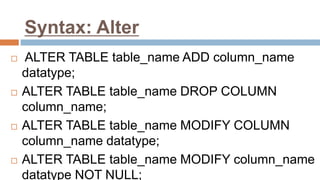
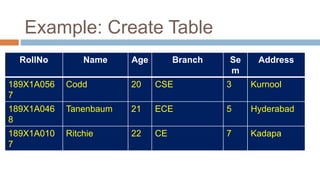
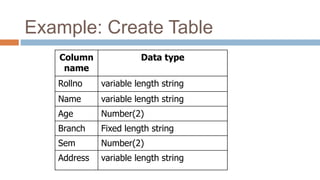
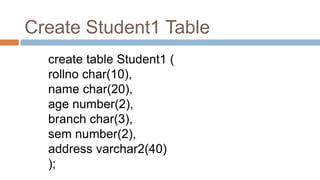
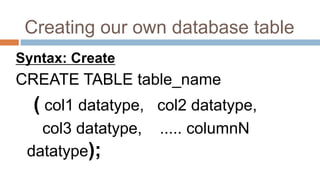
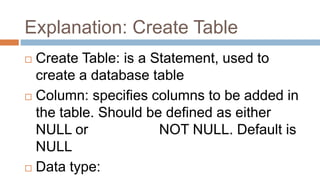
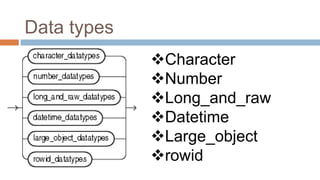
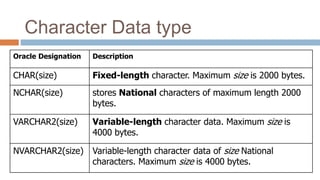
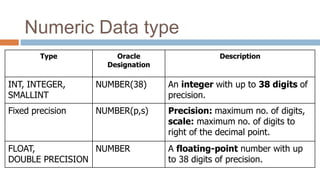
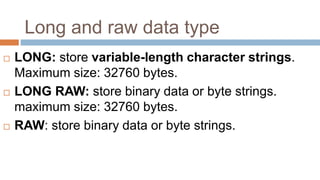
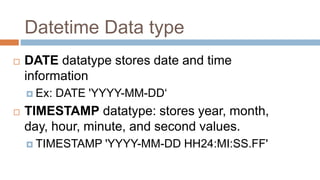
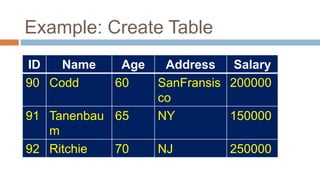
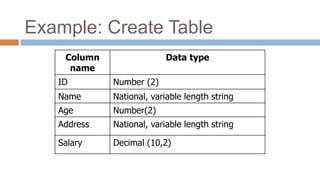
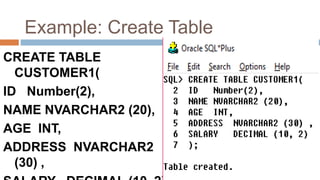
This document discusses creating and manipulating database tables in Oracle. It provides the syntax for creating a table using CREATE TABLE and defines common data types like character, number, date, etc. Examples are given to demonstrate creating a CUSTOMER table with various columns, inserting data using INSERT, updating data using UPDATE, and altering the table structure using ALTER TABLE. Lab exercises are provided asking students to create tables for customers and students, insert sample data, and practice update and alter commands.






![Update statement
Syntax:
UPDATE table_name SET column1 =
value1, column2 = value2...., columnN =
valueN WHERE [condition];
Example
UPDATE CUSTOMER1 SET ADDRESS = 'Pune'
WHERE ID = 91;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbms1-190706023822/85/GPREC-DBMS-Notes-1-18-320.jpg)