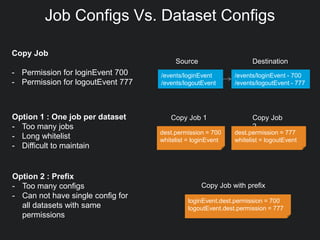
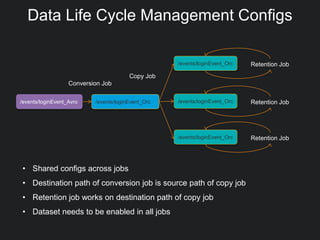
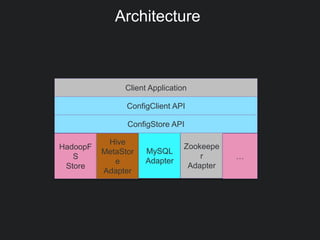
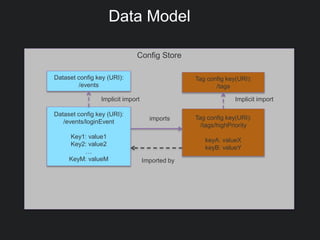
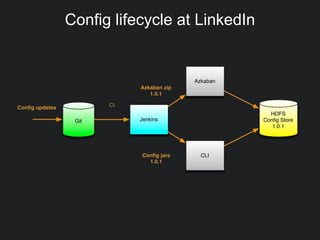
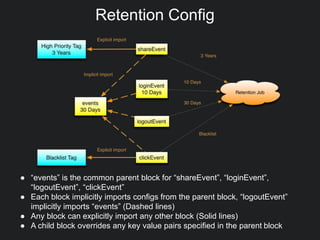
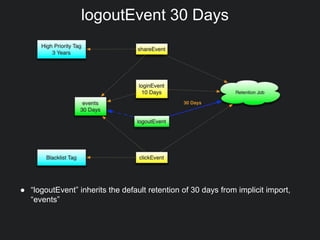
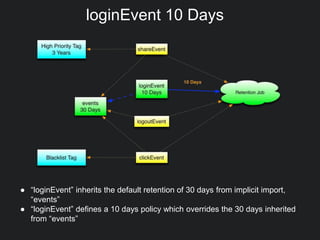
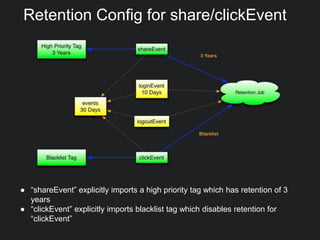
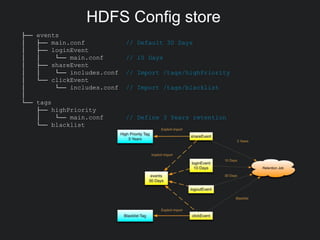
This document discusses Gobblin configuration management. It describes the motivation for building a Gobblin configuration system to manage dataset and job configurations. It outlines the architecture of the Gobblin configuration system, including how it extends Typesafe config and supports versioning, imports, and traversal of configuration relationships. Finally, it provides an example of how data retention policies can be configured using the Gobblin configuration system across different datasets.