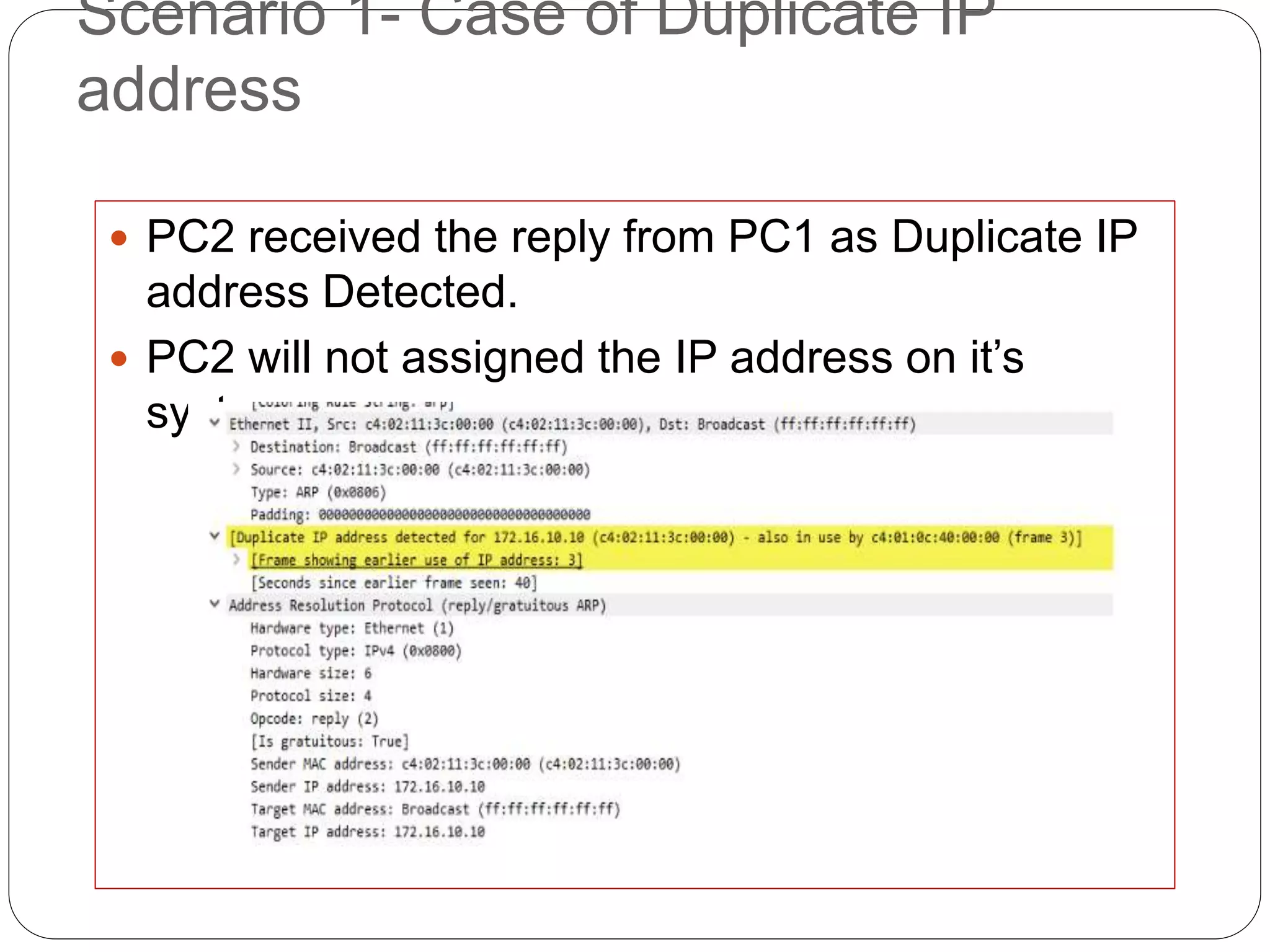
The document discusses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and gratuitous ARP. ARP is used to map IP addresses to MAC addresses on a local network. It maintains an ARP cache table mapping addresses. Gratuitous ARP occurs when a device sends an ARP request for its own IP address, broadcasting its IP-MAC mapping to update switches and detect duplicate IP addresses on the network. It helps ensure unique IP addresses and informs switches of end device locations. The document provides examples of gratuitous ARP detecting and resolving a duplicate IP address scenario.