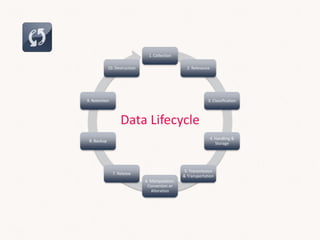
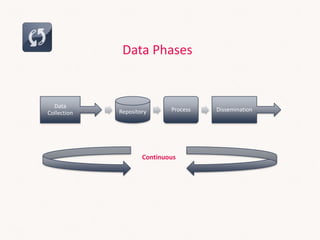
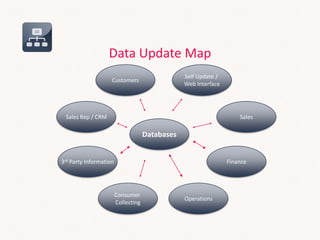
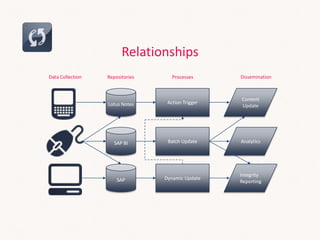
This document discusses sales systems from a global and local perspective. It begins with an introduction to the evolution of sales systems from pen and paper to modern CRM and business intelligence tools. It then covers the framework for how sales data is handled within organizations. The benefits of global and local approaches to sales systems are analyzed. Globally, there are benefits like an integrated view of business and leveraging investments across markets. Locally, systems can be faster to implement and tailored to unique needs. However, risks include lack of support globally and overkill for smaller markets locally. The document seeks to establish an understanding of data lifecycles and determine the appropriate level at which to collect sales data.