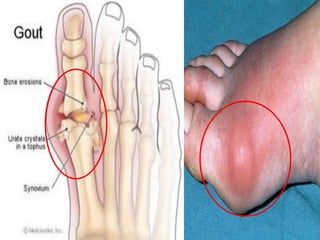
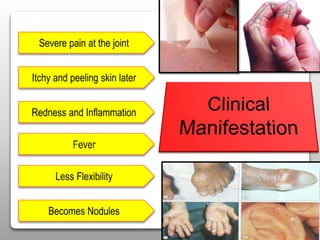
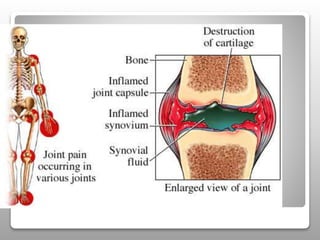
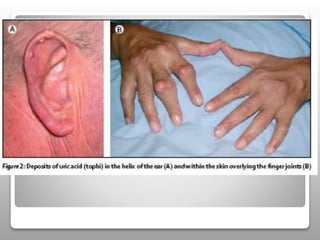
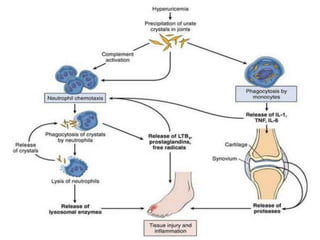
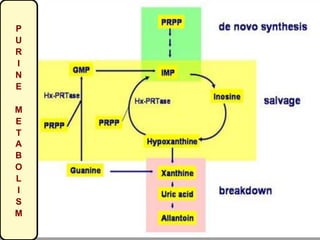
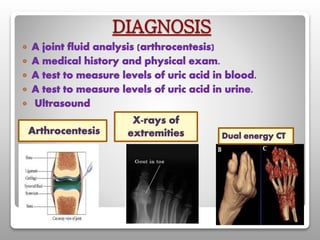
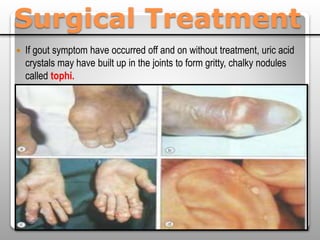
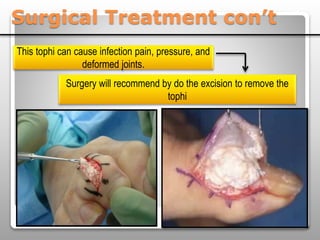
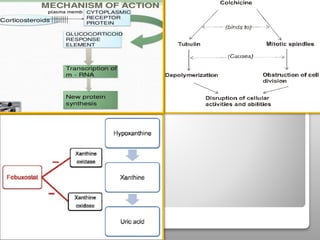
Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by recurrent attacks of inflammatory arthritis caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. It is classified as acute or chronic gout. Risk factors include age, sex, lifestyle, medical conditions, and family history. Treatment involves drugs that inhibit uric acid synthesis like allopurinol, increase uric acid excretion like probenecid, reduce inflammation like NSAIDs, and control symptoms like colchicine. Diet, exercise, medication adherence and surgery are also used to manage gout.