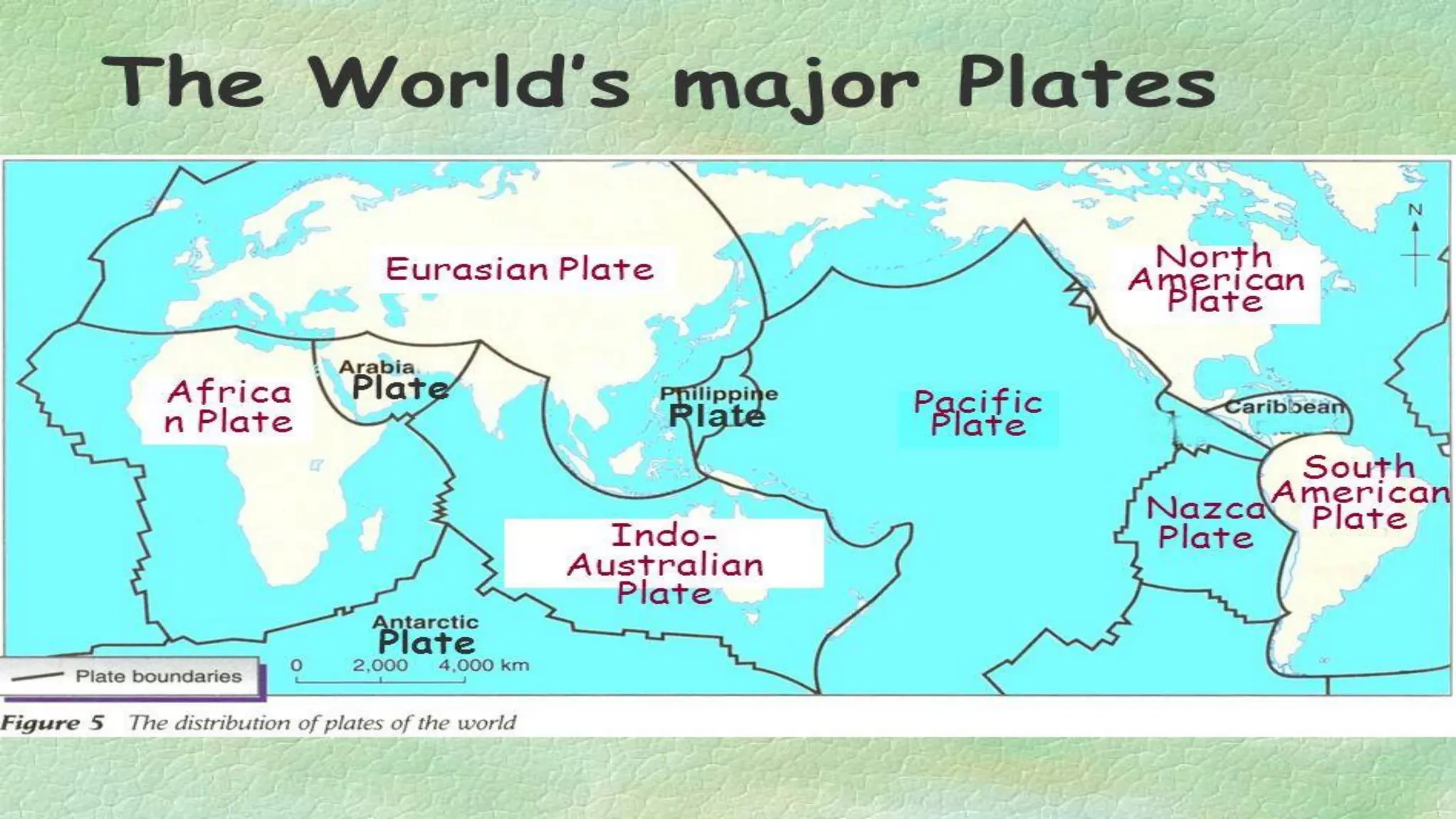
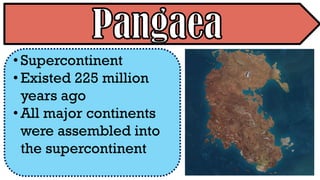
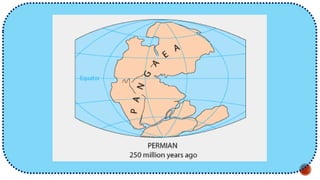
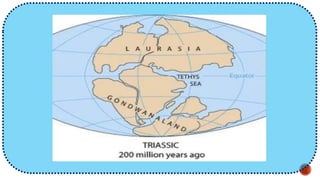
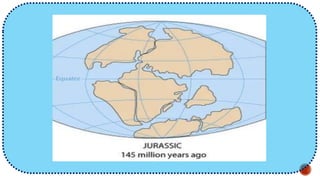
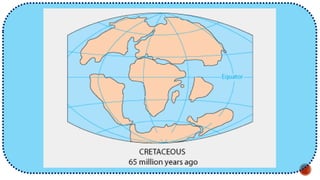
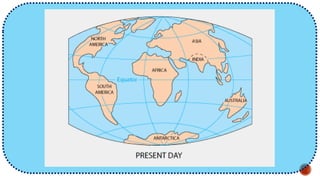
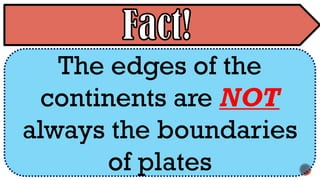
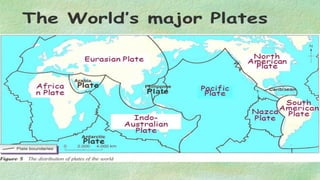
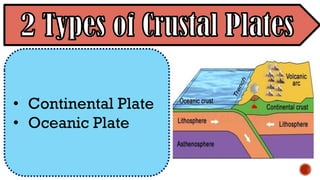
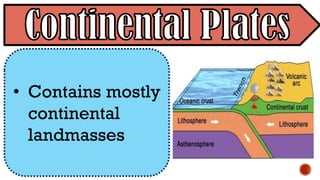
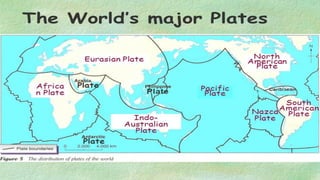
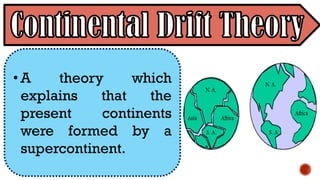
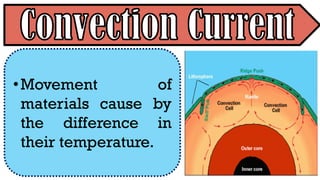
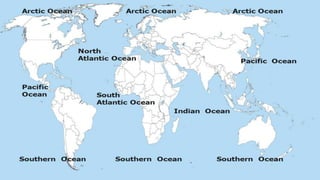
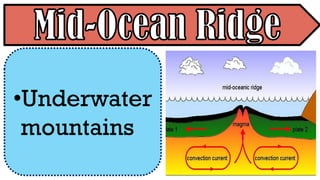
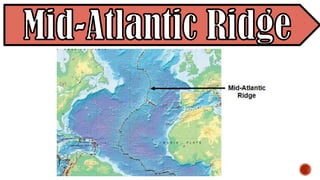
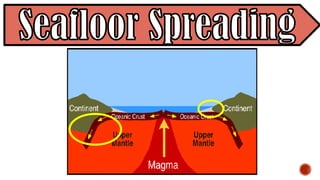
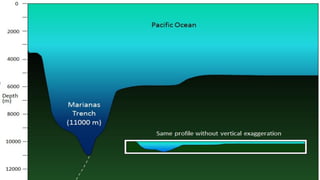
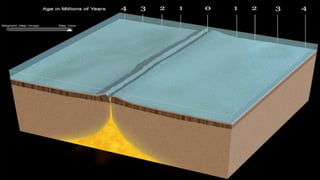
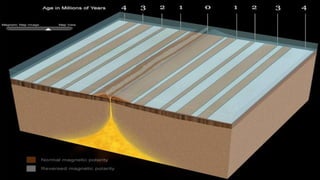
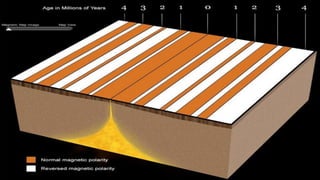
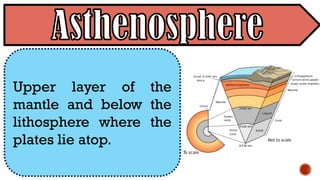
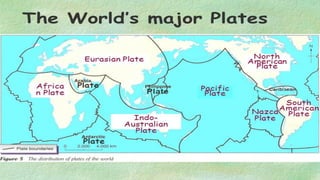
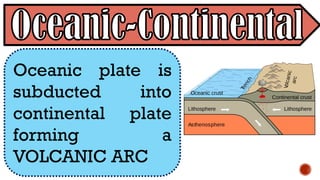
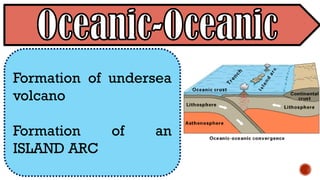
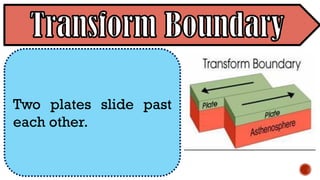
The document explains the plate tectonics theory, detailing evidence supporting its existence and processes such as convection currents and seafloor spreading. It discusses the historical context of landmasses, supercontinents, and the geological effects of plate movements, including earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain formation. Additionally, it highlights fossil and rock evidence that confirms the shifting of Earth's continents.