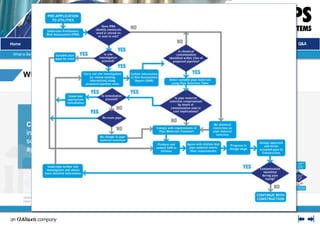
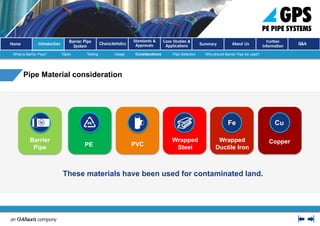
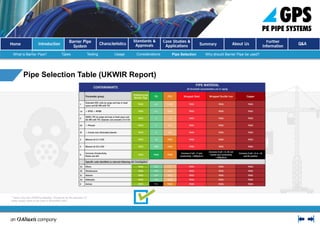
The document presents an introduction to barrier pipes for potable water supply in contaminated land, focusing on educating relevant stakeholders about their features, benefits, and applications. It outlines types of barrier pipes, their testing requirements, jointing methods, and the advantages of using a complete barrier pipe system. Additionally, it showcases case studies demonstrating the reliability and long service life of these systems in ensuring water quality and protection against contaminants.