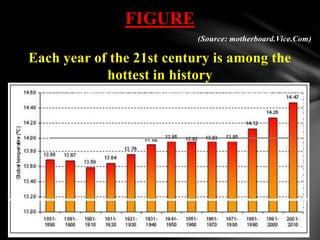
The seminar presented by Ankur Mishra highlights the critical issue of global warming, its causes including greenhouse gas emissions, and its severe impacts on climate patterns, food security, and natural resources. It emphasizes the role of social workers in promoting environmental awareness and sustainable practices, alongside India’s national action plan to address climate change. The document concludes with suggestions on personal and community actions to mitigate global warming effects.