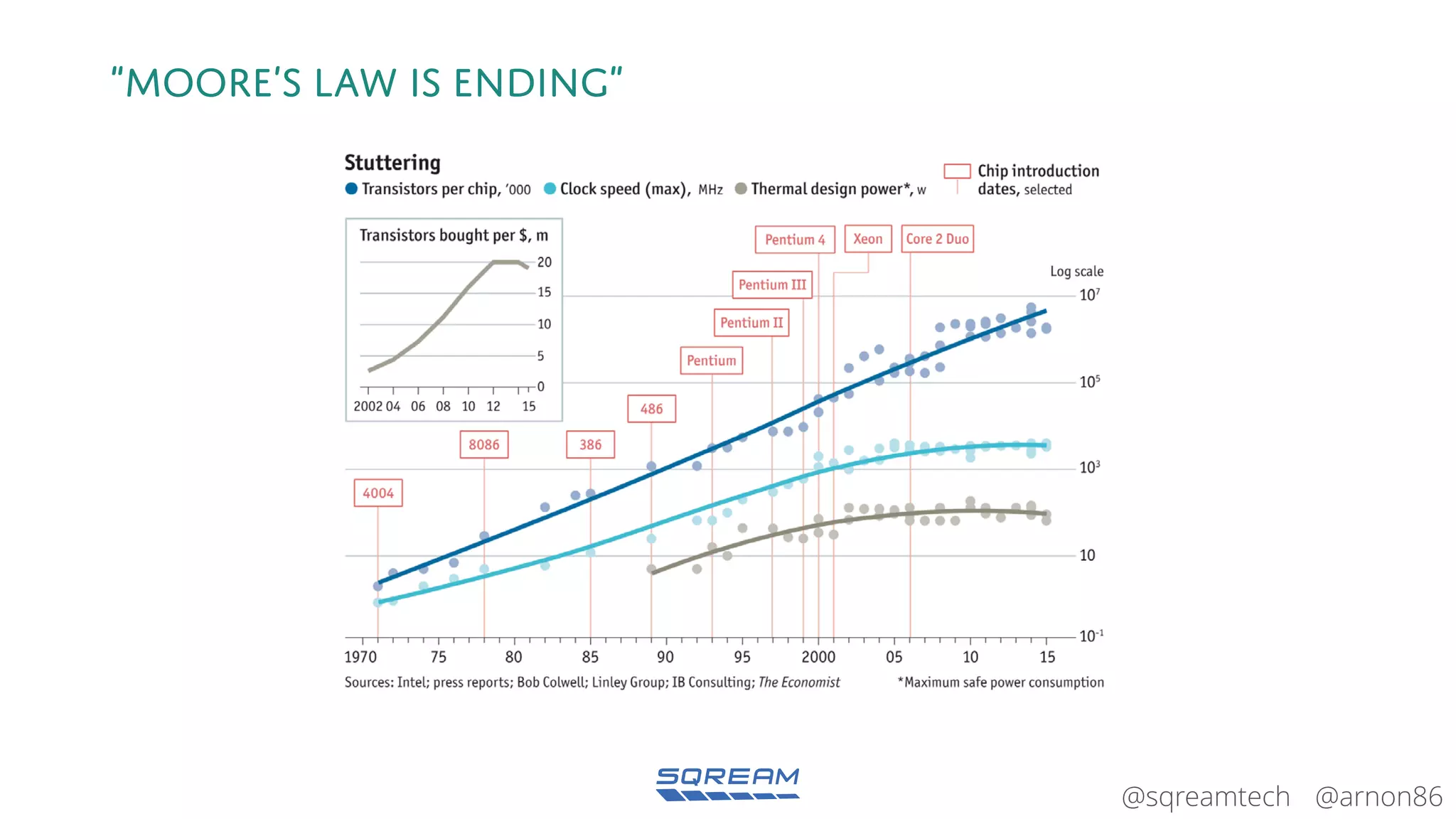
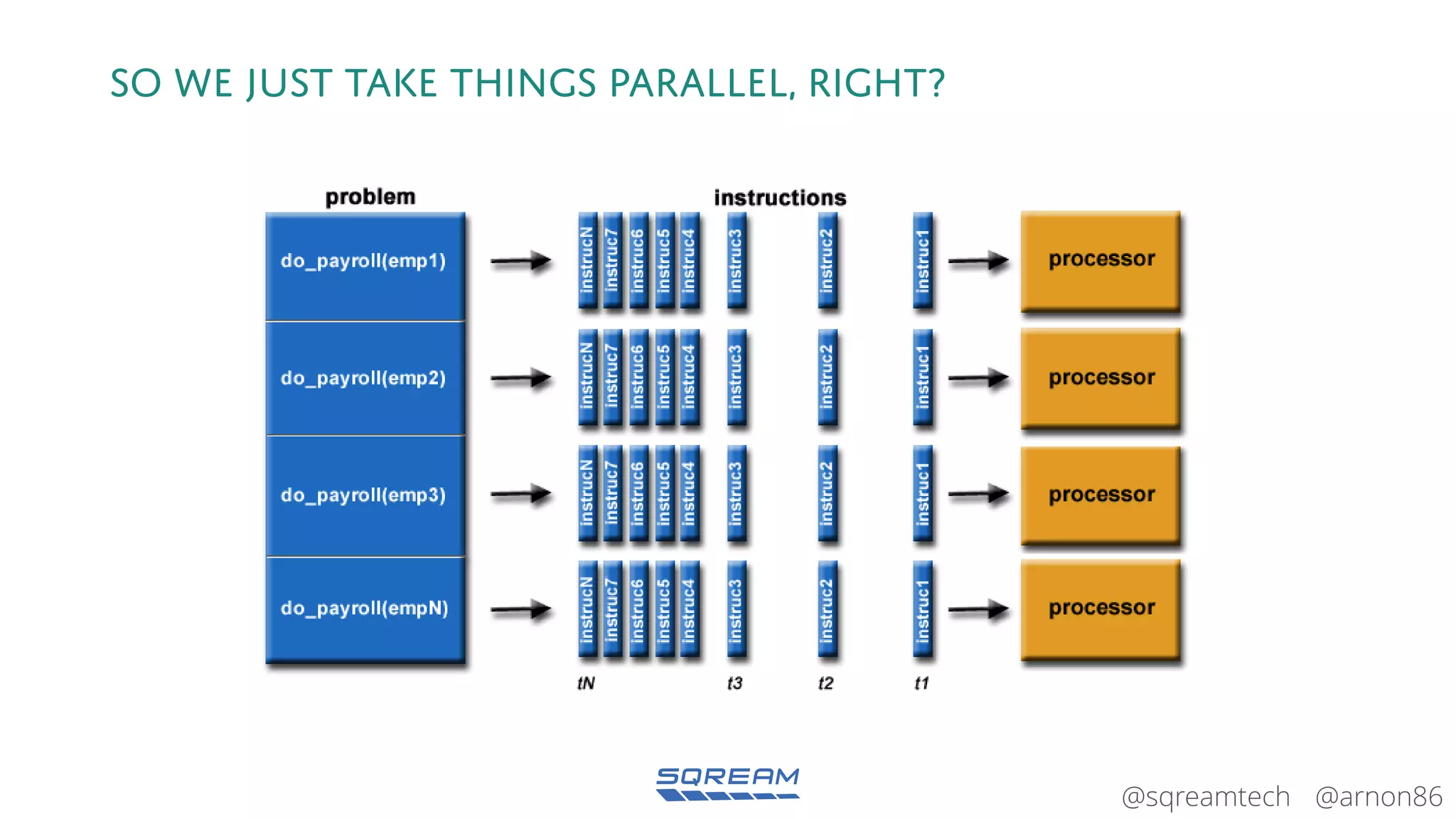
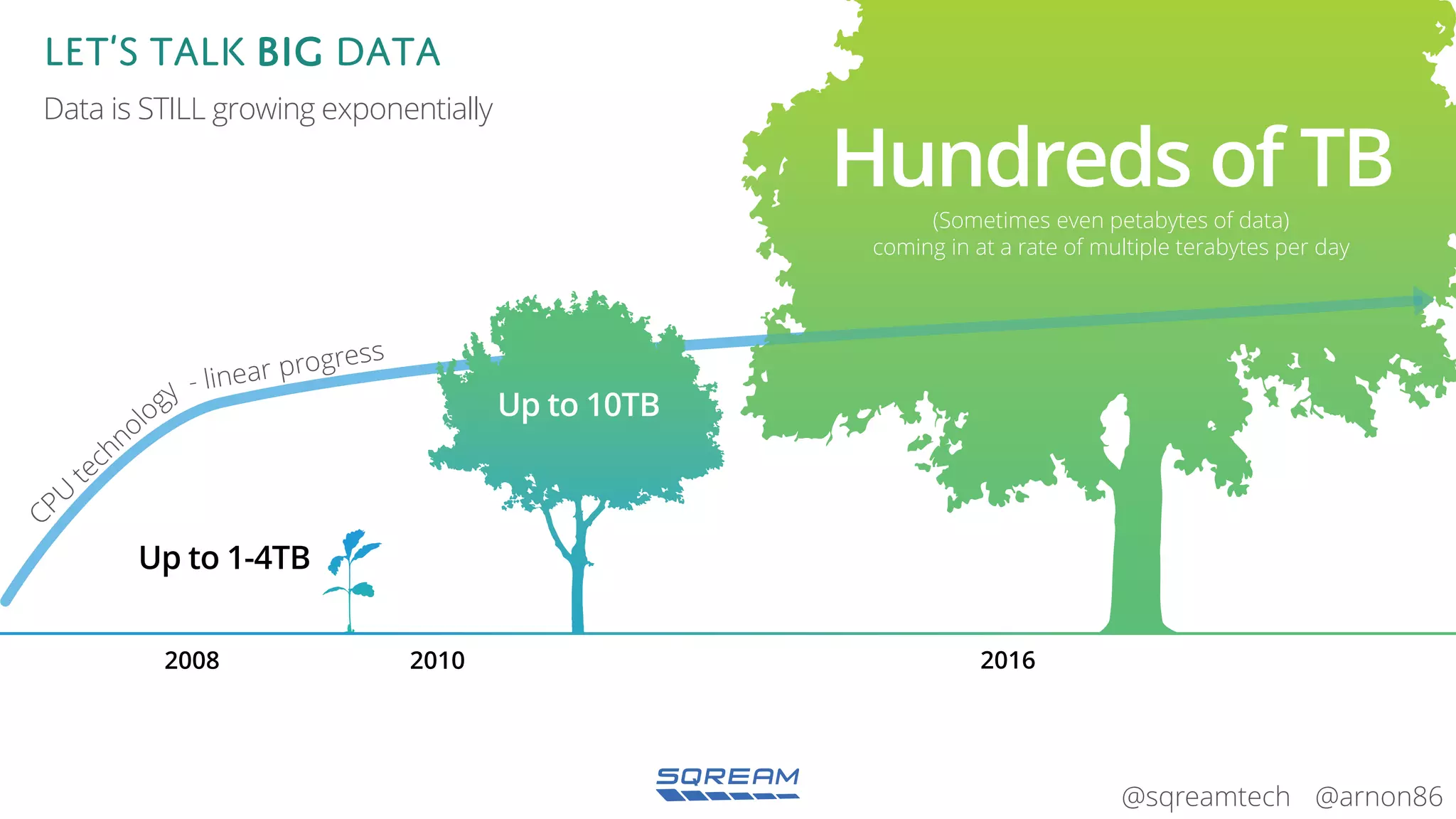
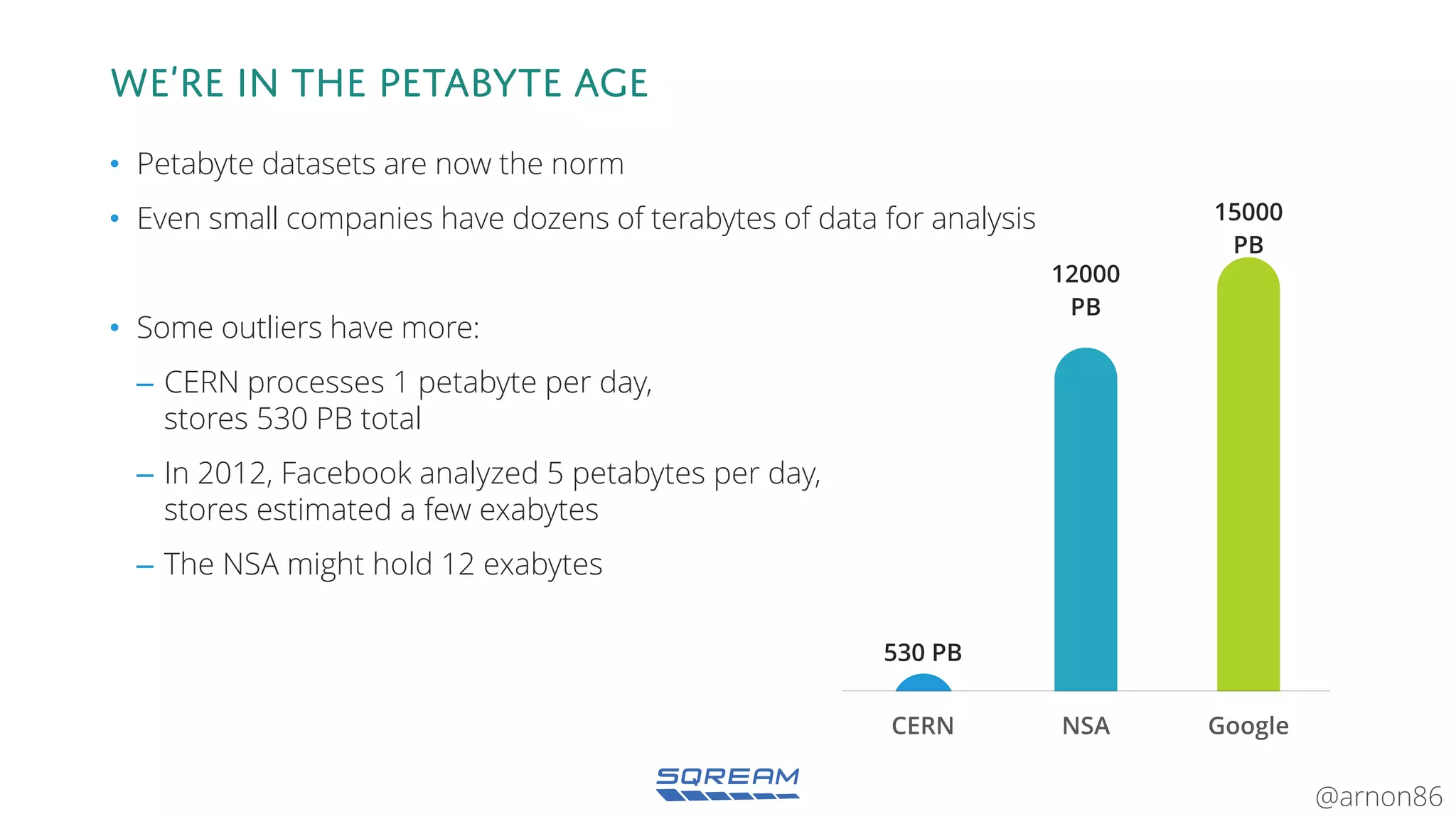
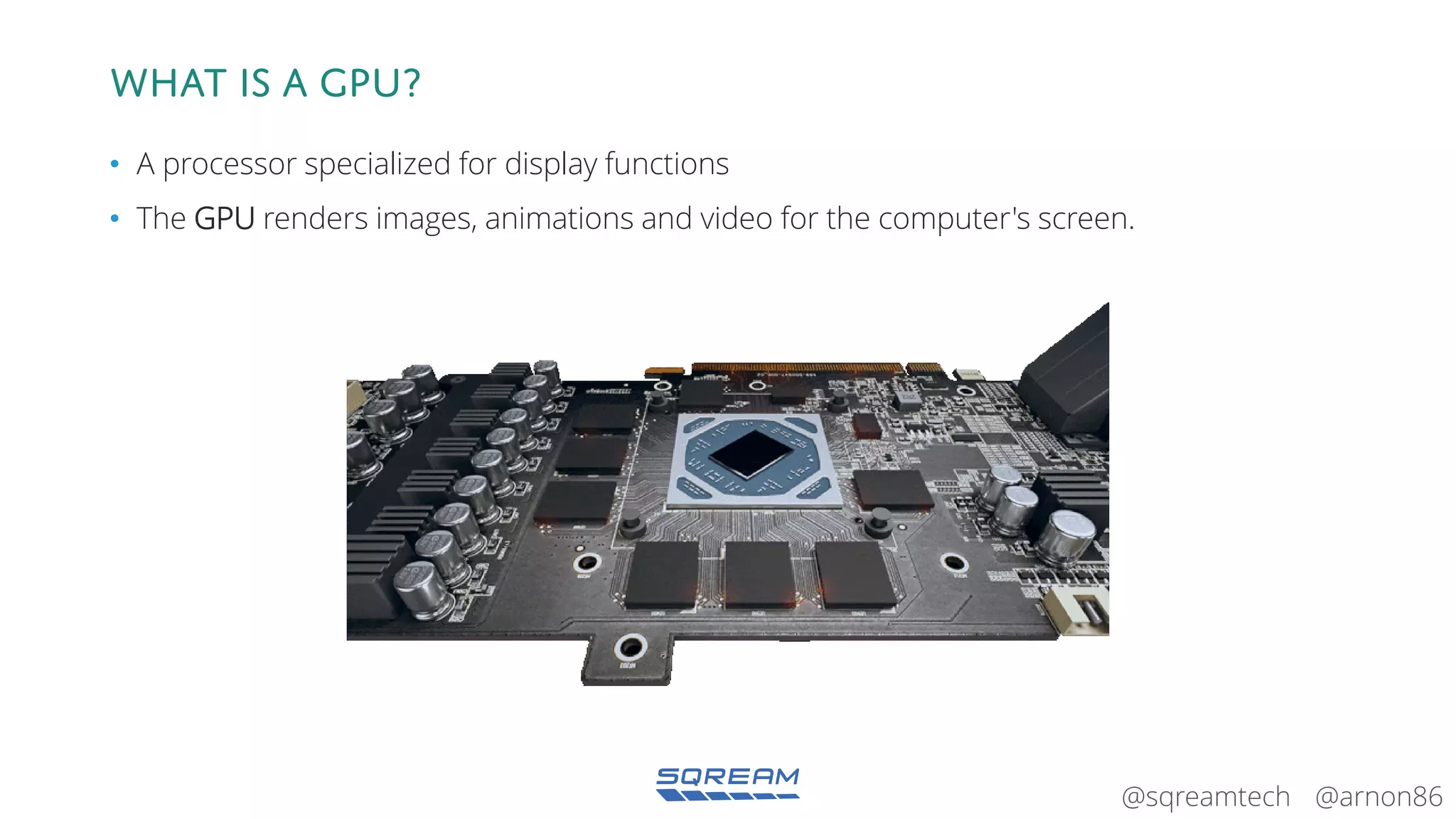
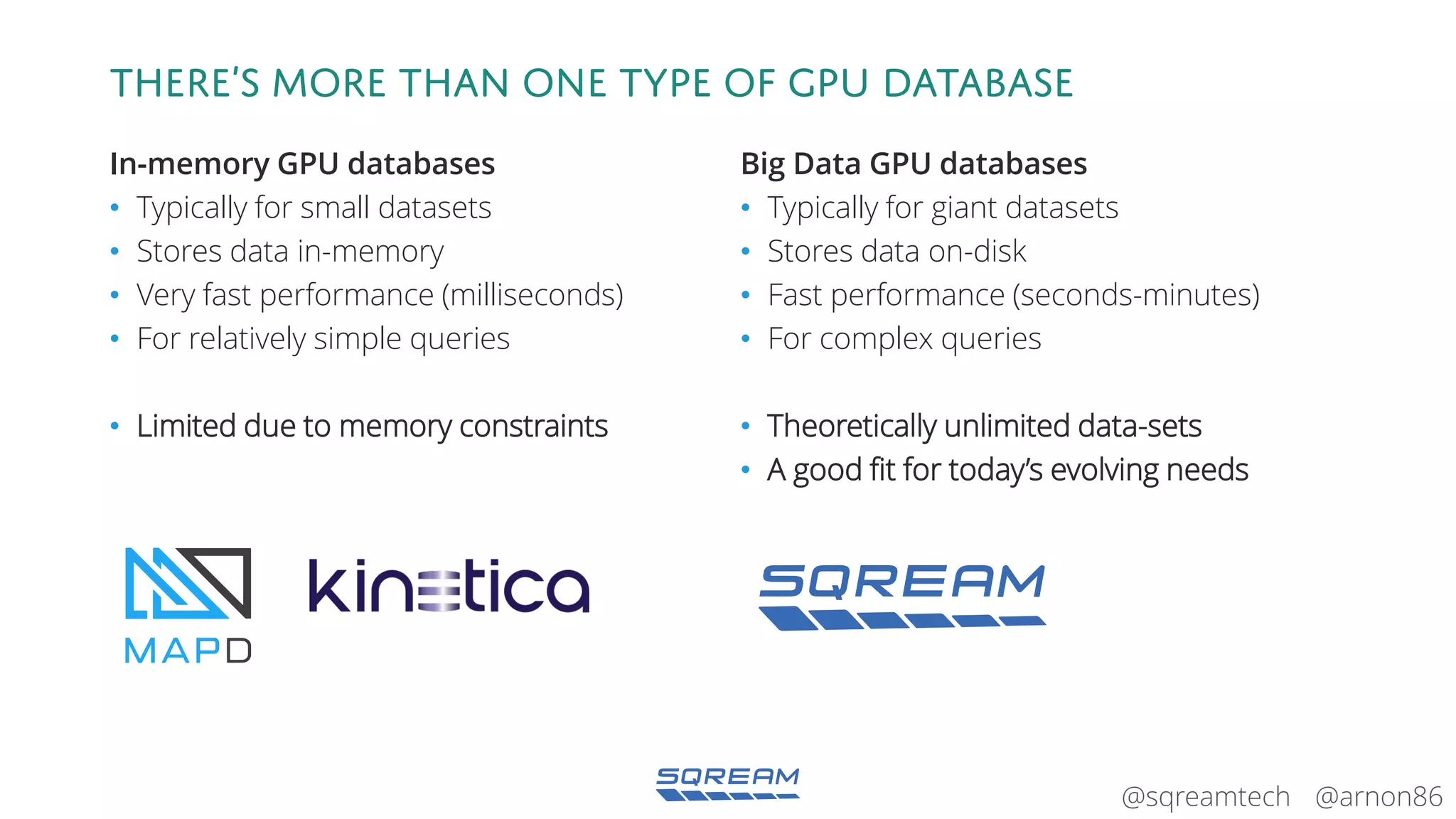
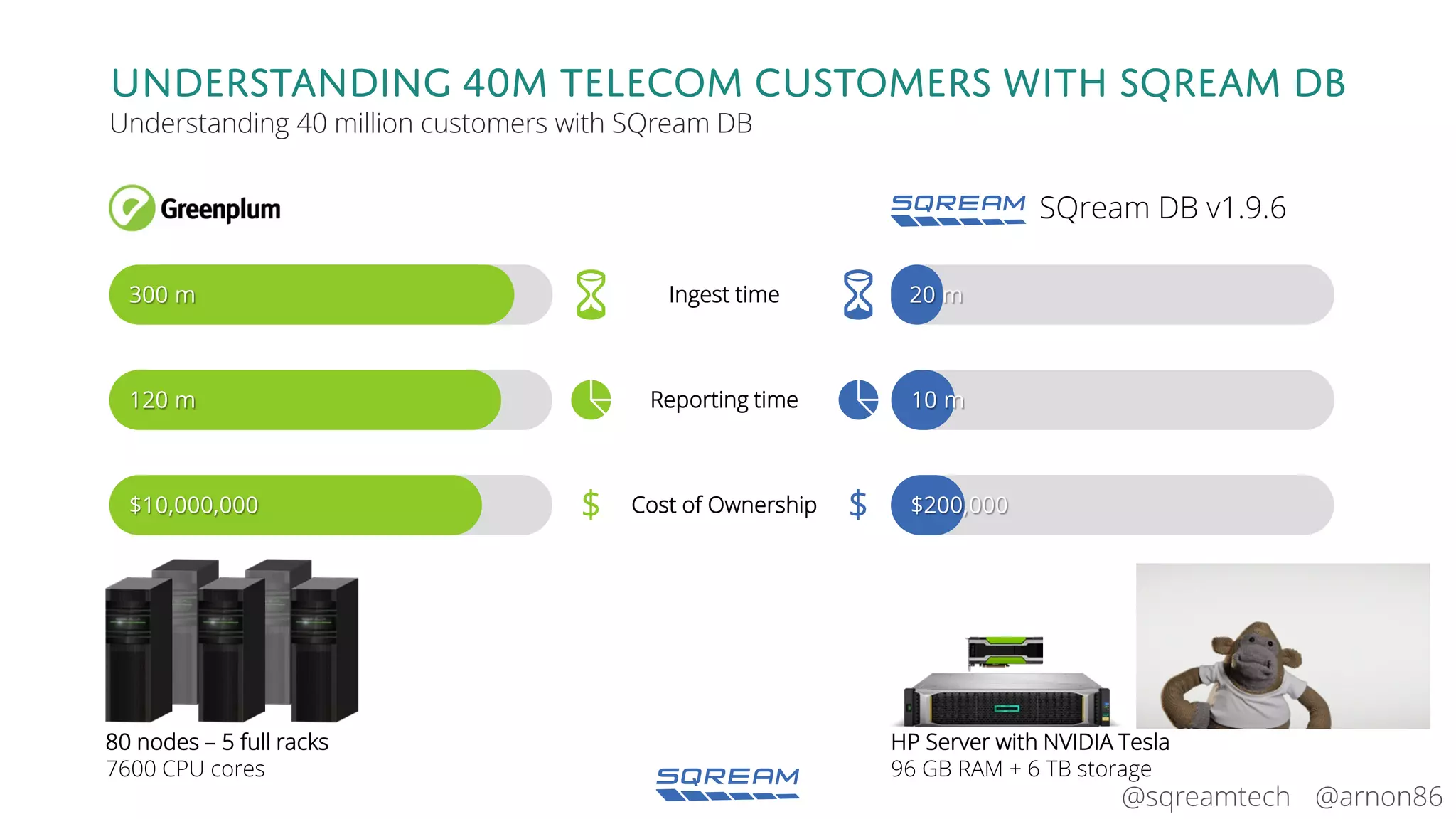
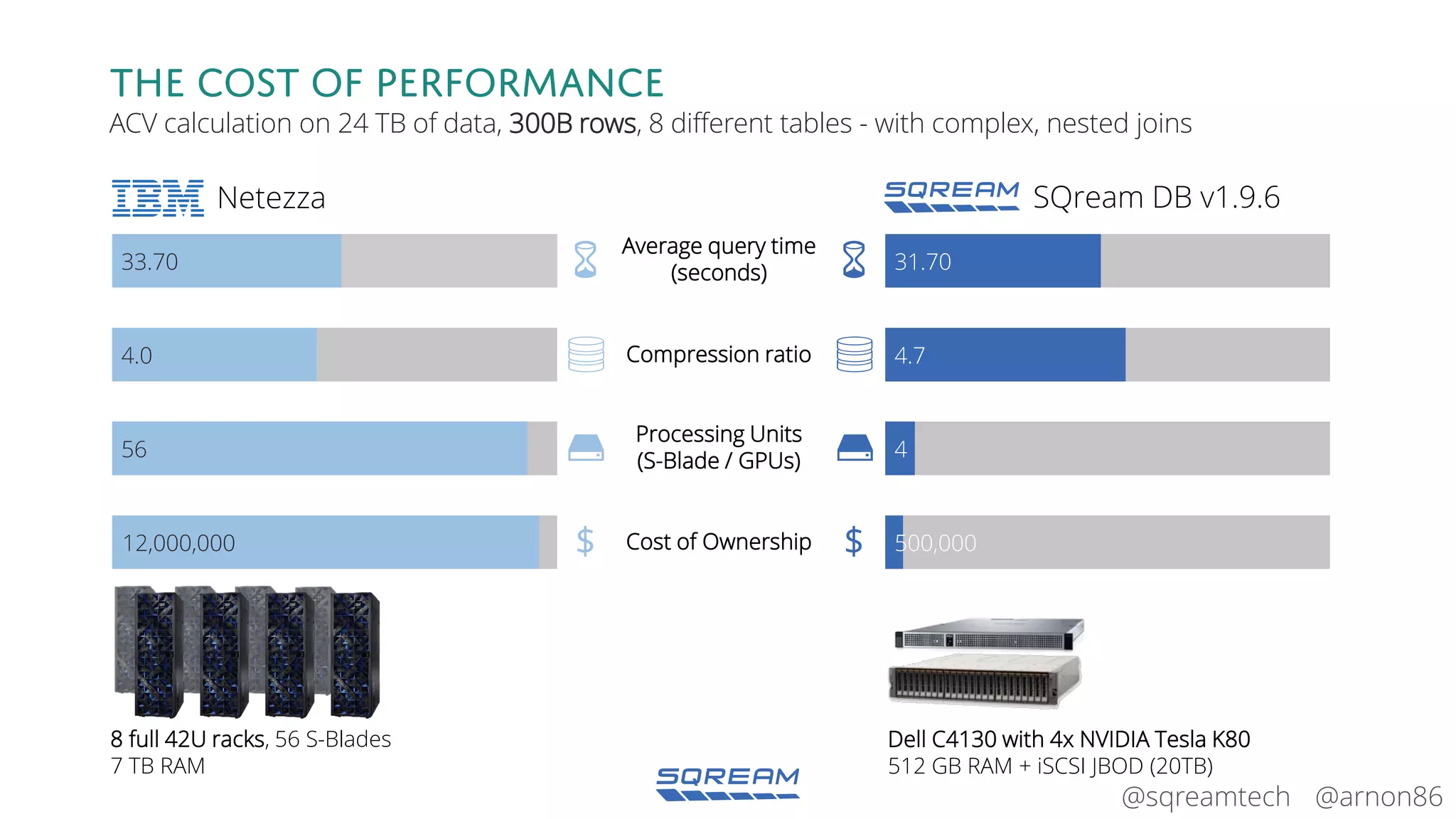
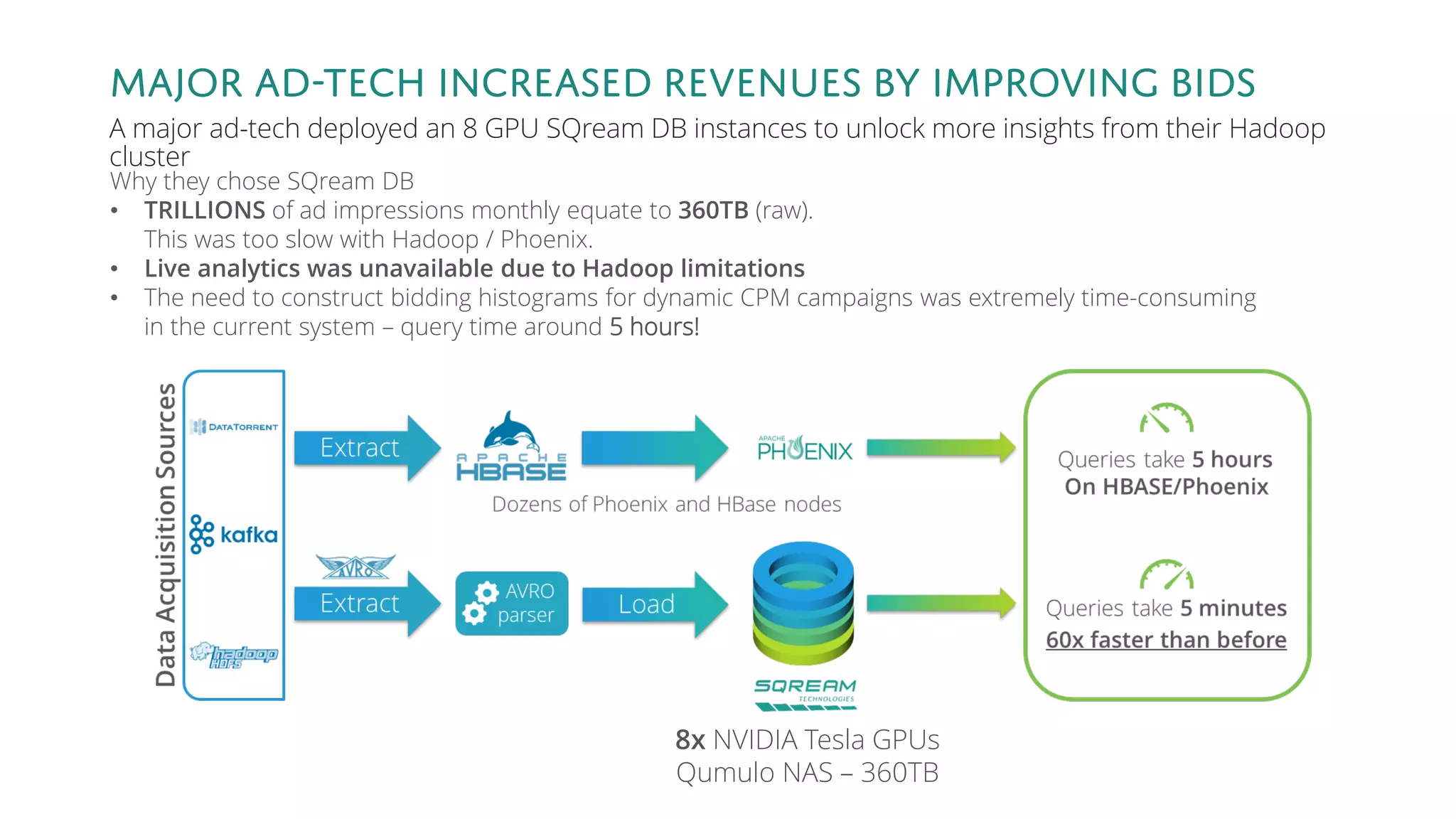
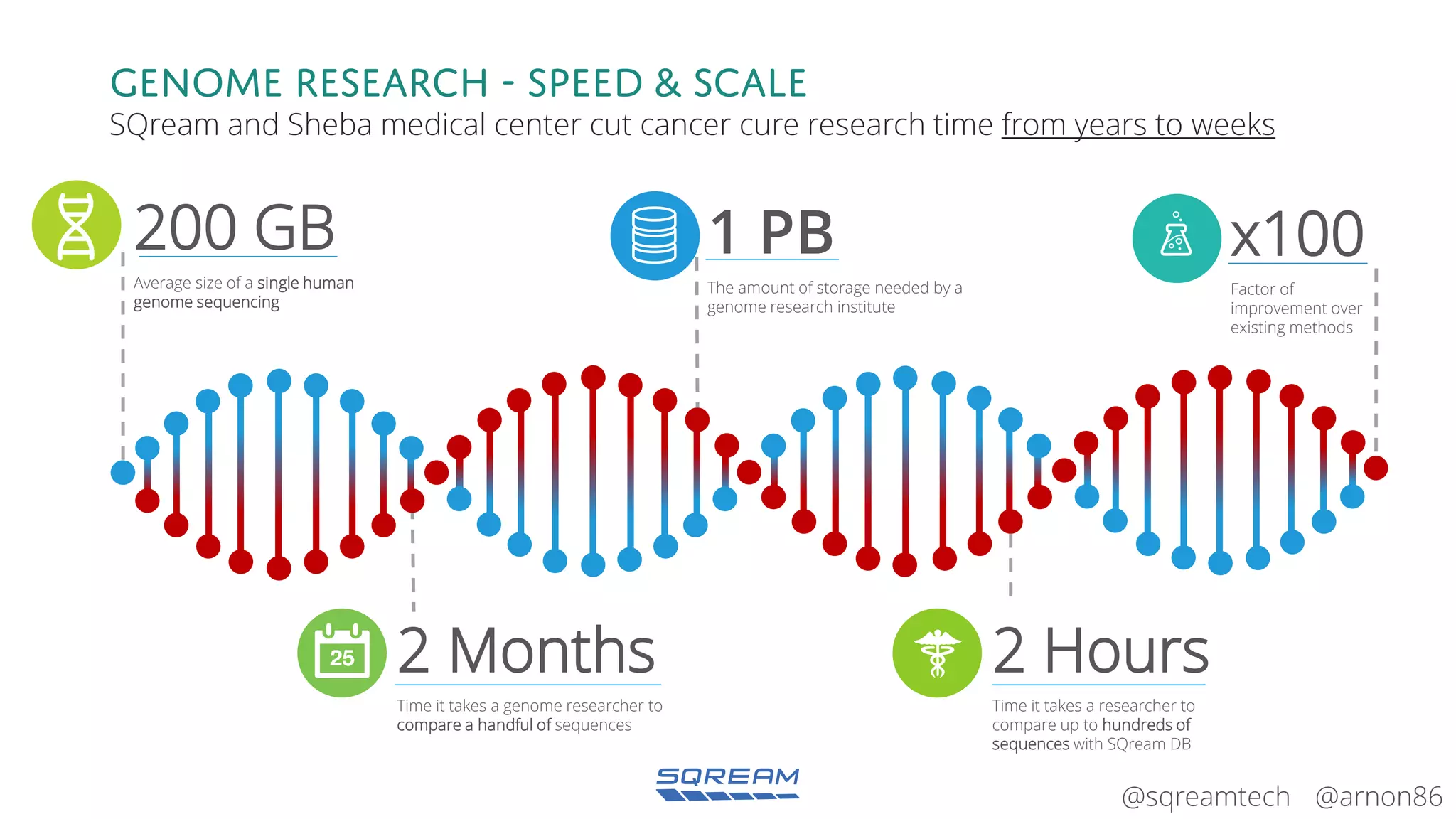
The document discusses the advantages and future of GPU databases, highlighting their ability to handle large volumes of data efficiently, particularly in analytics and big data scenarios. It explains the distinction between in-memory and big data GPU databases and emphasizes the importance of functionality over hardware specifications. The presentation also addresses the evolving landscape of data processing and the increasing relevance of GPU databases in various applications, from telecom to genome research.