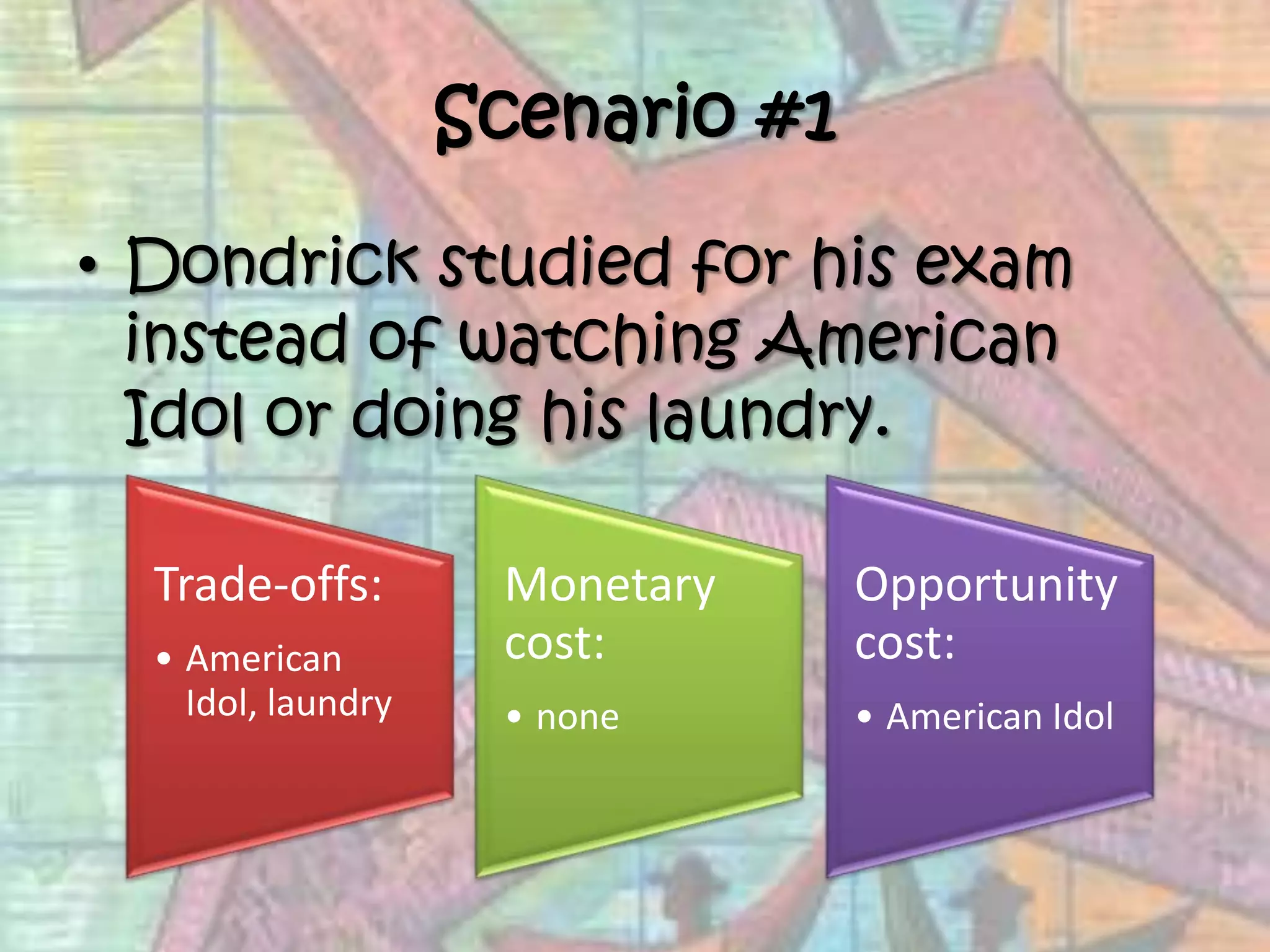
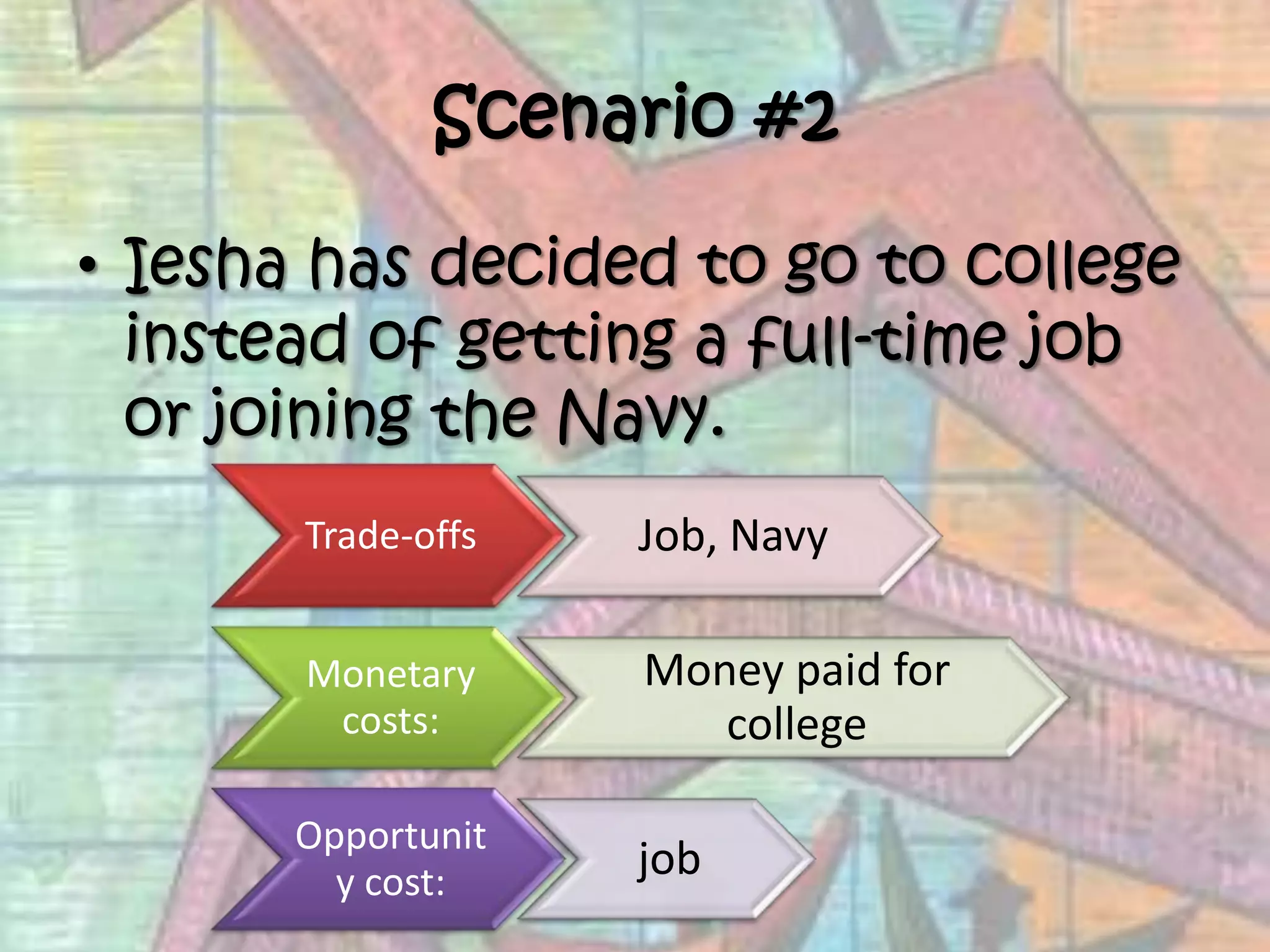
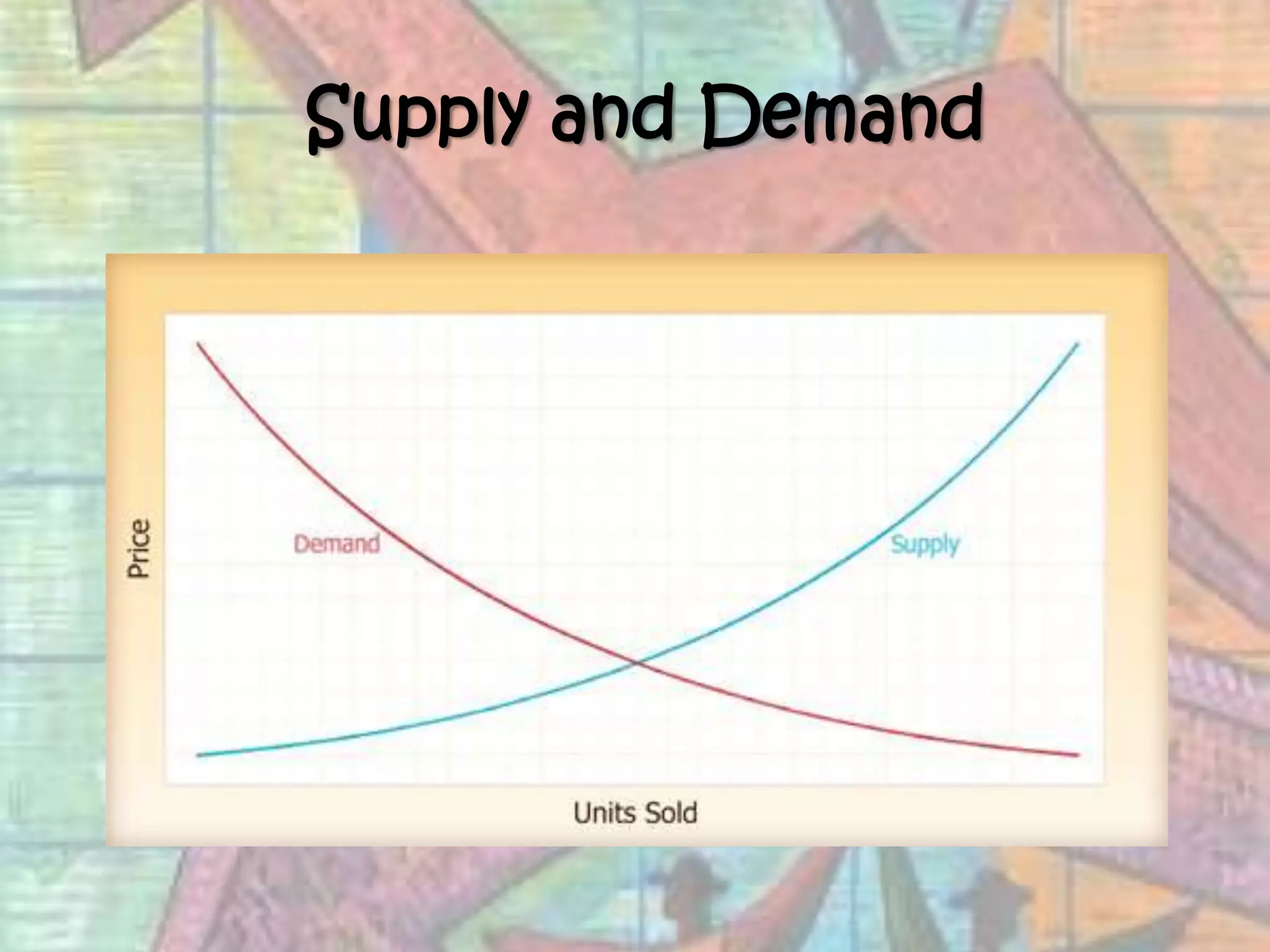
This document provides an introduction to economics, covering the four factors of production (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship), the three basic economic questions (what, how, and for whom to produce goods and services), types of economies (traditional, command, market, mixed), and key economic concepts like productivity, division of labor, supply and demand, and comparative advantage. It defines economics as the study of how individuals and societies make choices to satisfy unlimited wants with limited resources.