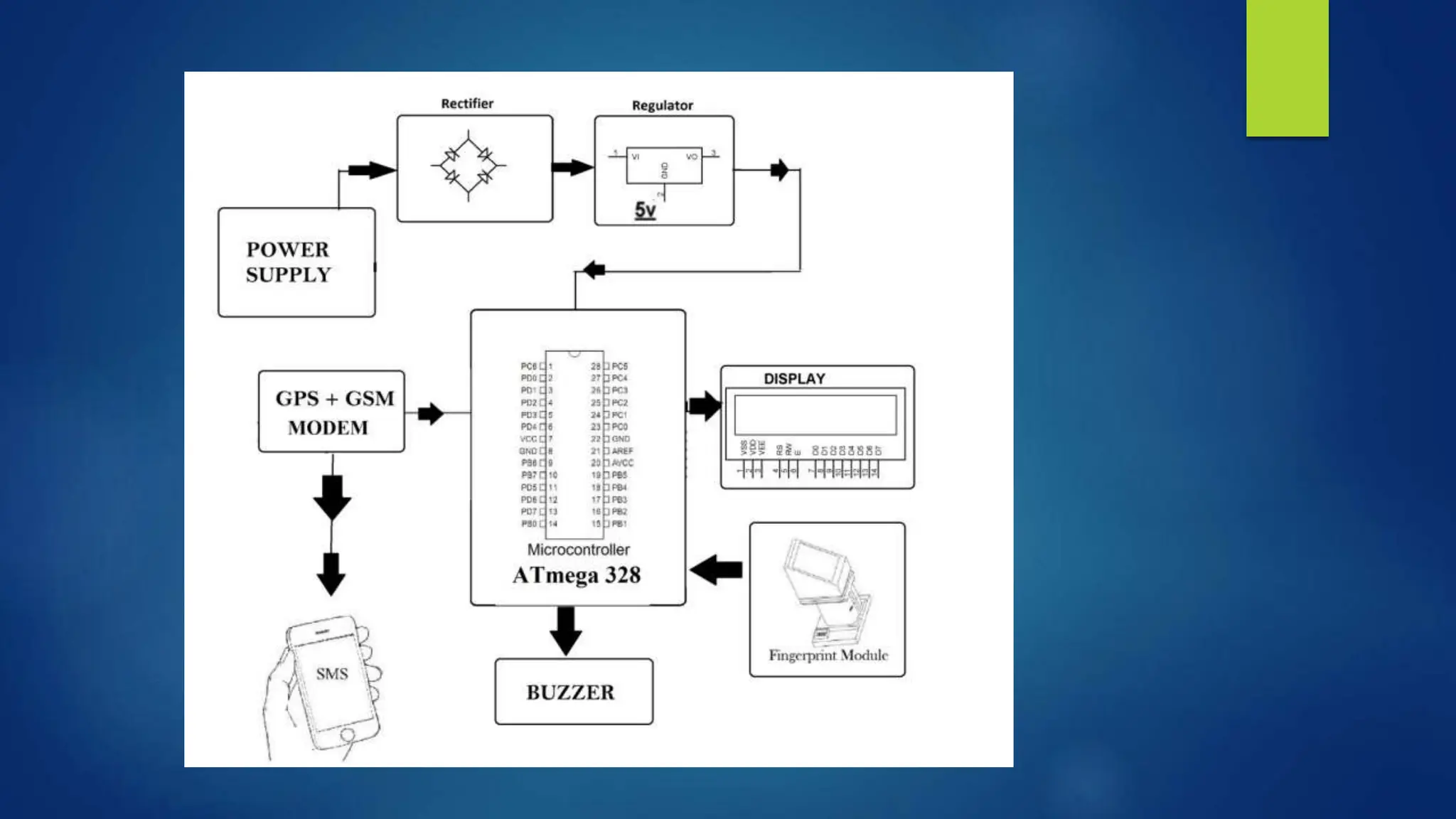
The document provides a detailed overview of GPS navigation using Arduino, explaining how GPS functions through a network of satellites and how it computes positions using trilateration. It discusses various Arduino GPS modules, including the neo-6m and grove modules, highlighting their specifications and applications in different environments. Additionally, it covers related technologies such as GSM modems and their integration with GPS systems for enhanced navigation capabilities.