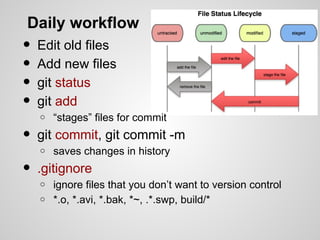
This document provides a comprehensive guide to using Git for version control, including configuration, repository management, daily workflows, branching, merging, and working with remote repositories. Key commands and best practices are outlined for initializing projects, managing files, and collaborating with others. It also includes resources for further learning about Git and version control terminology.