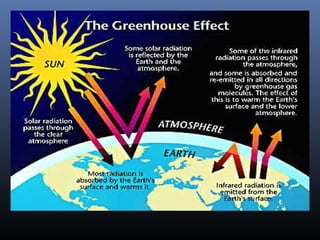
This document defines and explains global warming, greenhouse gases, and the greenhouse effect. It states that global warming is caused by an accumulation of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere from human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation. This traps heat from the sun and warms the planet. The effects of global warming include rising sea levels, more extreme weather, species extinction, and changes to ecosystems. Ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate global warming are also presented, such as using less fossil fuels, alternative energy sources, and planting trees.