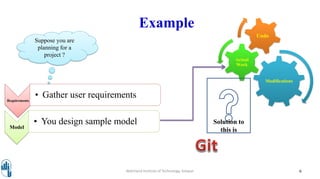
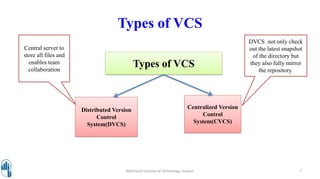
This document provides an introduction to the basic concepts of Git. It begins by stating the learning objective is for students to understand basic Git concepts. It then provides prerequisites for understanding Git, which include experience with software development life cycles and developing various types of applications. The document goes on to introduce Git, describing it as a distributed version control system created by Linus Torvald to manage merging of source code from different contributors. It also provides examples of using Git in a sample project workflow. Key terminology related to Git such as local repositories, blobs, trees, commits, branches, cloning, pulling, pushing, and revisions are defined. Finally, it depicts the basic Git workflow involving the working directory, staging area, and Git repository.