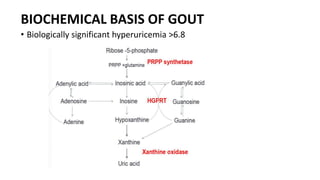
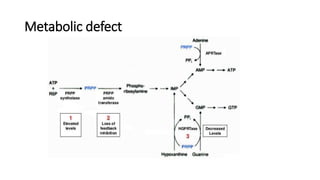
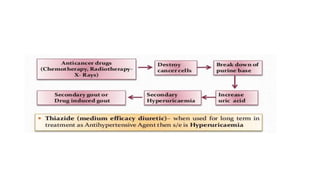
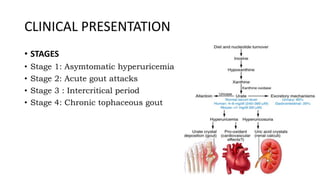
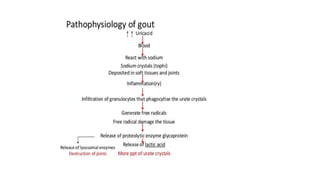
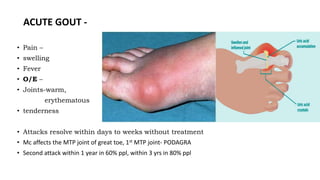
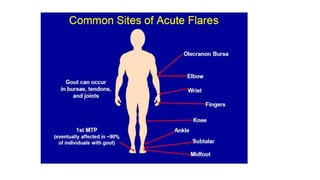
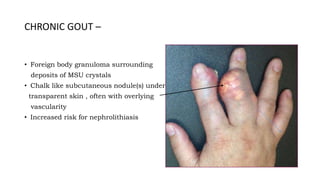
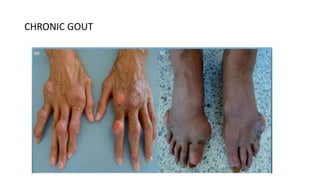
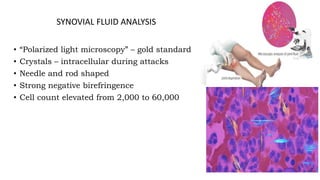
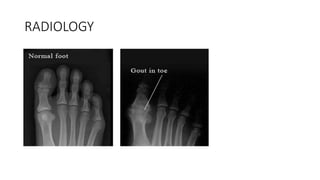
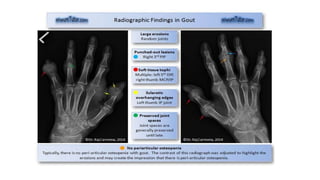
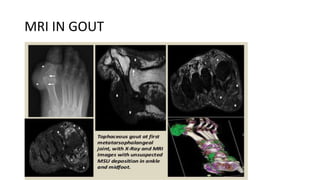
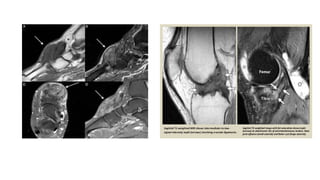
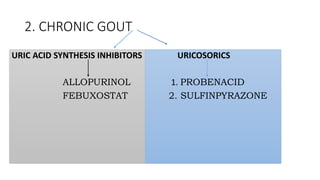
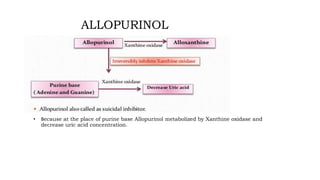
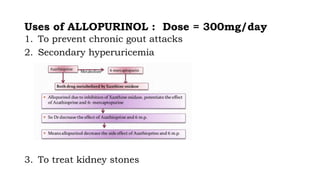
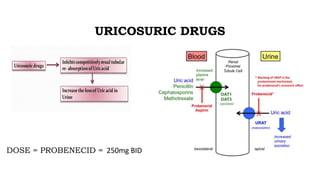
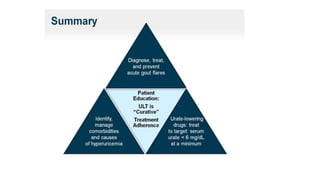
Gout is a chronic disorder of urate metabolism that causes recurrent attacks of inflammatory arthritis. It is most common in men over 40 years of age. Risk factors include purine-rich foods, alcohol, caffeine, trauma, and certain genetic mutations. An acute gout attack causes sudden severe pain, swelling, and tenderness in joints like the toe. Chronic gout results in deposits of urate crystals that form chalk-like tophi under the skin. Treatment involves medications to prevent attacks like NSAIDs, colchicine, allopurinol, and febuxostat or uricosurics. Surgery may be needed in advanced cases with joint destruction.