- Git is a free and open source distributed version control system that allows users to manage and track changes to source code. GitHub is a hosting service that offers additional features for Git repositories like wikis and issue tracking. Git is the tool and GitHub is the hosting service.
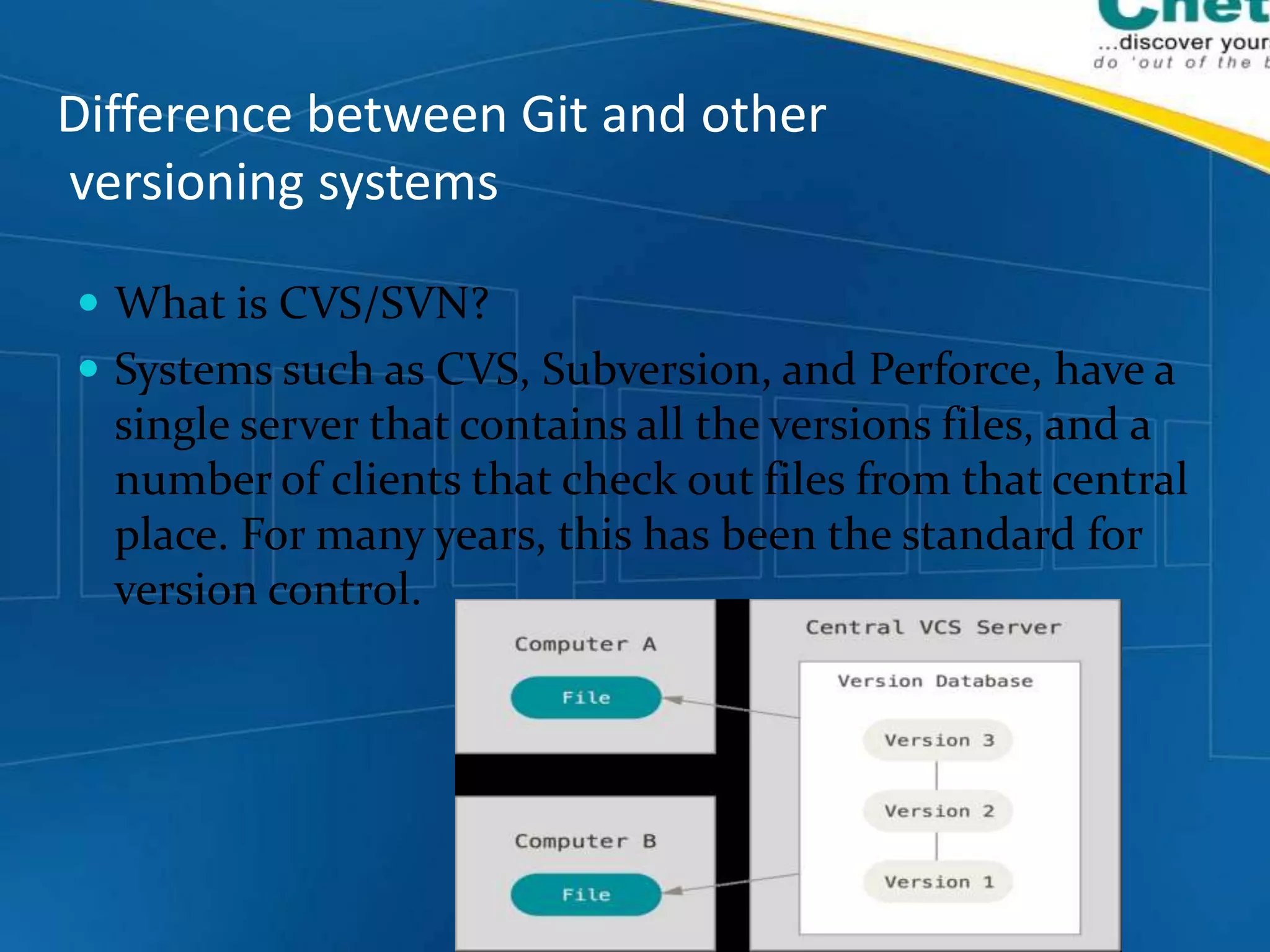
- Unlike centralized version control systems like CVS and SVN, Git allows for distributed collaboration where any clone of a Git repository is a full backup that can be used to restore the repository if the main server goes down.
- The presentation covers how to set up Git on Windows, Mac and Linux, how to initialize and clone repositories, and provides an overview of basic Git commands.