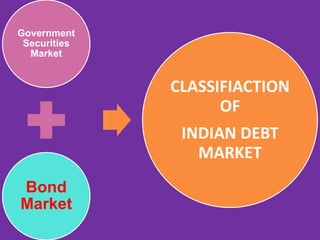
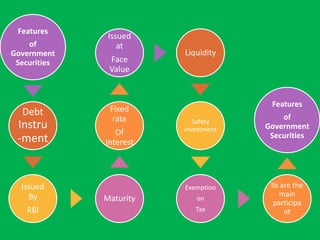
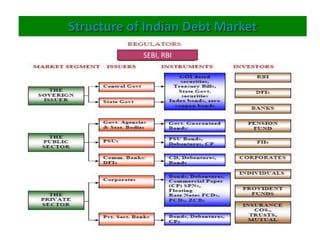
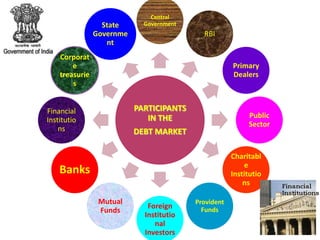
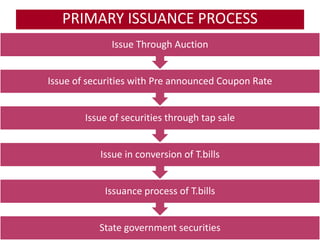
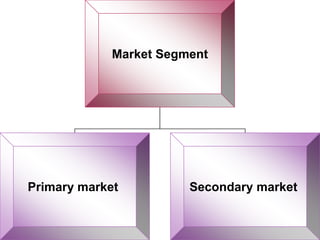
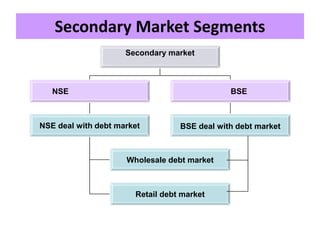
The document discusses the Indian debt market, including government securities market and bond market. It describes the major participants which include central/state governments, banks, financial institutions, companies, and individual investors. It also covers the primary and secondary market structures, issuance and trading processes, clearing and settlement procedures, and debt instruments like STRIPS. The debt market plays a key role in India by facilitating resource mobilization and supporting government/corporate financing needs.