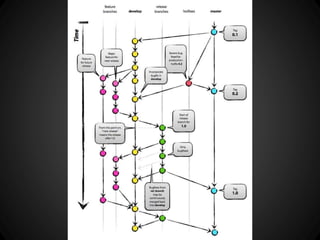
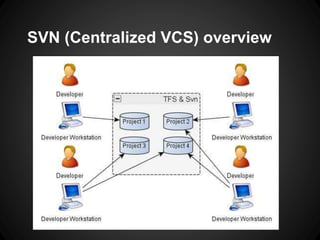
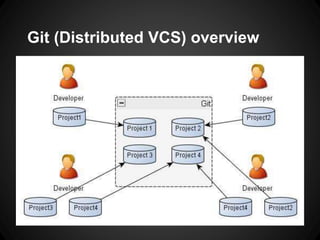
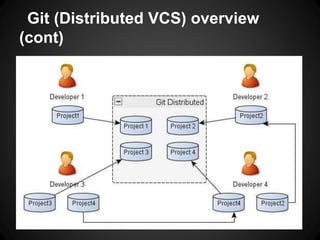
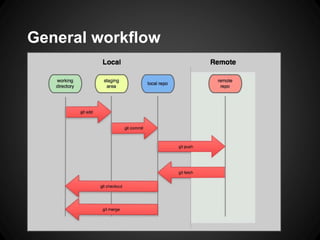
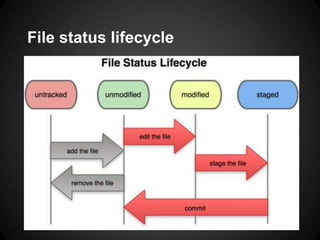
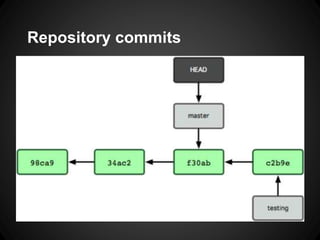
The document provides an overview of Git, including what it is, its benefits over centralized version control systems, basic workflows and commands, branching, tagging, and best practices. Git is an open source distributed version control system designed to manage source code and other files. It allows users to work offline and commit changes incrementally to a local repository before pushing to a remote server.









![Branching
git branch <branchname>
git checkout <branchname>
git checkout -b <branchname>
Create new branch and switch to
git branch [-a -l -r]
List branches (all, local, remote)
git merge <branchname>
Merge branch into current branch (ex. master)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/git-170112073423/85/Git-16-320.jpg)
![Stashing
git stash
git stash [save message]
git stash list
git status apply
git stash clear
git stash branch <branchname>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/git-170112073423/85/Git-17-320.jpg)


![Updating (Push/Pull)
git fetch / git merge
Fetch latest changes from origin, need to
use git merge to apply.
git pull
Pull latest changes from origin (fetch +
merge)
git push [remote_name] [branch_name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/git-170112073423/85/Git-20-320.jpg)