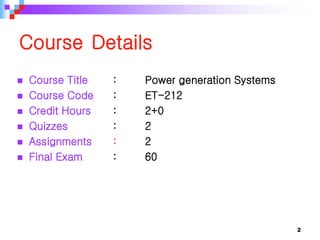
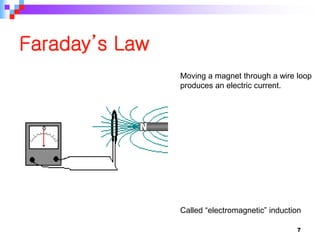
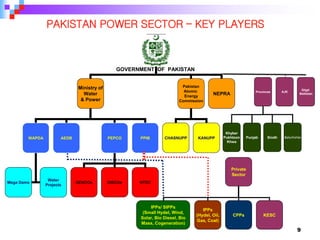
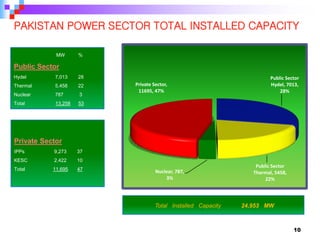
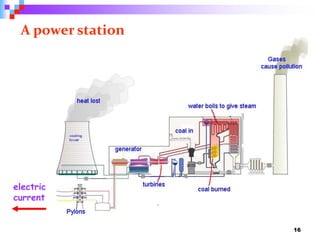
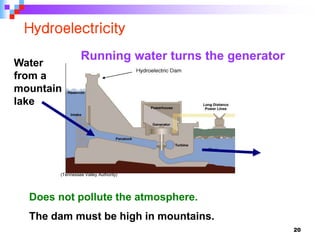
This document provides an overview of a course on power generation systems. The course covers conventional power sources like thermal and hydroelectric plants as well as non-conventional renewable sources like solar and wind. It discusses different methods of power generation including using steam to turn turbines, using the kinetic energy of moving water or wind, and exploiting nuclear reactions. The document compares various energy sources based on their initial costs, running costs, limitations, and sustainability. Students will learn about electrical power generation and the key players and sources that make up Pakistan's power sector.